A Shifting Landscape: Understanding the Middle East in 1900
Related Articles: A Shifting Landscape: Understanding the Middle East in 1900
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Shifting Landscape: Understanding the Middle East in 1900. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Shifting Landscape: Understanding the Middle East in 1900

The Middle East in 1900 presented a complex tapestry of empires, territories, and emerging national identities. This region, often perceived as a single entity today, was a mosaic of diverse political entities, each with its own history, culture, and aspirations. A detailed examination of the Middle East map in 1900 reveals the intricate power dynamics and the seeds of future conflicts that would shape the region for decades to come.
A Mosaic of Empires and Territories:
The Middle East in 1900 was dominated by the crumbling Ottoman Empire, a vast and aging entity that had once stretched across vast swathes of the region. The empire’s decline, marked by internal strife and external pressures from European powers, had paved the way for the rise of new forces.
-
The Ottoman Empire: Despite its declining power, the Ottoman Empire still held significant territory in the Middle East. Its vast expanse encompassed present-day Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Palestine, Jordan, Iraq, and parts of Egypt and the Arabian Peninsula. However, the empire’s control over these territories was increasingly tenuous, with nationalist movements gaining momentum in various regions.
-
The British Empire: Britain, a rising power in the 19th century, had established a strong presence in the region through trade and strategic alliances. The British Empire controlled Egypt, Sudan, and Cyprus, and had significant influence in the Persian Gulf. British ambitions in the region were fueled by the desire to secure access to vital trade routes and resources, particularly oil.
-
The French Empire: France, another European power seeking to expand its influence, had established control over Algeria and Tunisia in North Africa. France also had significant influence in Lebanon, which was under the control of the Ottoman Empire but heavily influenced by French culture and education.
-
The Russian Empire: Russia, seeking to expand its influence in the region, had gained control over the Caucasus region and was eyeing territories within the Ottoman Empire. The Russian Empire’s ambitions in the Middle East were fueled by its desire to secure access to warm-water ports and control over strategic trade routes.
-
Independent States: Despite the dominance of empires, some independent states existed in the Middle East in 1900. These included Persia (modern-day Iran), Afghanistan, and the Arabian Peninsula, which was divided into various independent sheikhdoms.
The Rise of Nationalism and the Seeds of Conflict:
The late 19th century witnessed the emergence of powerful nationalist movements in the Middle East, challenging the existing empires and paving the way for future upheavals.
-
Arab Nationalism: Arab nationalism, fueled by a shared language, culture, and history, emerged as a powerful force against Ottoman rule. Arab intellectuals and leaders began advocating for self-determination and the creation of an independent Arab state.
-
Zionism: The Zionist movement, advocating for the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine, gained traction in the late 19th century. The movement was supported by European Jews seeking refuge from persecution and by international powers seeking to establish a strategic foothold in the region.
-
Persian Nationalism: In Persia, nationalist sentiments were fueled by the country’s growing economic and political dependence on foreign powers, particularly Britain and Russia. Persian nationalists sought to modernize the country and assert its independence.
The Impact of European Powers:
The influence of European powers in the Middle East was profound, shaping the region’s political landscape and fueling tensions.
-
The Scramble for Resources: European powers were driven by a desire to secure access to the region’s abundant resources, particularly oil, which was becoming increasingly important in the growing industrial world.
-
Strategic Rivalries: European powers engaged in intense rivalry for control over strategic territories and trade routes in the Middle East, leading to conflicts and alliances that had a profound impact on the region.
-
The Sykes-Picot Agreement: The secret agreement between Britain and France in 1916, known as the Sykes-Picot Agreement, divided the Ottoman Empire’s Arab territories into British and French spheres of influence. This agreement laid the foundation for the creation of modern-day Middle Eastern states and sowed the seeds of future conflicts.
The Legacy of 1900:
The Middle East in 1900 was a region on the cusp of dramatic change. The decline of the Ottoman Empire, the rise of nationalism, and the increasing influence of European powers set the stage for the tumultuous 20th century. The map of the Middle East in 1900 serves as a reminder of the complex historical forces that shaped the region and the enduring challenges it faces today.
Understanding the Significance:
Examining the Middle East map in 1900 provides crucial insights into the region’s current political landscape. It highlights the historical roots of modern conflicts, the enduring legacy of colonialism, and the complex interplay of cultural, religious, and political identities. Understanding the past is essential for navigating the present and building a more stable and prosperous future for the Middle East.
