Navigating Germany: A Comprehensive Guide to its Geography and Symbolism
Related Articles: Navigating Germany: A Comprehensive Guide to its Geography and Symbolism
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating Germany: A Comprehensive Guide to its Geography and Symbolism. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Germany: A Comprehensive Guide to its Geography and Symbolism
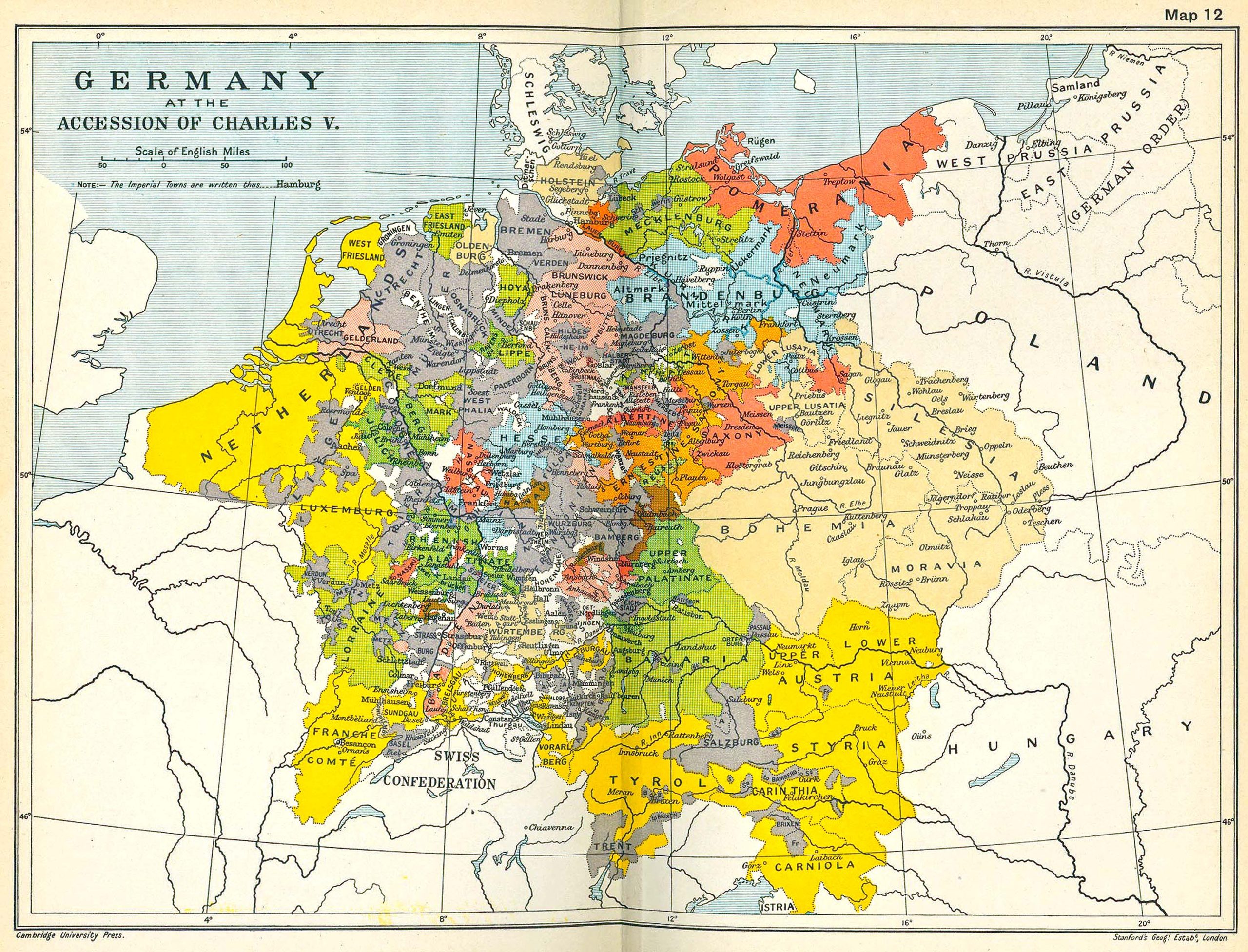
Germany, a nation steeped in history, culture, and innovation, is a land of diverse landscapes and vibrant cities. Understanding its geography and its symbolic representation through the national flag is essential to appreciating its multifaceted identity. This article delves into the intricacies of Germany’s map and its flag, exploring their significance and offering a comprehensive guide to the nation’s spatial and symbolic character.
