A Comparative Look at the Maps of Germany and Denmark: Exploring Similarities, Differences, and Historical Significance
Related Articles: A Comparative Look at the Maps of Germany and Denmark: Exploring Similarities, Differences, and Historical Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Look at the Maps of Germany and Denmark: Exploring Similarities, Differences, and Historical Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Look at the Maps of Germany and Denmark: Exploring Similarities, Differences, and Historical Significance

The maps of Germany and Denmark, two geographically and culturally distinct nations, offer a fascinating glimpse into their unique identities and historical trajectories. While sharing a common European heritage, their landscapes, political structures, and cultural influences have shaped their individual maps in remarkable ways. This article delves into a comparative analysis of these maps, highlighting key geographical features, historical developments, and cultural nuances that contribute to their distinctive character.
Geographical Landscape: A Contrasting Tapestry
Germany, a land of diverse landscapes, presents a complex map. Its geographic features are characterized by:
- Central European Location: Situated in the heart of Europe, Germany borders nine countries, creating a dynamic cultural and political landscape.
- Variety of Terrain: From the North Sea coast and the flat plains of the north to the rugged Alps in the south, Germany boasts a rich tapestry of geographical features.
- Major Rivers: The Rhine, Elbe, and Danube rivers are vital waterways, playing a crucial role in transportation, trade, and cultural exchange.
- Dense Forest Cover: The Black Forest and Harz Mountains are home to extensive forests, contributing to Germany’s natural beauty and ecological importance.
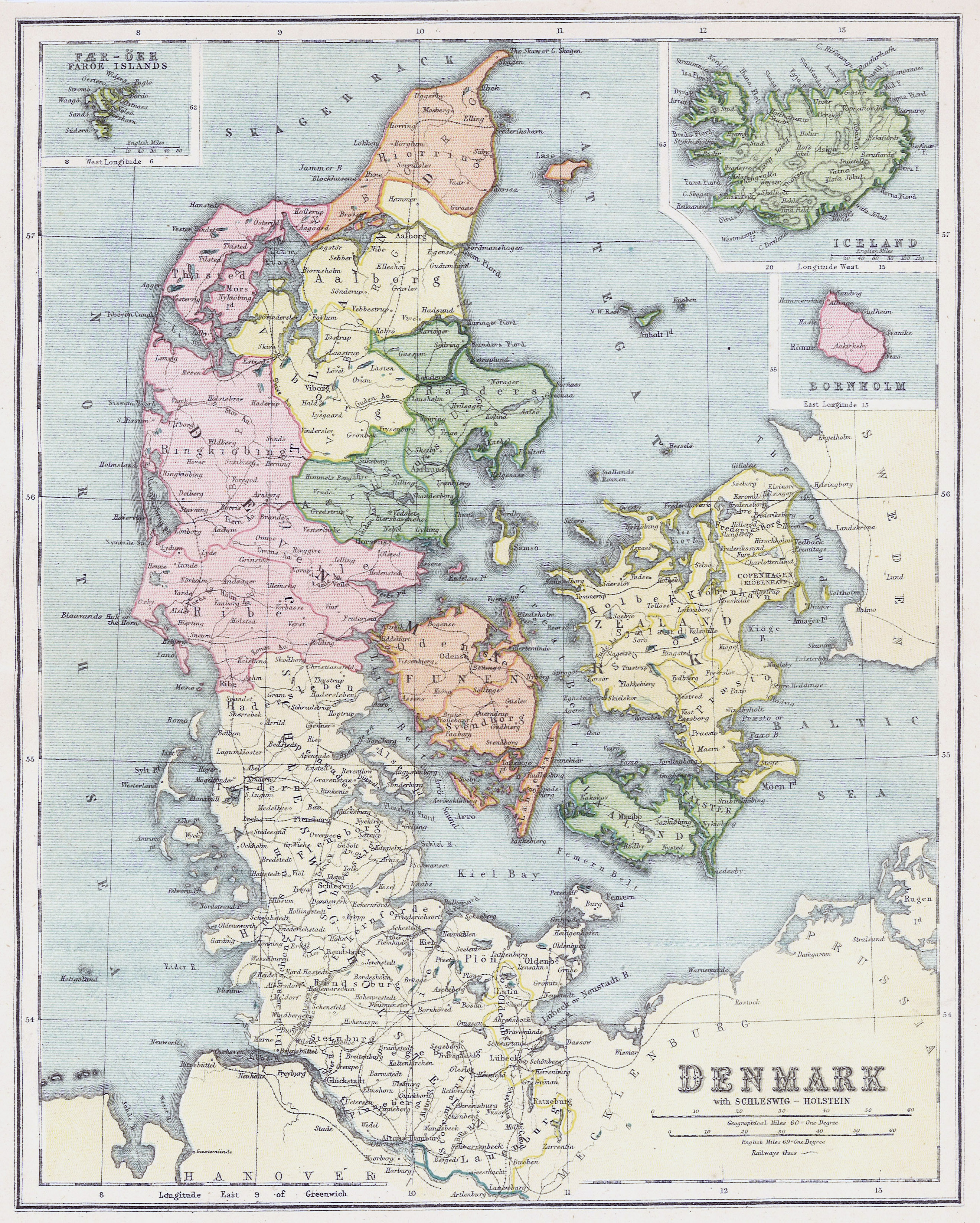
In contrast, Denmark, a nation defined by its proximity to the sea, exhibits a less varied map:
- Scandinavian Peninsula: Denmark occupies the southernmost portion of the Jutland Peninsula and a collection of islands, including Zealand, Funen, and Bornholm.