FAQs:
1. What were the major empires that controlled the Middle East in 1900?
The major empires that controlled the Middle East in 1900 were the Ottoman Empire, the British Empire, the French Empire, and the Russian Empire.
2. What were the main factors contributing to the decline of the Ottoman Empire?
The decline of the Ottoman Empire was due to a combination of factors, including internal strife, economic stagnation, military defeats, and the growing influence of European powers.
3. What were the main nationalist movements that emerged in the Middle East in the late 19th century?
The main nationalist movements that emerged in the Middle East in the late 19th century were Arab nationalism, Zionism, and Persian nationalism.
4. What was the significance of the Sykes-Picot Agreement?
The Sykes-Picot Agreement divided the Ottoman Empire’s Arab territories into British and French spheres of influence, laying the foundation for the creation of modern-day Middle Eastern states and sowing the seeds of future conflicts.
5. How did the influence of European powers shape the Middle East in the late 19th century?
European powers sought to secure access to the region’s resources, particularly oil, and to establish strategic footholds in the region. This led to intense rivalry, conflicts, and alliances that had a profound impact on the Middle East.
Tips for Studying the 1900 Middle East Map:
- Focus on the major empires and their territories: Identify the territories controlled by each empire and understand the boundaries and overlapping areas of influence.
- Pay attention to the rise of nationalism: Analyze the location of nationalist movements and their potential for challenging existing empires.
