A Century of Transformation: Mapping the Middle East from 1900 to 2000
Related Articles: A Century of Transformation: Mapping the Middle East from 1900 to 2000
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Century of Transformation: Mapping the Middle East from 1900 to 2000. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Century of Transformation: Mapping the Middle East from 1900 to 2000
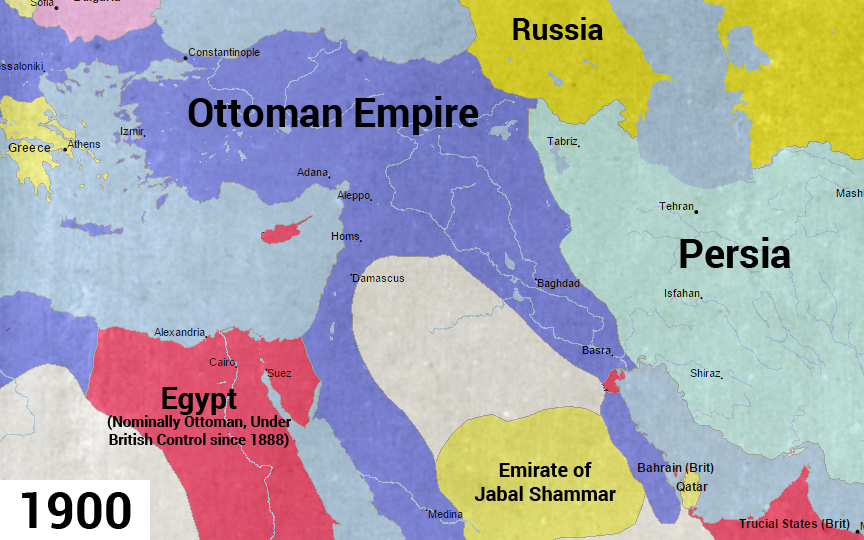
The Middle East, a region steeped in history and marked by diverse cultures, has undergone a dramatic metamorphosis over the past century. Understanding the geopolitical landscape of the region in 1900 provides a crucial foundation for comprehending the complexities of the 21st century. This article delves into the map of the Middle East in 1900, examining its key features, the forces that shaped it, and the profound changes that transformed it into the region we know today.
The Middle East in 1900: A Mosaic of Empires and Protectorates
The map of the Middle East in 1900 presented a fragmented picture, dominated by the influence of European powers. The Ottoman Empire, once a formidable force, was in decline, its vast territories stretching from southeastern Europe to the Arabian Peninsula and North Africa.
- The Ottoman Empire: Despite its waning power, the Ottoman Empire still held sway over significant portions of the Middle East. Its territories included present-day Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Palestine, Iraq, Kuwait, Jordan, Egypt, and parts of the Arabian Peninsula.
- British Influence: Britain had established a strong presence in the region through its control of Egypt, which it occupied in 1882. British influence extended further, encompassing protectorates in Kuwait, Bahrain, and Aden. The British also held significant economic and political power in the Persian Gulf region.
- French Influence: France, another major European power, exerted its influence in the Levant. It controlled Lebanon and Syria, establishing a system of mandates after World War I.
- The Persian Empire: Persia, now known as Iran, remained an independent state but faced increasing pressure from both Britain and Russia, who sought to control its oil resources.
Key Features of the 1900 Map:
- Colonial Boundaries: The boundaries of the Middle Eastern states in 1900 were largely determined by colonial powers, often without regard for existing ethnic, cultural, or linguistic divisions. This artificial division of territories would sow the seeds of future conflicts.
- The Rise of Nationalism: The late 19th and early 20th centuries witnessed the emergence of nationalist movements throughout the Middle East. Arabs, Persians, and other groups sought to break free from colonial rule and establish independent nation-states.
- The Discovery of Oil: The discovery of vast oil reserves in the Persian Gulf region in the early 20th century would have a profound impact on the Middle East’s geopolitical landscape. It would transform the region into a strategic prize for global powers and fuel economic development, but also sow the seeds of conflict and instability.
The Transformation of the Middle East: From 1900 to 2000
The century between 1900 and 2000 witnessed a dramatic reshaping of the Middle East. The decline of European empires, the rise of nationalism, and the discovery of oil were the driving forces behind this transformation.
- The End of Colonialism: The aftermath of World War II saw the dismantling of colonial empires, leading to the emergence of independent states in the Middle East. The Ottoman Empire collapsed, and its territories were divided into new nations, including Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, Jordan, and Palestine.
- The Rise of New States: The creation of independent states, such as Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates, marked a significant shift in the region’s political landscape. These states, fueled by oil wealth, became major players in global affairs.