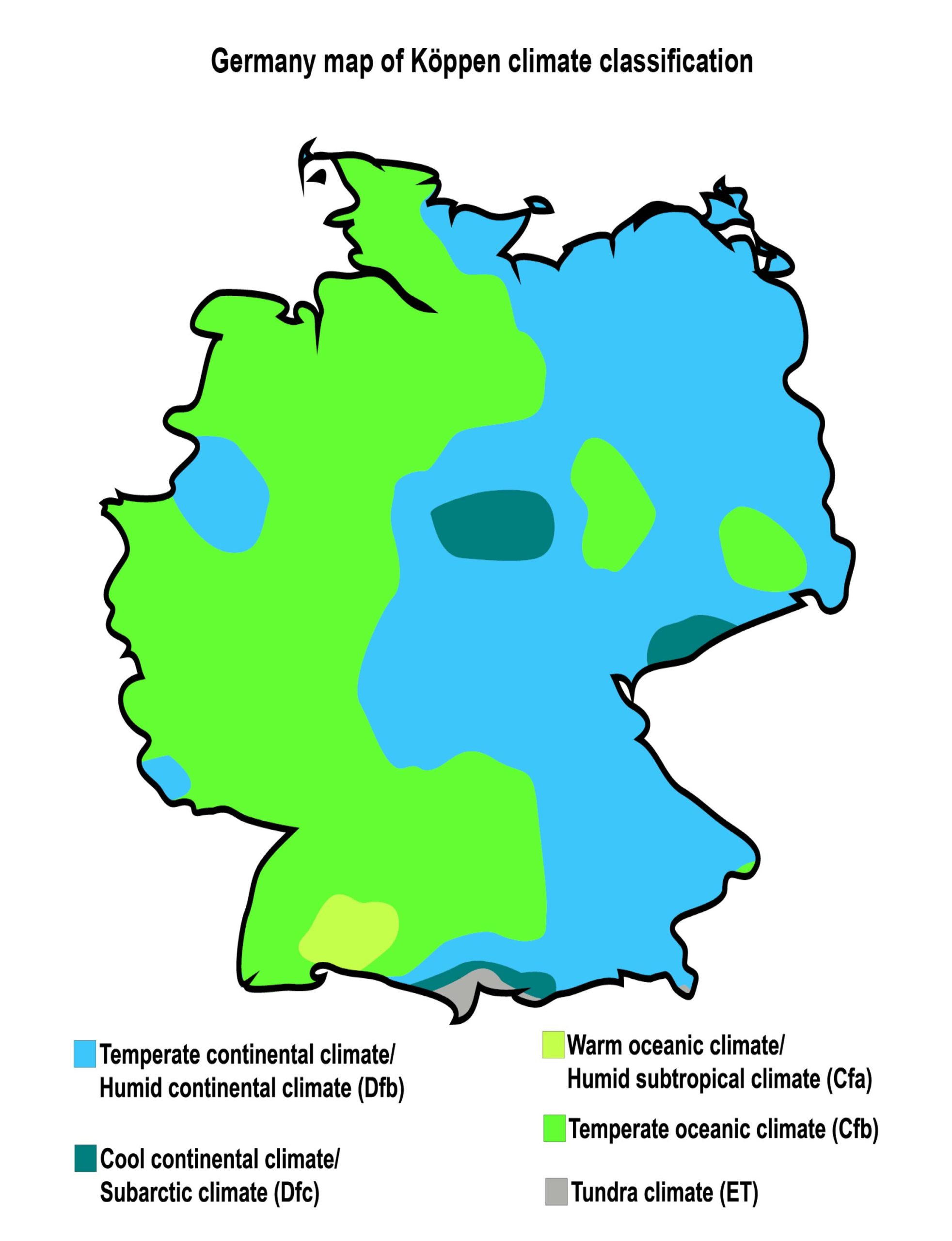
Germany’s Geographical Landscape: A Tapestry of Diverse Regions
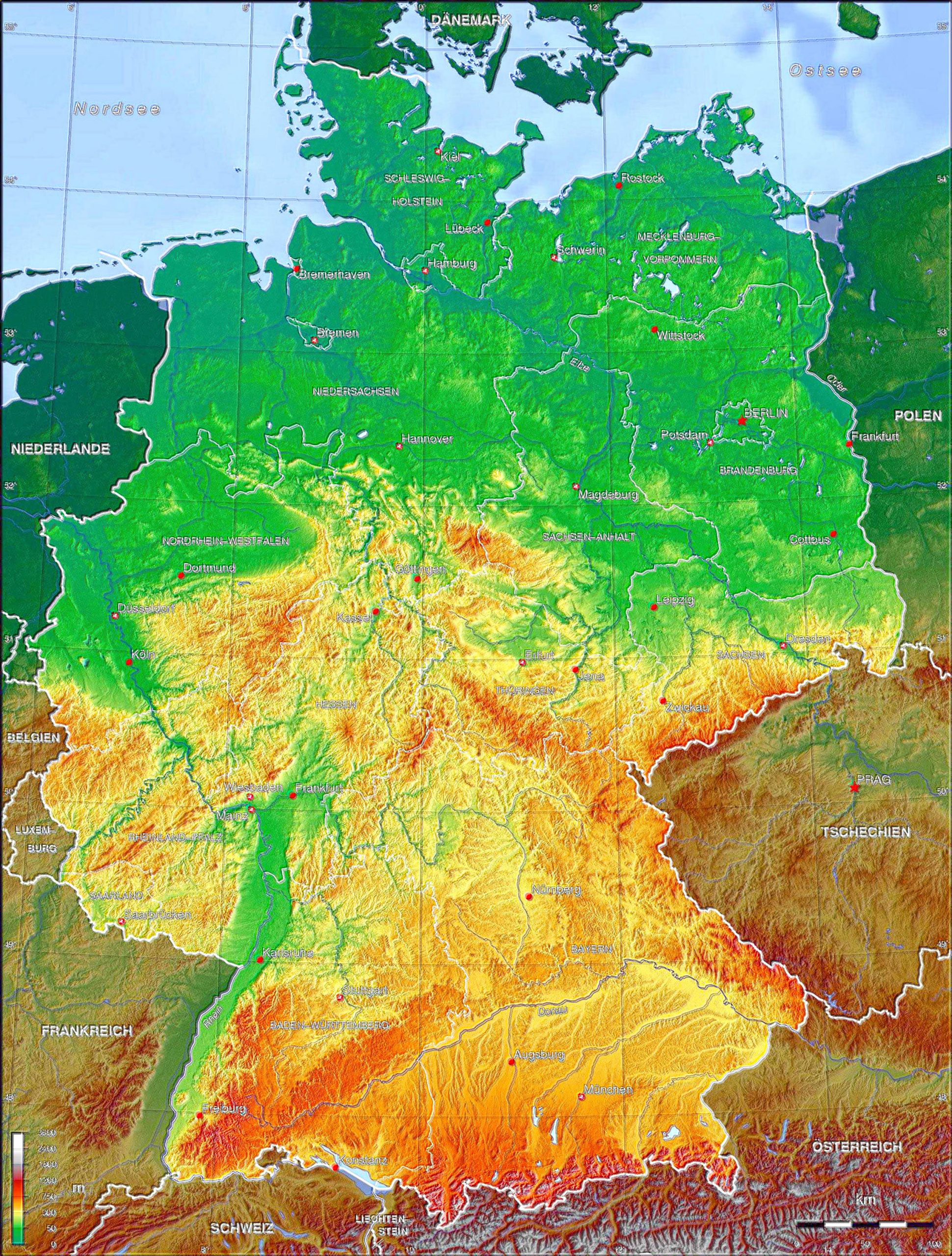
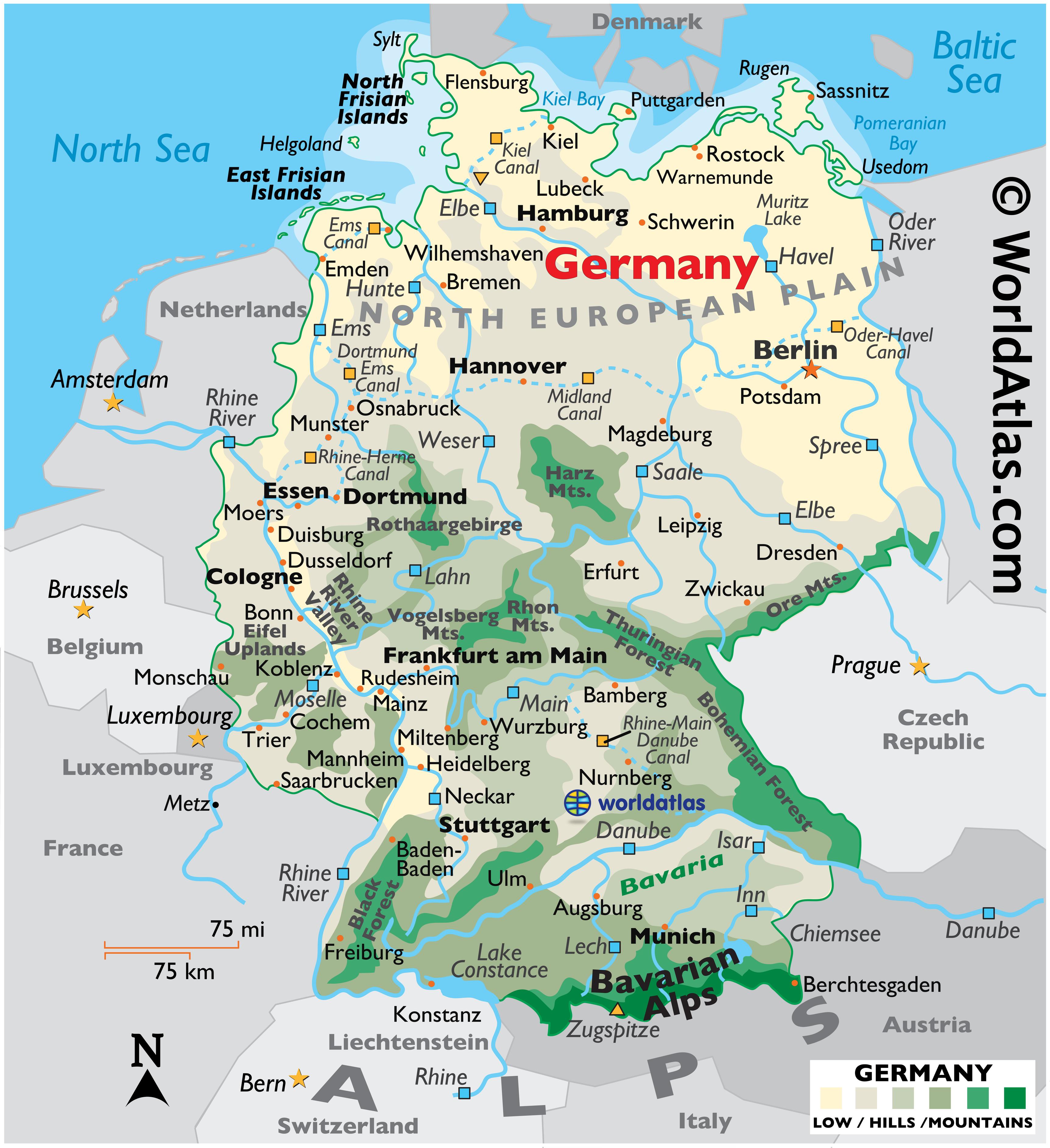
