Navigating India’s Road Network: Understanding Class 6 Roads and the National Highway Map
Related Articles: Navigating India’s Road Network: Understanding Class 6 Roads and the National Highway Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating India’s Road Network: Understanding Class 6 Roads and the National Highway Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating India’s Road Network: Understanding Class 6 Roads and the National Highway Map
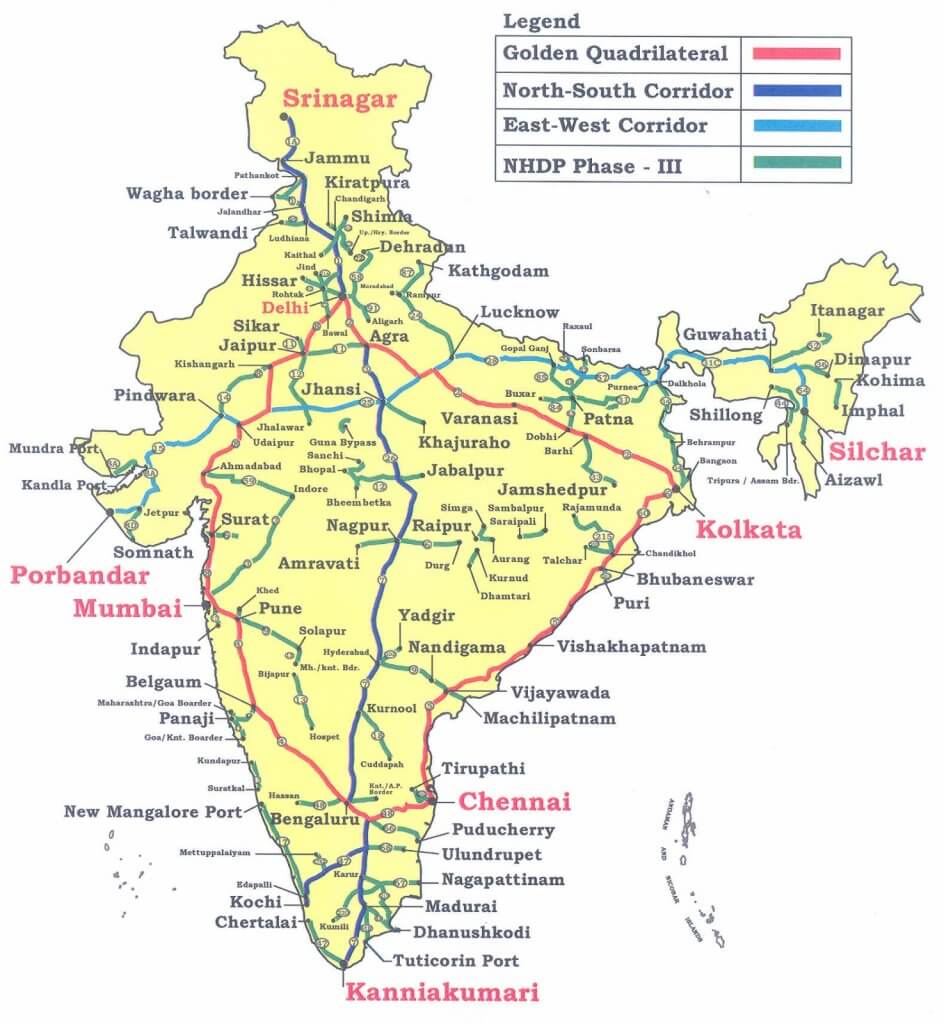
India’s vast and intricate road network is a vital artery for transportation, connecting its diverse regions and facilitating economic growth. Within this network, a hierarchical classification system categorizes roads based on their importance and maintenance standards. Class 6 roads, often referred to as "Other District Roads," play a crucial role in connecting rural areas and smaller towns to the broader national infrastructure. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Class 6 roads within the context of the National Highway Map, highlighting their significance and contribution to the Indian transportation landscape.