- The Arab-Israeli Conflict: The establishment of the state of Israel in 1948 sparked a series of wars and conflicts that continue to shape the region today. The Arab-Israeli conflict has been a major source of instability and tension in the Middle East.
- The Cold War: The Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union had a significant impact on the Middle East. Both superpowers sought to align countries with their respective blocs, leading to proxy wars and regional conflicts.
- The Islamic Revolution: The Islamic Revolution in Iran in 1979 marked a turning point in the Middle East. The overthrow of the Shah and the establishment of an Islamic republic challenged the existing order and led to a rise in Islamic fundamentalism.
The Map of the Middle East in 2000: A New Reality
The map of the Middle East in 2000 reflected the dramatic changes that had taken place over the past century. The region was no longer dominated by European powers. Instead, it was a mosaic of independent states, each with its own unique history, culture, and political system.
- New Boundaries: The boundaries of the Middle Eastern states in 2000 were largely defined by the post-colonial era. These boundaries, although often reflecting historical and cultural realities, also served as sources of conflict.
- Oil and Geopolitics: The oil wealth of the Gulf states had transformed their economies and political influence. The region became a vital energy supplier to the world, making it a strategic target for global powers.
- The Rise of Islamic Fundamentalism: The Islamic Revolution in Iran and the subsequent rise of Islamic fundamentalism in other parts of the region had a profound impact on the political landscape.
- The Arab Spring: The Arab Spring uprisings of 2011, which began in Tunisia and spread across the Middle East, demonstrated the growing desire for democracy and social change in the region.
Understanding the Importance of the 1900 Map
The map of the Middle East in 1900 provides a crucial historical lens through which to understand the complexities of the region today. It highlights the impact of colonialism, the rise of nationalism, and the discovery of oil on the region’s political and economic landscape. Understanding the forces that shaped the Middle East in the early 20th century is essential for navigating the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century.
FAQs about the Map of the Middle East in 1900:
1. What were the major European powers that held influence in the Middle East in 1900?
The major European powers that held influence in the Middle East in 1900 were the Ottoman Empire, Great Britain, France, and Russia.
2. Why was the discovery of oil in the Middle East so significant?
The discovery of oil in the Middle East transformed the region’s economic and geopolitical landscape. It turned the region into a strategic prize for global powers and fueled economic development, but also sowed the seeds of conflict and instability.
3. What were the main causes of the Arab-Israeli conflict?
The Arab-Israeli conflict is rooted in competing claims to the land of Palestine. The conflict has been fueled by historical grievances, religious beliefs, and political ambitions.
4. How did the Cold War impact the Middle East?
The Cold War led to the involvement of both the United States and the Soviet Union in the Middle East, often through proxy wars and support for different factions in regional conflicts.
5. What were the main outcomes of the Islamic Revolution in Iran?
The Islamic Revolution in Iran led to the overthrow of the Shah and the establishment of an Islamic republic. It challenged the existing order in the Middle East and led to a rise in Islamic fundamentalism.
Tips for Studying the Map of the Middle East in 1900:
- Use historical maps and atlases: Refer to historical maps and atlases to visualize the boundaries of the Middle Eastern states in 1900.
- Read historical accounts: Explore historical accounts and scholarly works that provide insights into the political, economic, and social conditions of the Middle East in the early 20th century.
- Focus on key events and figures: Pay attention to key events, such as the decline of the Ottoman Empire, the rise of nationalism, and the discovery of oil, and the individuals who played significant roles in shaping the region.
- Analyze the impact of colonialism: Consider the lasting impact of colonialism on the Middle East, including the artificial boundaries it created and the legacy of political and economic dependence.
- Understand the role of oil: Recognize the profound impact of oil on the Middle East’s economy, geopolitics, and social structure.
Conclusion
The map of the Middle East in 1900 offers a valuable window into the region’s history and its transformation over the past century. It highlights the complex interplay of colonial powers, nationalist movements, and global events that shaped the region’s political landscape. Understanding the forces that shaped the Middle East in the early 20th century is crucial for comprehending the challenges and opportunities the region faces today. As the Middle East continues to evolve, its history remains a vital guide for navigating the complexities of its present and future.



