Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Guide to Geographic Map Symbols
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Guide to Geographic Map Symbols
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Guide to Geographic Map Symbols. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Guide to Geographic Map Symbols
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Guide to Geographic Map Symbols
- 3.1 The Importance of Geographic Map Symbols
- 3.2 A Comprehensive Overview of Geographic Map Symbols
- 3.3 Understanding the Language of Maps: A Case Study
- 3.4 FAQs Regarding Geographic Map Symbols
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Map Interpretation
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Power of Visual Communication
- 4 Closure
Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Guide to Geographic Map Symbols

Maps, those ubiquitous representations of the world, are more than just static images. They are intricate visual languages, employing a diverse array of symbols to convey a wealth of information about our planet. Understanding these symbols is crucial for interpreting maps effectively, enabling us to navigate unfamiliar landscapes, grasp geographical relationships, and gain insights into the complexities of the world around us.
The Importance of Geographic Map Symbols
Geographic map symbols are essential for several reasons:
- Clarity and Conciseness: Symbols provide a concise and efficient way to represent a multitude of features on a map, from cities and rivers to mountains and forests. They eliminate the need for lengthy descriptions, allowing for a clear and concise representation of information.
- Visual Communication: Symbols act as a universal language, transcending linguistic barriers. Their visual nature allows for intuitive understanding, regardless of the reader’s native tongue.
- Spatial Relationships: Map symbols help establish spatial relationships between different features. Their placement and arrangement convey the relative locations and distances between objects, providing a visual understanding of geographical connections.
- Data Visualization: Symbols can be used to represent various data points, such as population density, elevation, or rainfall. This visual representation allows for quick and easy interpretation of complex data sets.
A Comprehensive Overview of Geographic Map Symbols
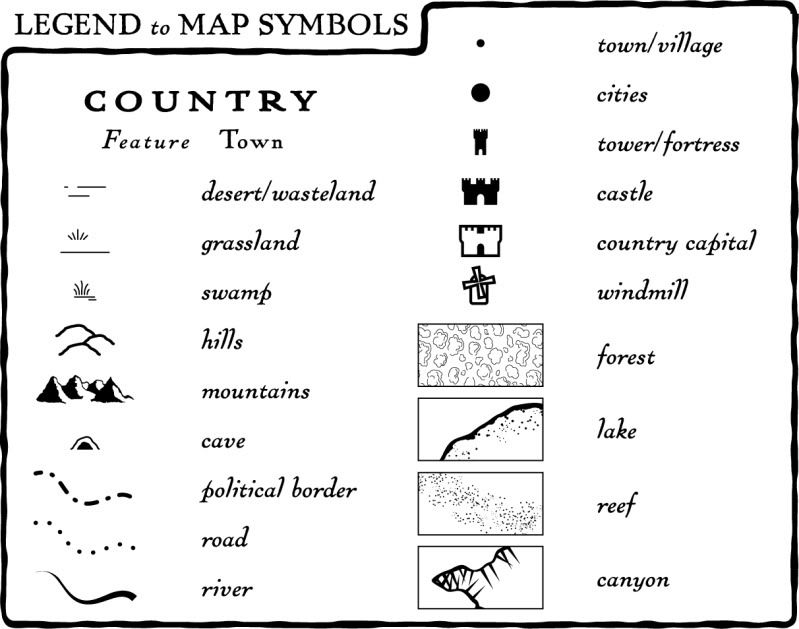
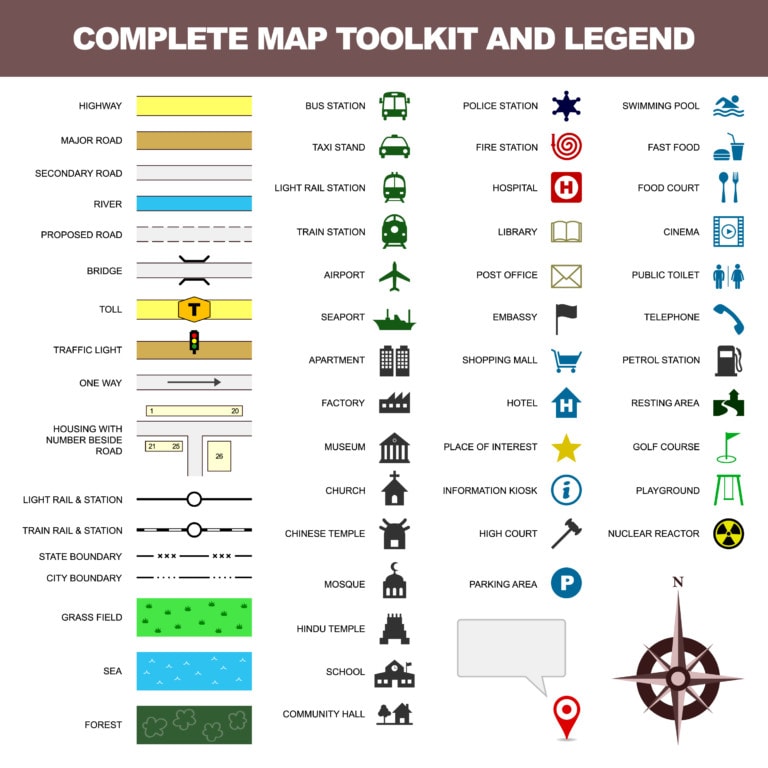
Geographic map symbols can be broadly categorized into several types:
1. Point Symbols:
Point symbols represent features that occupy a specific point in space, such as:
- Cities and Towns: Often represented by circles, squares, or stars, with size indicating population.
- Points of Interest: Symbols like churches, airports, or lighthouses use specific icons to denote their function.
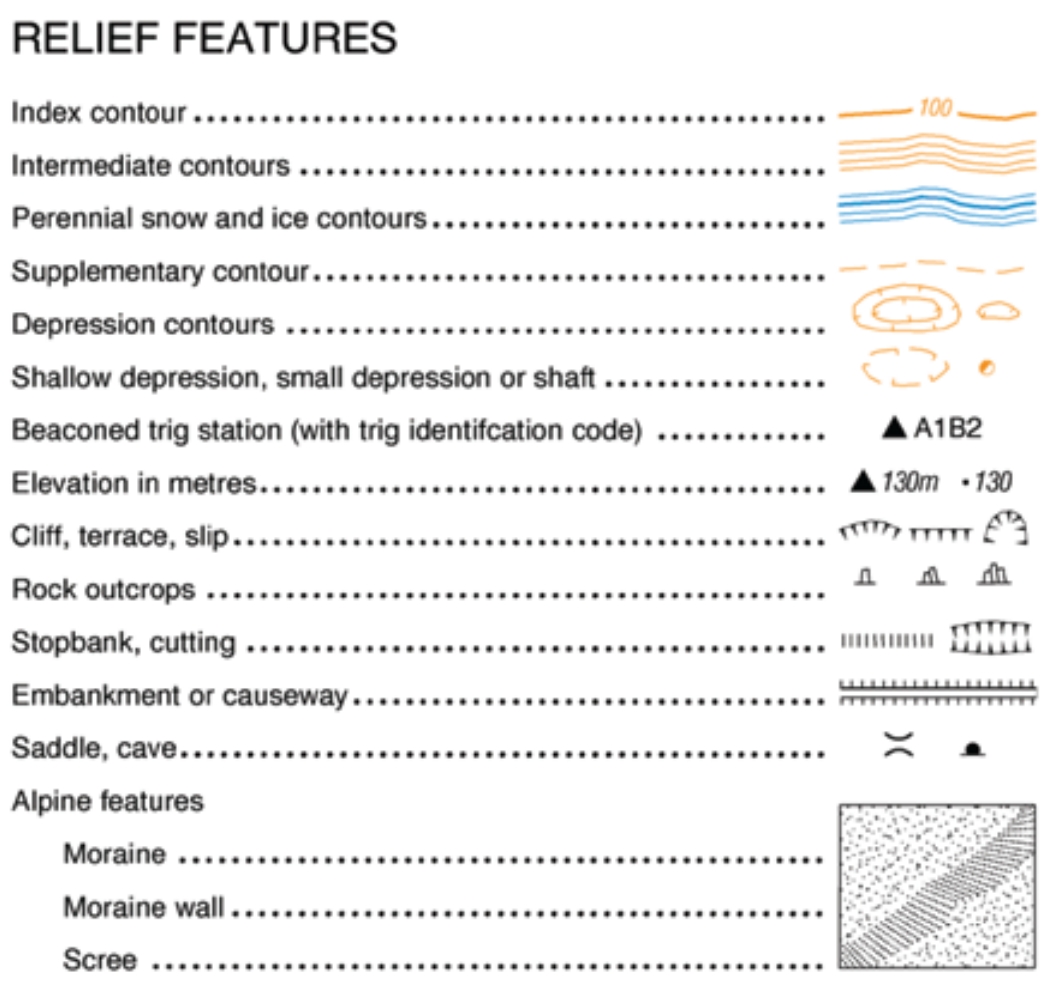
- Geographical Features: Mountains, volcanoes, and waterfalls are often represented by triangular or cone-shaped symbols.