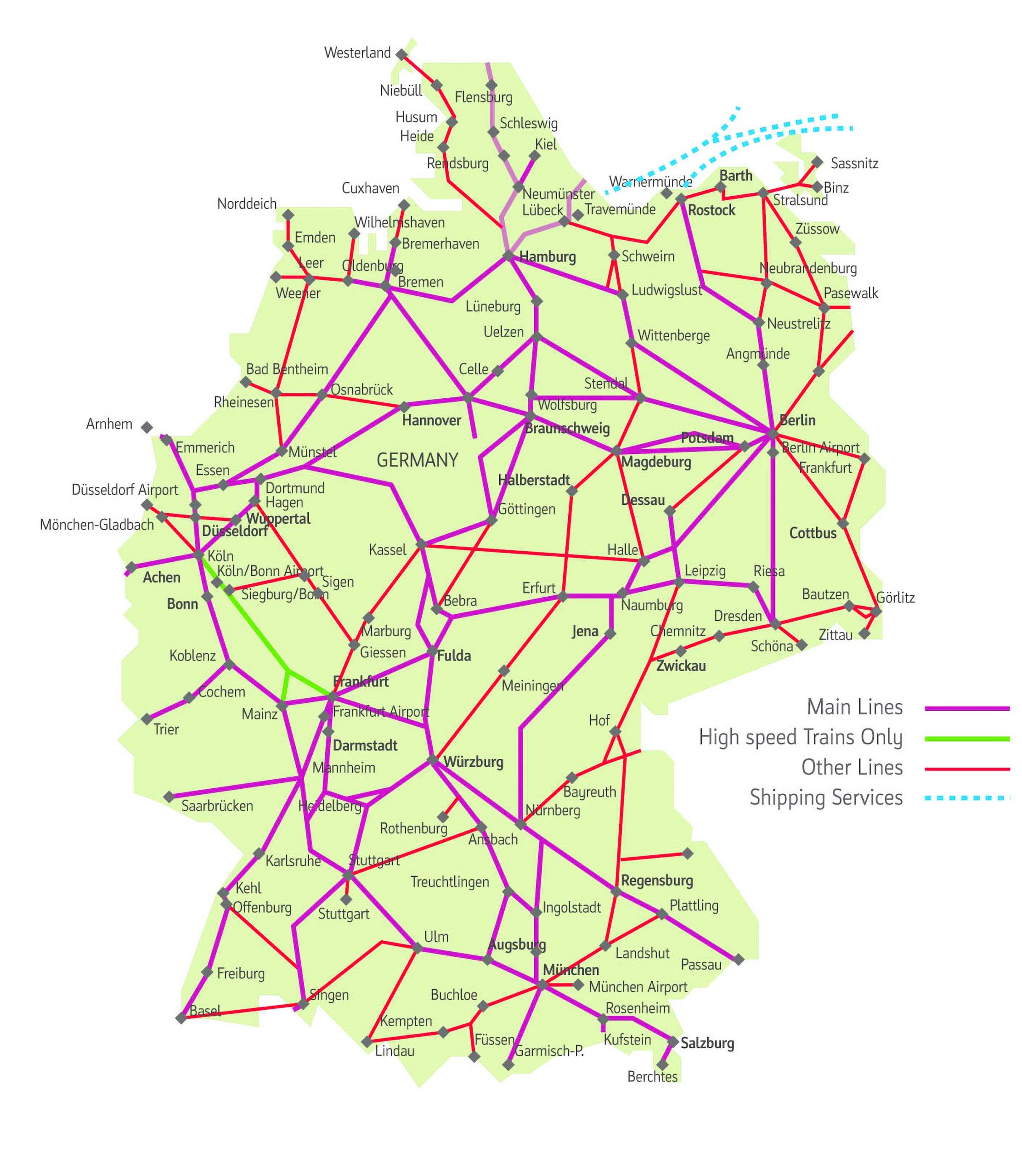
Germany’s map reveals a country shaped by its diverse geographical features. Its central location in Europe, bordering nine countries, has played a pivotal role in its history and cultural development. The country’s landscape is a mosaic of distinct regions, each contributing to its unique character:
- The North German Plain: This expansive lowland stretches from the Baltic Sea to the North Sea, characterized by fertile soils and vast agricultural lands. It is home to major cities like Hamburg and Bremen, important ports connected to global trade routes.
