Delving into Plantation Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Historical Landscapes
Related Articles: Delving into Plantation Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Historical Landscapes
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delving into Plantation Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Historical Landscapes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into Plantation Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Historical Landscapes
Plantation maps, often overlooked in the broader realm of historical cartography, hold a significant place in understanding the complex and often-fraught history of agriculture, particularly in the context of colonial expansion and the transatlantic slave trade. These maps, which depict the layout and organization of large-scale agricultural estates, offer a unique window into the past, revealing not only the physical landscape but also the social and economic structures that underpinned plantation life.
Understanding the Significance of Plantation Maps
Plantation maps are more than just depictions of land ownership and agricultural practices. They provide a nuanced understanding of the intricate systems that shaped the lives of individuals, communities, and economies. They offer insights into:
- Land Ownership and Distribution: Plantation maps clearly delineate property boundaries, revealing the power dynamics and landholding patterns prevalent in a given region. This information is crucial for understanding the concentration of wealth and the social stratification of the time.
- Agricultural Practices and Production: These maps illustrate the layout of fields, the types of crops cultivated, and the infrastructure associated with plantation operations. This data provides valuable insights into the economic activities and the scale of agricultural production.
- Labor Systems and Social Hierarchy: Plantation maps often depict the locations of slave quarters, overseer’s houses, and other structures. These details shed light on the spatial separation and social hierarchy inherent in the plantation system.
- Environmental Impact: By revealing the patterns of land use and resource extraction, plantation maps offer insights into the ecological transformations wrought by large-scale agricultural practices.
Types of Plantation Maps and their Uses
Plantation maps can be broadly classified into two categories:
- Survey Maps: These maps, typically created by professional surveyors, provide detailed measurements and accurate representations of the land’s topography, property boundaries, and infrastructure. They were often used for legal purposes, such as land transactions and tax assessments.
- Plan Maps: These maps, often drawn by plantation owners or managers, focus on the functional layout and organization of the plantation. They depict the arrangement of fields, buildings, and other features relevant to agricultural operations.
Reading and Interpreting Plantation Maps
Deciphering plantation maps requires a keen eye for detail and an understanding of the conventions and symbols used in cartography. Some key elements to consider include:
- Scale: The scale of the map determines the level of detail and the area it represents.
- Legend: The legend provides a key to understanding the symbols and abbreviations used on the map.
- Land Features: Rivers, streams, roads, and other natural and man-made features are depicted on the map, offering insights into the physical landscape and its impact on plantation operations.
- Buildings and Structures: The map may depict the location and size of the plantation house, slave quarters, barns, mills, and other structures, revealing the hierarchy and organization of the plantation.
- Field Layout: The arrangement of fields, the types of crops cultivated, and the rotation patterns can be gleaned from the map.
- Boundaries: Property lines and other boundaries are often depicted on the map, highlighting the ownership patterns and landholding arrangements.
The Importance of Archival Research
Plantation maps are often housed in archives, libraries, and historical societies. Accessing and studying these maps requires careful archival research. This process involves:
- Identifying relevant repositories: Researching online databases and contacting institutions to locate collections of plantation maps.
- Requesting access: Obtaining permission to view and study the maps, following the institution’s guidelines.
- Understanding archival materials: Familiarizing oneself with the history and context of the maps, including their creation date, creator, and purpose.
- Analyzing and interpreting data: Closely examining the map’s details and drawing conclusions based on the information presented.
FAQs about Plantation Maps
1. How can I find plantation maps online?
Numerous online resources offer access to digitized plantation maps. The Library of Congress, the National Archives and Records Administration, and various state archives provide searchable databases and online collections.
2. What are some common symbols used on plantation maps?
Common symbols include:
- Squares: Represent buildings or structures.
- Lines: Represent roads, fences, or property boundaries.
- Dots: Represent trees, wells, or other features.
- Abbreviations: Represent specific crops or types of buildings.
3. How can I learn more about the history of a specific plantation?
Consult historical records, plantation diaries, and other primary sources to gain a deeper understanding of the plantation’s history, its owners, and its inhabitants.
4. How can plantation maps be used in education?
Plantation maps can be used in classrooms to teach students about history, geography, economics, and social studies. They provide a visual and interactive way to explore the complexities of the plantation system.
Tips for Using Plantation Maps
- Contextualize the Map: Understand the time period, location, and purpose of the map to interpret its information accurately.
- Cross-Reference Data: Compare the map with other historical sources to verify information and gain a broader understanding.