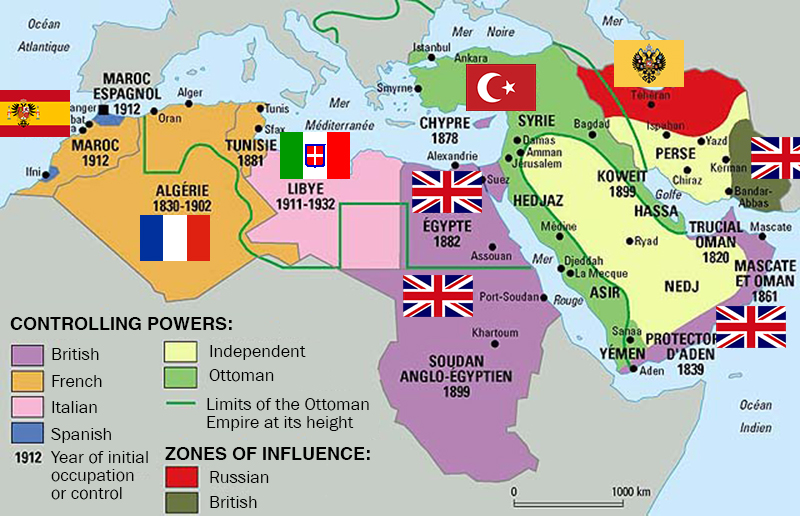



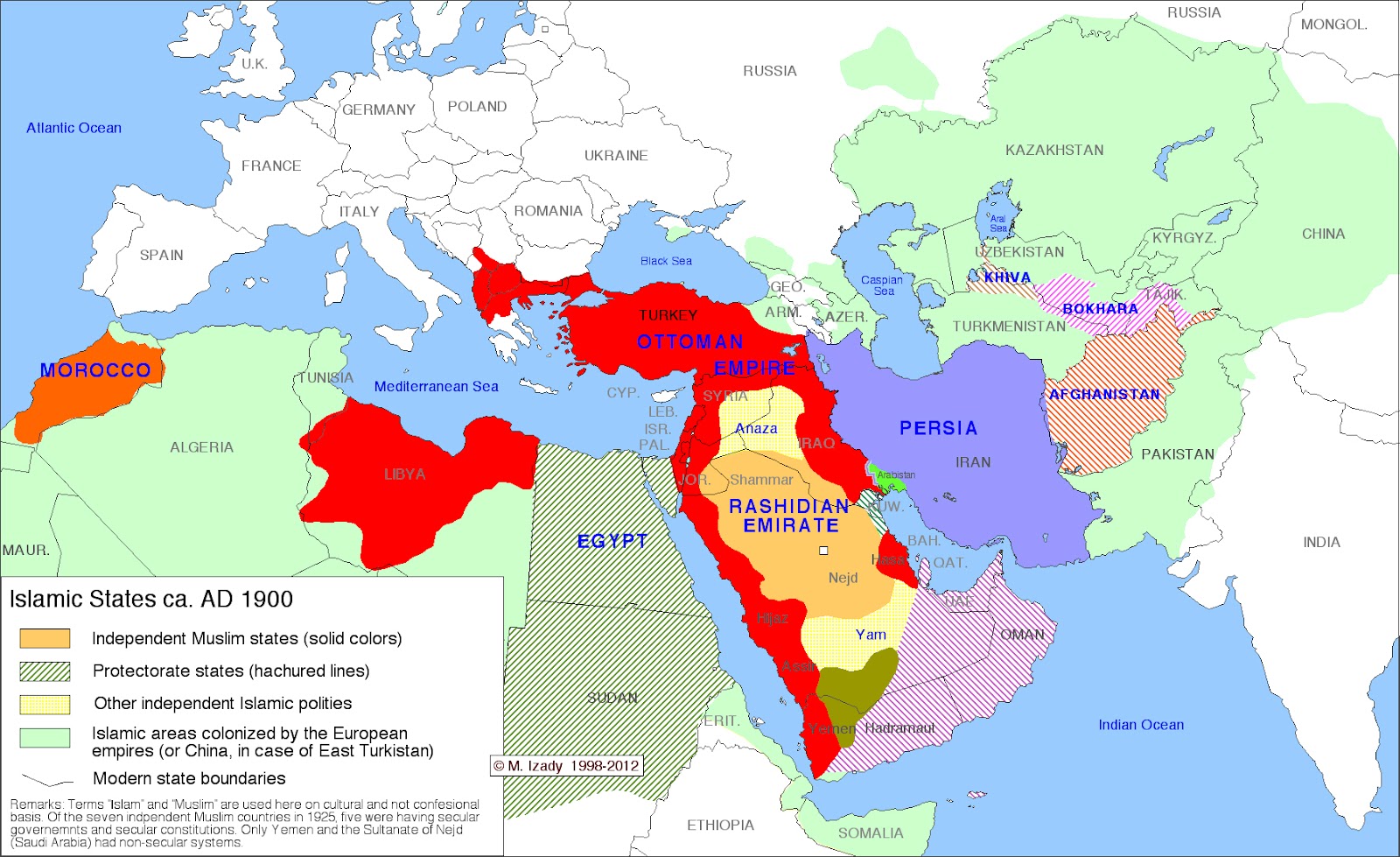
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Century of Transformation: Mapping the Middle East from 1900 to 2000. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!