- The Central Uplands: This region features rolling hills, forests, and valleys, offering picturesque landscapes and scenic beauty. It is home to the country’s largest forest, the Black Forest, and harbors the historic cities of Frankfurt and Cologne.
- The Alps: The southernmost region of Germany boasts the majestic Alps, towering peaks, and breathtaking glacial landscapes. It is a popular destination for hiking, skiing, and outdoor recreation, and is home to the city of Munich, renowned for its cultural heritage and Bavarian traditions.
- The Baltic Coast: This region along the Baltic Sea offers sandy beaches, coastal towns, and picturesque islands. It is known for its maritime heritage and its charming seaside resorts.
Understanding the German Flag: A Symbol of Unity and Heritage
The German flag, a tricolour of black, red, and gold, is a powerful symbol of national identity and unity. Its design, adopted in 1949, reflects the country’s historical journey and its aspirations for a united and democratic future:
- Black: Represents the dark times of Germany’s past, symbolizing the challenges and hardships the nation has faced.
- Red: Represents the blood shed in the fight for freedom and independence, signifying the sacrifices made to achieve national unity.
- Gold: Represents the hope for a brighter future, symbolizing prosperity, unity, and the nation’s aspirations for peace and progress.
The Importance of the German Map and Flag
The German map and flag are more than just geographical and symbolic representations. They serve as powerful tools for understanding the nation’s history, culture, and identity. The map helps visualize the country’s diverse regions, highlighting the unique characteristics and contributions of each. The flag, a visible symbol of unity and shared values, fosters a sense of national pride and belonging among its citizens.
FAQs about Germany’s Map and Flag
Q: What is the area of Germany?
A: Germany covers an area of approximately 357,022 square kilometers (137,847 square miles).
Q: What is the population of Germany?
A: As of 2023, the population of Germany is estimated to be around 83.2 million.