2. Line Symbols:
Line symbols represent features that extend over a distance, such as:
- Roads: Solid lines, dashed lines, or dotted lines indicate different types of roads, including highways, local roads, and trails.
- Rivers and Streams: Blue lines, with varying thickness to indicate size, depict flowing water bodies.
- Boundaries: Solid lines, dashed lines, or dotted lines represent national, state, or county boundaries.
3. Area Symbols:
Area symbols represent features that occupy a defined area, such as:
- Forests: Green shading or patterns represent forested areas.
- Lakes and Oceans: Blue shading or patterns depict bodies of water.
- Political Divisions: Different colors or patterns are used to differentiate countries, states, or provinces.
4. Symbol Conventions:
Beyond the basic types, there are established conventions for specific symbols:
- Color: Color plays a significant role in map interpretation. Blue typically represents water, green represents vegetation, and brown represents landforms.
- Size: The size of a symbol often indicates the importance or magnitude of a feature. Larger cities are represented by larger circles, while smaller towns are represented by smaller circles.
- Shape: The shape of a symbol can convey specific information. For example, a star might represent a capital city, while a triangle might represent a mountain peak.
- Pattern: Patterns within symbols can be used to represent different types of features. For instance, different types of roads might be distinguished by different line patterns.
Understanding the Language of Maps: A Case Study
Let’s consider a simple example: a map of a national park. This map might use a variety of symbols to represent different features, such as:
- Point Symbols: Campgrounds, hiking trails, and visitor centers might be marked with specific icons.
- Line Symbols: Trails, roads, and rivers might be represented by different types of lines.
- Area Symbols: Forests, meadows, and lakes might be indicated by different colors or patterns.
By interpreting these symbols, a visitor can quickly understand the layout of the park, locate key points of interest, and plan their hiking route.
FAQs Regarding Geographic Map Symbols
1. What is the purpose of map symbols?
Map symbols provide a concise and efficient way to represent a multitude of features on a map, allowing for clear and intuitive communication. They facilitate understanding of spatial relationships and the visual representation of data.
2. How can I learn to interpret map symbols?
The best way to learn is through practice. Start by studying maps with a legend, which explains the meaning of each symbol. As you become familiar with common symbols, you’ll be able to interpret maps with increasing confidence.
3. What are some common map symbol conventions?
Common conventions include using blue for water, green for vegetation, brown for landforms, and larger symbols for more important features. Shapes and patterns also convey specific information.
4. Are map symbols standardized?
While there are common conventions, there is no universal standard for map symbols. Different organizations and mapmakers may use slightly different symbols. It’s always important to refer to the legend to ensure accurate interpretation.
5. How can I create my own maps using symbols?
There are numerous software programs available for creating maps, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, and Google My Maps. These programs allow you to choose from a library of symbols or create your own custom symbols.
Tips for Effective Map Interpretation
- Always refer to the legend: The legend is the key to understanding the meaning of symbols on a map.
- Pay attention to color, size, and shape: These elements convey important information about the features represented.
- Consider the scale of the map: The scale indicates the ratio between the map distance and the actual distance, which affects the size and detail of symbols.
- Use a compass: A compass helps you orient yourself on the map and understand the direction of features.
- Practice makes perfect: The more you use maps, the more familiar you’ll become with different symbols and conventions.
Conclusion: The Power of Visual Communication
Geographic map symbols are an integral part of our understanding of the world. They provide a powerful tool for visual communication, allowing us to navigate, explore, and analyze the complexities of our planet. By understanding the language of maps, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the world around us and unlock a wealth of information that lies hidden within their intricate visual representations.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Guide to Geographic Map Symbols. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!