- Consider the Perspective: Recognize that plantation maps are often created from the perspective of the plantation owners, reflecting their biases and interests.
- Engage in Critical Analysis: Question the information presented on the map, considering the historical context and the potential biases of the creator.
Conclusion
Plantation maps are invaluable historical documents that offer a unique perspective on the past. They illuminate the complex relationship between land, labor, and power during the colonial era and provide insights into the social, economic, and environmental impacts of plantation agriculture. By studying these maps, we gain a deeper understanding of the history of the Americas and the lasting legacies of the plantation system.

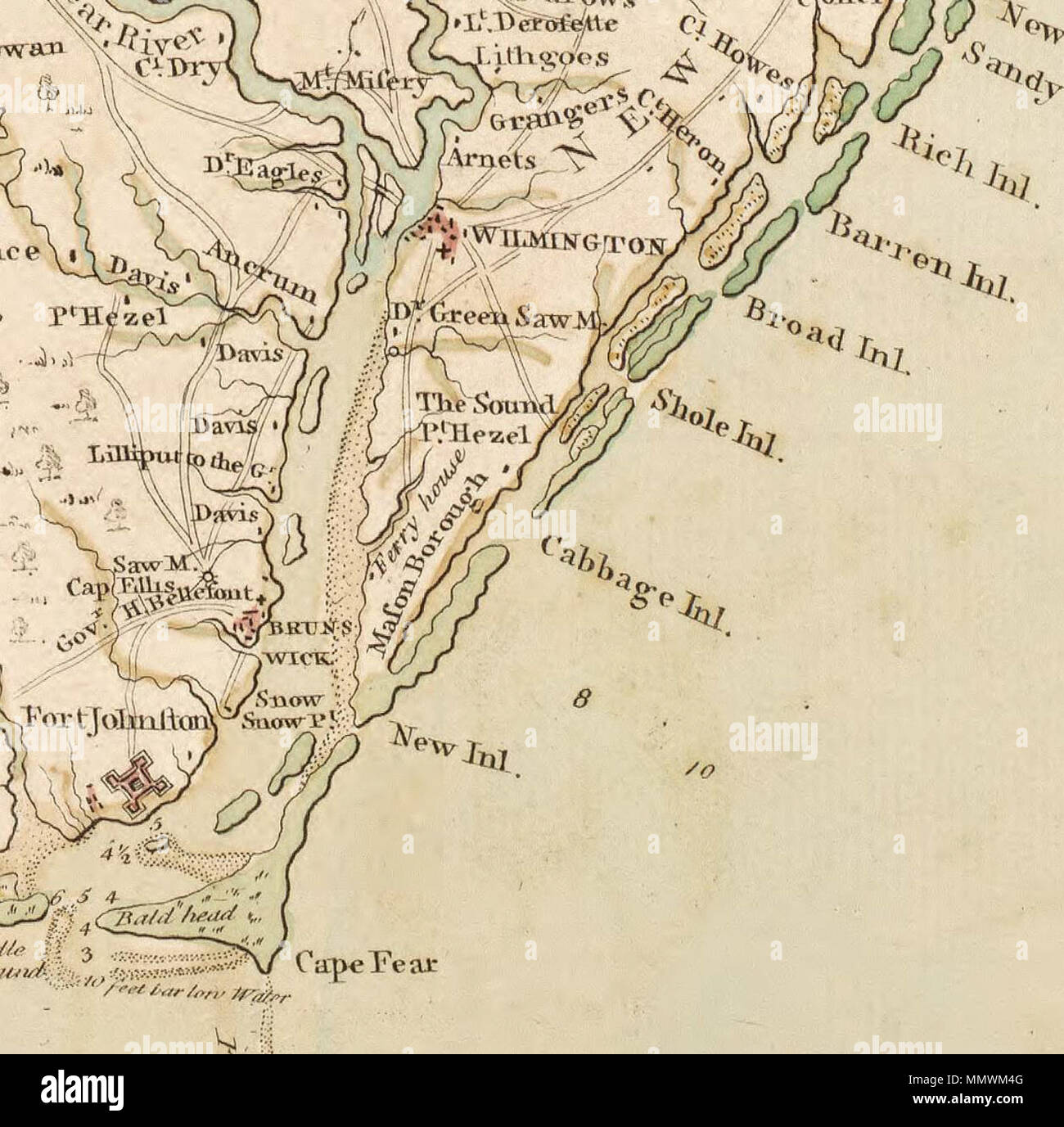




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into Plantation Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Historical Landscapes. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!