- Consider the influence of European powers: Examine the strategic interests of European powers in the region and their impact on the political landscape.
- Connect the map to historical events: Use the map to understand the context of major historical events, such as the decline of the Ottoman Empire, the emergence of Arab nationalism, and the Sykes-Picot Agreement.
- Compare the 1900 map with modern maps: Analyze the changes in borders and political entities over time and understand the historical forces that shaped the current map of the Middle East.
Conclusion:
The Middle East in 1900 was a region in transition, marked by the decline of empires, the rise of nationalism, and the growing influence of European powers. Understanding the map of the Middle East in 1900 is essential for appreciating the complex historical forces that shaped the region and the challenges it faces today. By analyzing the political landscape of 1900, we gain a deeper understanding of the enduring legacy of colonialism, the roots of modern conflicts, and the intricate interplay of cultural, religious, and political identities that continue to shape the Middle East.
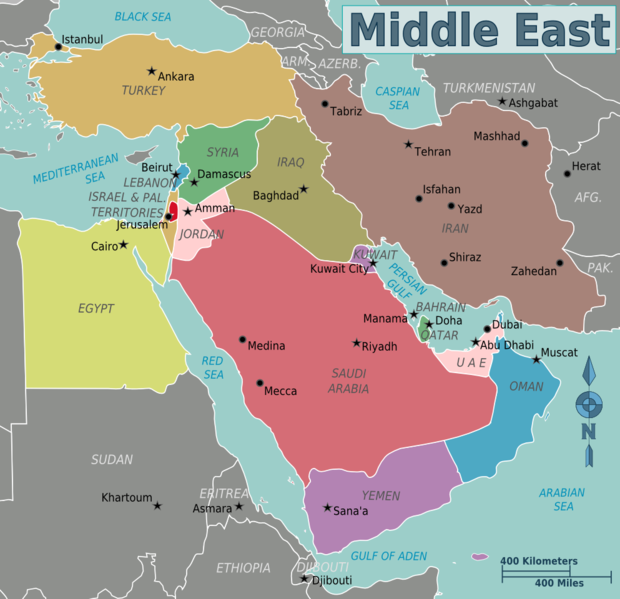


![Historical Cultural Zones of the Middle East.[2000x1520] : r/MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/SUb4-OCNhIBbDEcDXUGF7KiVLg1nCJPTKl8dwGcaj5I.png?auto=webpu0026s=763bb03878b9ffc49d61a2dafe7d0be27d2cce5c)
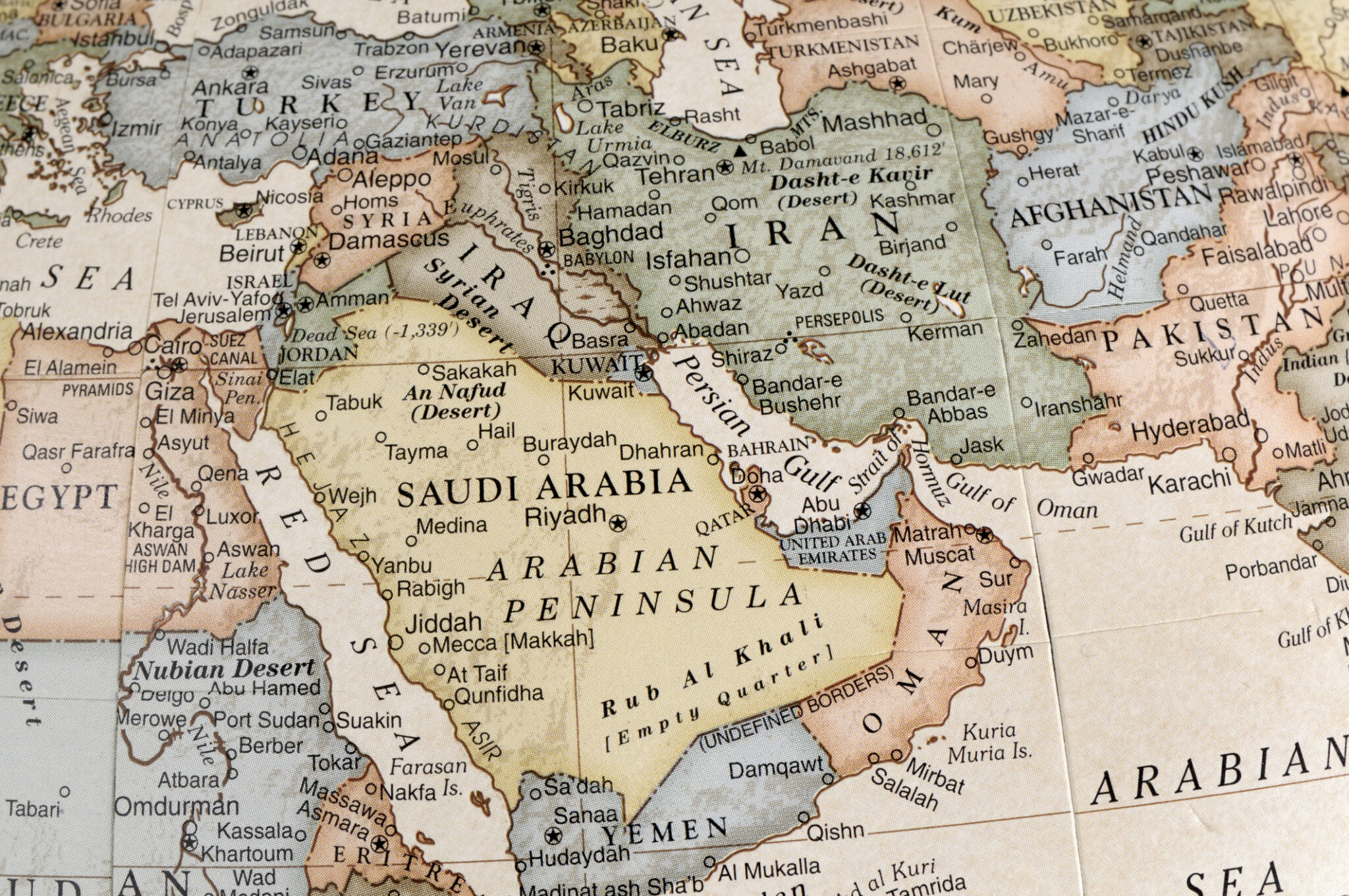

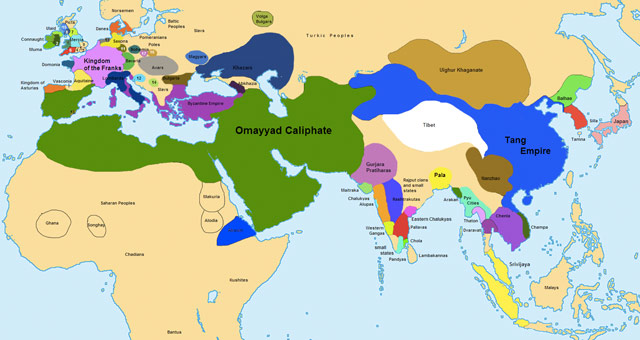
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Shifting Landscape: Understanding the Middle East in 1900. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!