- Coastal Dominance: The country’s coastline is extensive, offering access to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea, influencing its maritime culture and trade.
- Flat Topography: Denmark’s landscape is predominantly flat, with rolling hills and low-lying areas, creating a distinct visual character.
- Limited Landmass: Compared to Germany, Denmark’s landmass is significantly smaller, emphasizing its insular nature and its dependence on maritime trade.
Historical Echoes: Shaping the Maps
The maps of Germany and Denmark reflect their rich histories, marked by political transformations, territorial shifts, and cultural influences.
Germany:
- Fragmentation and Unification: Germany’s map has been shaped by centuries of fragmentation and reunification. The Holy Roman Empire, the German Confederation, and the rise of Prussia led to a complex patchwork of states and territories.
- World Wars and Division: The devastating World Wars, particularly World War II, resulted in significant territorial changes, culminating in the division of Germany into East and West.
- Reunification and Stability: The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 and the subsequent reunification of Germany marked a significant moment in its history, leading to a unified map and a stable political structure.
Denmark:
- Viking Expansion: The Vikings, originating from Scandinavia, played a crucial role in shaping Denmark’s history and its map. Their raids and settlements extended their influence across Europe.
- Danish Empire: During the Middle Ages, Denmark emerged as a powerful empire, controlling territories in Scandinavia, the Baltic region, and even parts of England.
- Loss of Territories: Over time, Denmark lost territories, including Norway, Sweden, and Schleswig-Holstein, leading to a gradual reduction in its landmass and a shift in its geopolitical influence.
Cultural Tapestry: A Blend of Traditions and Influences
The maps of Germany and Denmark also reflect their distinct cultural identities, shaped by centuries of tradition, artistic expression, and global exchange.
Germany:
- Regional Diversity: Germany’s map reflects its cultural diversity, with distinct regional traditions, languages, and dialects. From the Bavarian Alps to the Hanseatic cities of the north, each region has its unique character.
- Artistic Heritage: Germany has a rich artistic heritage, encompassing music, literature, philosophy, and visual arts. Figures like Beethoven, Goethe, and Kant have left an indelible mark on European culture.
- Industrial Powerhouse: Germany’s map also reflects its economic prowess, with major industrial centers and technological advancements, contributing to its global standing.
Denmark:
- Scandinavian Identity: Denmark’s map reflects its strong Scandinavian identity, characterized by a focus on social welfare, sustainability, and a strong sense of community.
- Maritime Culture: Denmark’s coastal location has fostered a maritime culture, evident in its fishing industry, shipbuilding, and its love for the sea.
- Design and Innovation: Denmark is renowned for its design aesthetic, with iconic brands like LEGO and Bang & Olufsen, reflecting its commitment to innovation and creativity.
Conclusion: A Comparative Perspective
The maps of Germany and Denmark, while distinct in their geographical features, historical trajectories, and cultural expressions, share a common thread of European identity and a rich tapestry of human experience. Their contrasting landscapes, political structures, and cultural influences offer a fascinating lens through which to understand their individual journeys and their enduring contributions to the broader European narrative.
FAQs
Q: What are the main geographical differences between Germany and Denmark?
A: Germany is characterized by a diverse landscape, ranging from flat plains to rugged mountains, while Denmark is predominantly flat and coastal. Germany has a larger landmass and borders nine countries, while Denmark is a smaller nation with an extensive coastline.
Q: How have historical events shaped the maps of Germany and Denmark?
A: Germany’s map has been influenced by centuries of fragmentation and unification, including the World Wars and the division of East and West Germany. Denmark’s map has been shaped by its Viking heritage, its expansion as a powerful empire, and its subsequent loss of territories.
Q: What are some key cultural differences reflected in the maps of Germany and Denmark?
A: Germany’s map reflects its regional diversity, artistic heritage, and industrial strength. Denmark’s map highlights its Scandinavian identity, maritime culture, and focus on design and innovation.
Tips
- Use a map of Germany and Denmark for reference: Visualizing the geographical relationship between the two countries is crucial for understanding their similarities and differences.
- Explore historical maps: Examining historical maps of Germany and Denmark can provide valuable insights into their territorial changes and political developments.
- Research regional differences: Delving into the cultural and linguistic variations within Germany and Denmark can enrich your understanding of their maps and their unique identities.
Conclusion
The maps of Germany and Denmark offer a compelling window into their individual histories, landscapes, and cultures. By comparing and contrasting these maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and nuances of these two European nations and their enduring contributions to the global stage.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Look at the Maps of Germany and Denmark: Exploring Similarities, Differences, and Historical Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!