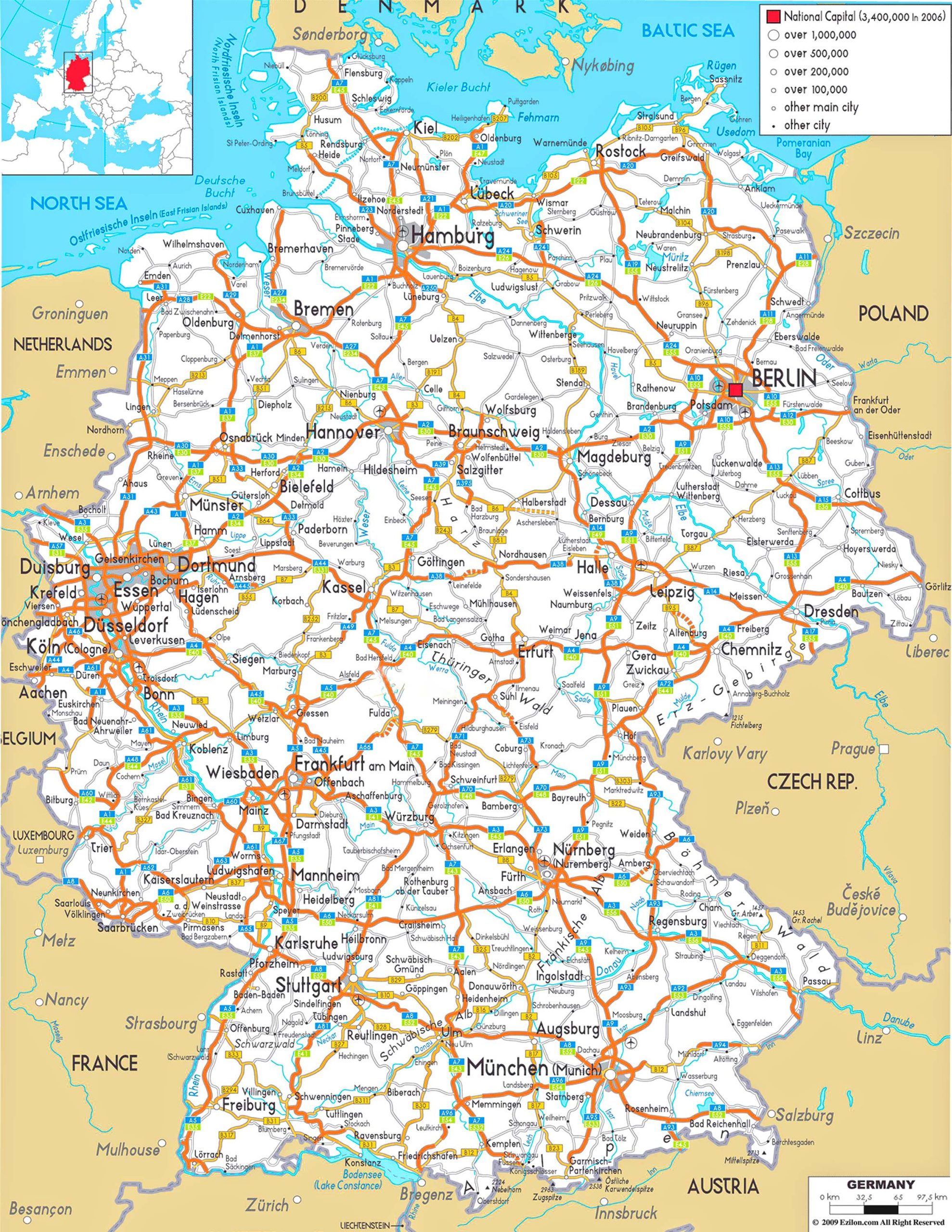
Q: What are the major cities in Germany?
A: Germany is home to several major cities, including Berlin (the capital), Hamburg, Munich, Cologne, Frankfurt, Stuttgart, and Düsseldorf.
Q: What is the significance of the black, red, and gold colors in the German flag?
A: The black, red, and gold colors of the German flag represent the nation’s history, struggles, and aspirations for a unified and democratic future.
Q: Why was the German flag changed to black, red, and gold in 1949?
A: The black, red, and gold colors were adopted in 1949 as a symbol of the Federal Republic of Germany’s commitment to democracy and unity after the Second World War.
Tips for Exploring Germany’s Map and Flag
- Use online maps and interactive tools: Explore interactive maps of Germany to gain a better understanding of its geographical features, major cities, and regional variations.
- Visit museums and historical sites: Museums and historical sites offer insights into Germany’s past, showcasing its cultural heritage and the evolution of its national identity.
- Learn about German history and culture: Reading books, watching documentaries, and attending cultural events can enhance your understanding of the country’s rich history and diverse cultural traditions.
- Engage with local communities: Interacting with people from different regions of Germany can provide valuable insights into their unique perspectives and cultural practices.
Conclusion
Germany’s map and flag are powerful symbols that encapsulate the nation’s geographic diversity, historical journey, and aspirations for a unified and prosperous future. Exploring these elements provides a deeper understanding of the country’s complex identity and its multifaceted character. By appreciating the intricate details of the map and the symbolic significance of the flag, we gain a richer perspective on Germany’s unique place in the world.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/83162764-58b9c9283df78c353c371ce1.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Germany: A Comprehensive Guide to its Geography and Symbolism. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!