Understanding the National Highway Map and Road Classification
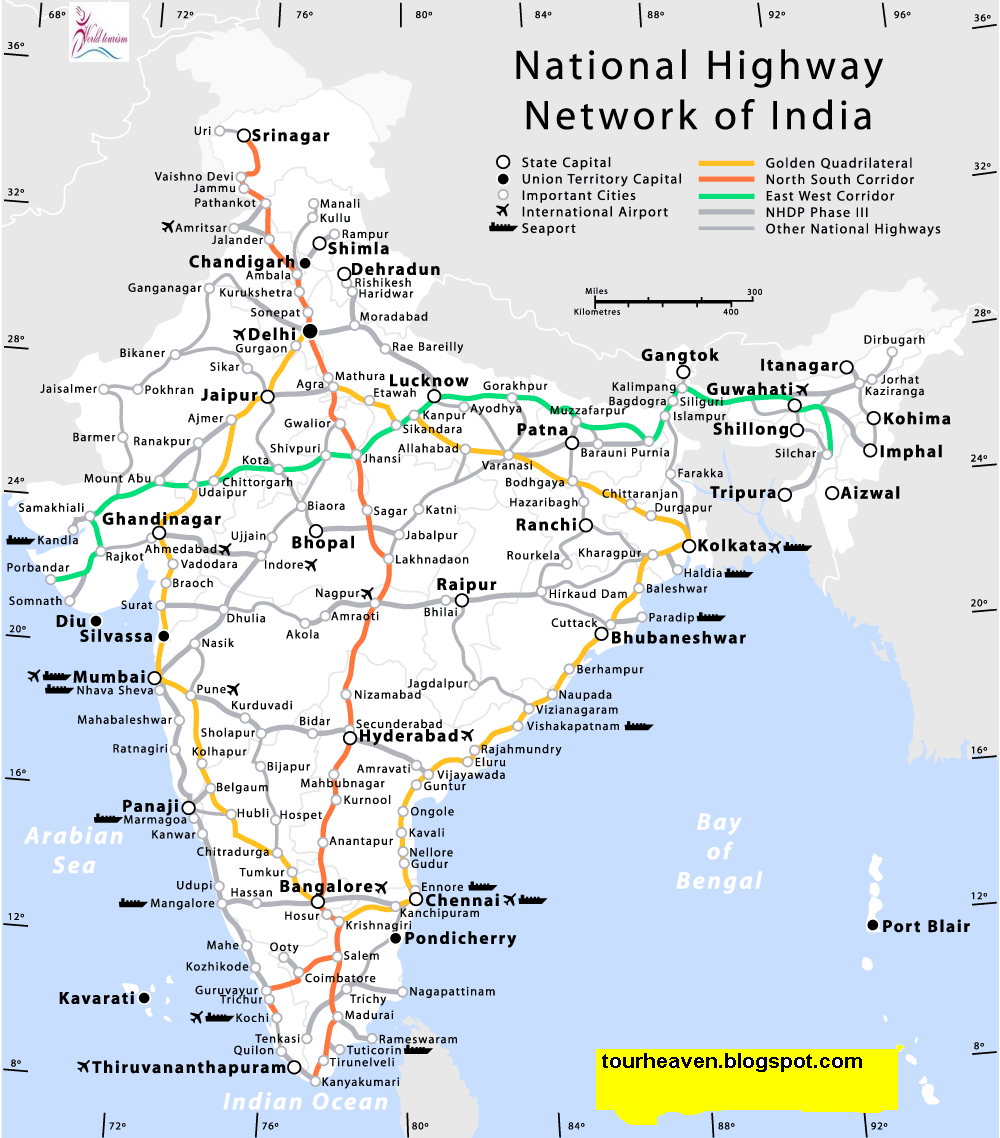
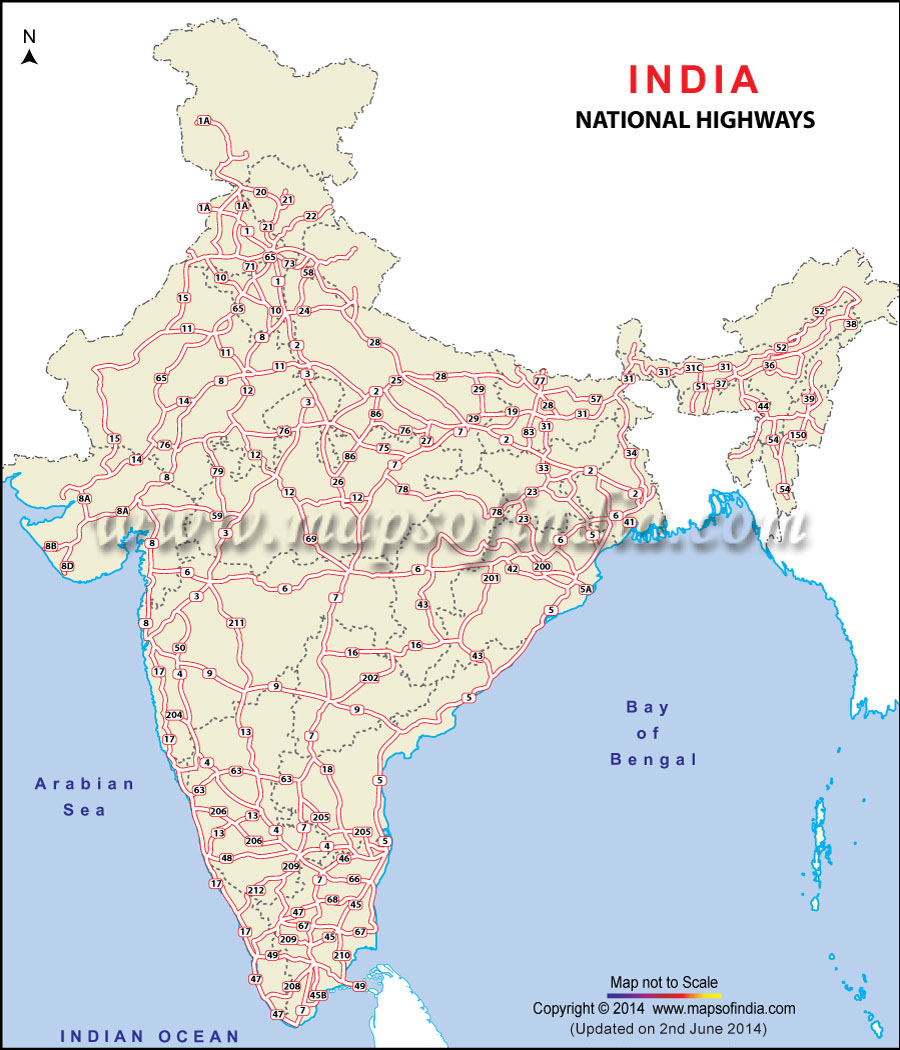
The National Highway Map, a visual representation of India’s road network, serves as a vital tool for understanding the country’s interconnectedness. It displays various road categories, each with distinct characteristics and functionalities.
- National Highways (NHs): These are the primary arterial roads, forming the backbone of the national transportation system. They connect major cities and facilitate long-distance travel.
- State Highways (SHs): These roads connect important towns and cities within a state, providing vital connectivity within the state’s boundaries.
- District Roads (DRs): These roads connect villages and smaller towns within a district, acting as feeder routes to the national and state highway networks.
- Other District Roads (Class 6): This category encompasses the most local roads, connecting rural areas, agricultural fields, and smaller settlements.
The Importance of Class 6 Roads
While often overlooked in favor of their higher-ranked counterparts, Class 6 roads play a crucial role in sustaining rural communities and driving economic development.
- Connecting Remote Areas: Class 6 roads provide vital access to remote villages, connecting them to markets, healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and other essential services. This access is crucial for improving the quality of life and fostering economic opportunities in rural areas.
- Facilitating Agricultural Trade: These roads are essential for transporting agricultural produce from farms to markets, ensuring the efficient flow of goods and supporting the livelihoods of farmers.
- Boosting Local Economies: By connecting rural areas to urban centers, Class 6 roads facilitate trade and commerce, creating employment opportunities and driving economic growth in local communities.
- Enhancing Social Mobility: Class 6 roads improve access to education, healthcare, and other essential services, contributing to social development and empowering rural communities.
Challenges Facing Class 6 Roads
Despite their importance, Class 6 roads often face significant challenges:
- Poor Maintenance: Due to limited funding and lack of attention, Class 6 roads often suffer from poor maintenance, leading to potholes, uneven surfaces, and other road hazards. This affects the safety and efficiency of transportation, hindering economic activity and access to essential services.
- Limited Infrastructure: Many Class 6 roads lack essential infrastructure like bridges, culverts, and drainage systems, making them prone to damage during monsoon seasons. This further exacerbates maintenance issues and disrupts connectivity.
- Lack of Connectivity: In some regions, Class 6 roads are poorly connected to higher-order roads, limiting their effectiveness in facilitating transportation and economic growth.
Addressing the Challenges and Enhancing Class 6 Roads
Addressing the challenges facing Class 6 roads is crucial for ensuring sustainable rural development and economic growth. Strategies for improving these roads include:
- Increased Funding: Prioritizing funding for the maintenance and improvement of Class 6 roads is essential for ensuring their long-term viability and effectiveness.
- Enhanced Infrastructure: Investing in essential infrastructure like bridges, culverts, and drainage systems can improve the resilience of Class 6 roads and minimize disruptions caused by weather events.
- Improved Connectivity: Connecting Class 6 roads to higher-order roads can enhance their effectiveness in facilitating transportation and economic growth.
- Community Participation: Engaging local communities in the planning, maintenance, and monitoring of Class 6 roads can ensure their sustainability and responsiveness to local needs.
FAQs on Class 6 Roads and the National Highway Map
Q: How can I find information about Class 6 roads on the National Highway Map?
A: The National Highway Map typically depicts different road categories using distinct colors and symbols. While the map may not specifically label Class 6 roads as "Other District Roads," it may show them as smaller, thinner lines connecting rural areas. To obtain detailed information about specific Class 6 roads, it is recommended to refer to local road maps or contact the relevant state or district authorities.
Q: How can I report issues or concerns related to Class 6 roads?
A: You can report issues like potholes, road damage, or lack of maintenance to the relevant state or district authorities. Many states have dedicated websites or toll-free numbers for reporting road-related problems. Contact details can be found on the website of the respective state’s Public Works Department or Roads and Buildings Department.
Q: What are the benefits of improving Class 6 roads?
A: Improving Class 6 roads offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Rural Connectivity: Improved roads facilitate the movement of people, goods, and services, connecting rural communities to urban centers and essential services.
- Economic Growth: Improved roads stimulate trade and commerce, creating employment opportunities and driving economic growth in rural areas.
- Social Development: Improved roads enhance access to education, healthcare, and other essential services, promoting social development and improving the quality of life for rural communities.
- Increased Safety: Well-maintained roads with proper infrastructure reduce the risk of accidents and injuries, improving safety for road users.
Tips for Navigating Class 6 Roads
- Plan your route: Before embarking on a journey on Class 6 roads, plan your route carefully, taking into account road conditions, weather forecasts, and potential delays.
- Check for updates: Stay informed about road closures, construction projects, or other disruptions by checking local news sources or websites of relevant authorities.
- Drive cautiously: Class 6 roads often have uneven surfaces, potholes, and other hazards. Drive cautiously, observe speed limits, and be aware of your surroundings.
- Carry essentials: Carry essential items like a first-aid kit, water, and snacks, especially if traveling long distances on Class 6 roads.
- Respect local communities: Be mindful of local customs and traditions when traveling through rural areas.
Conclusion
Class 6 roads, though often overlooked, are vital arteries connecting rural areas to the broader national infrastructure. Their improvement is crucial for sustainable rural development, economic growth, and social progress. By addressing the challenges facing these roads, prioritizing their maintenance, and enhancing their connectivity, India can unlock the full potential of its rural areas and create a more inclusive and prosperous nation.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating India’s Road Network: Understanding Class 6 Roads and the National Highway Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!