Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to South Sudan on the World Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to South Sudan on the World Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to South Sudan on the World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to South Sudan on the World Map

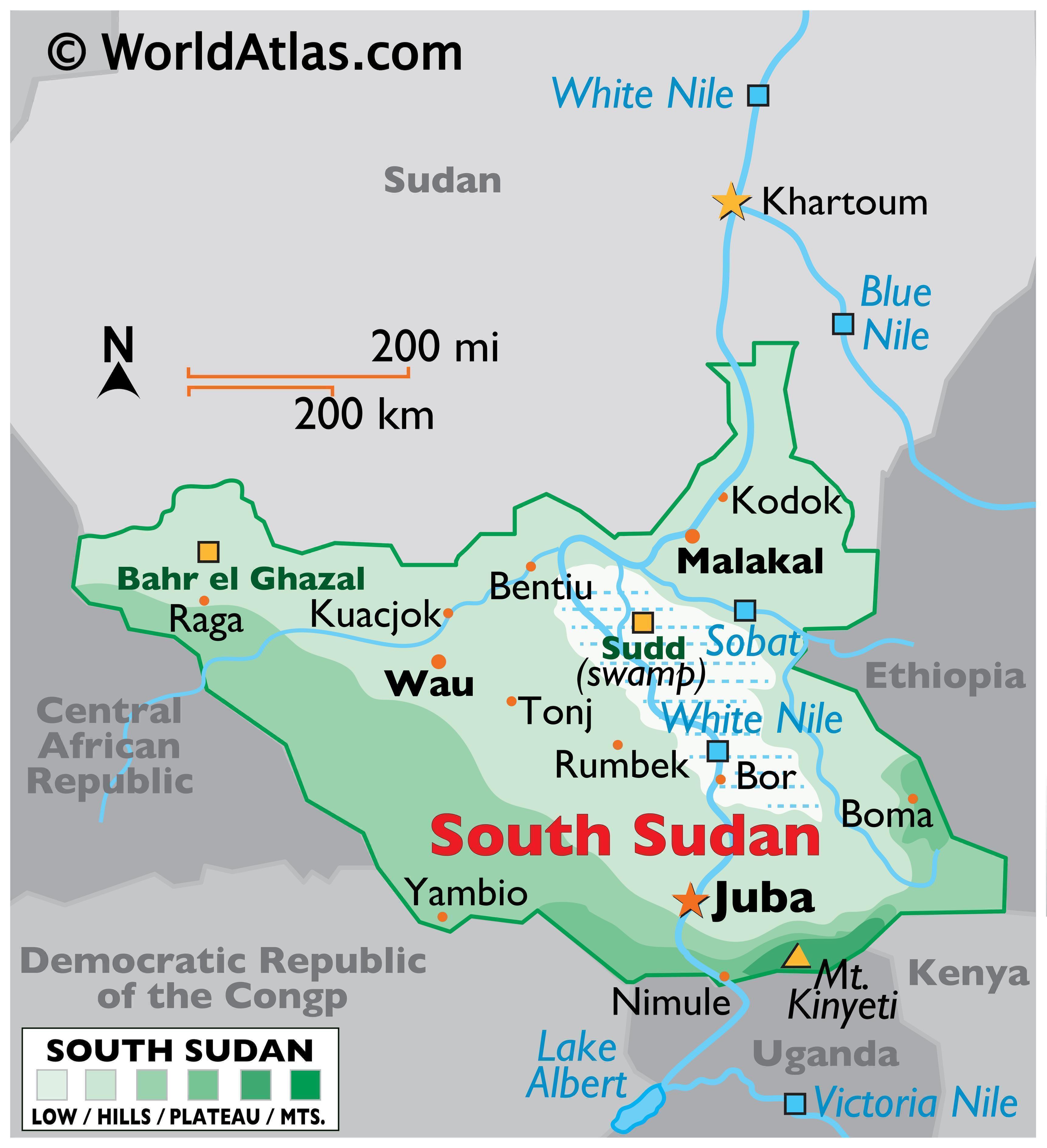
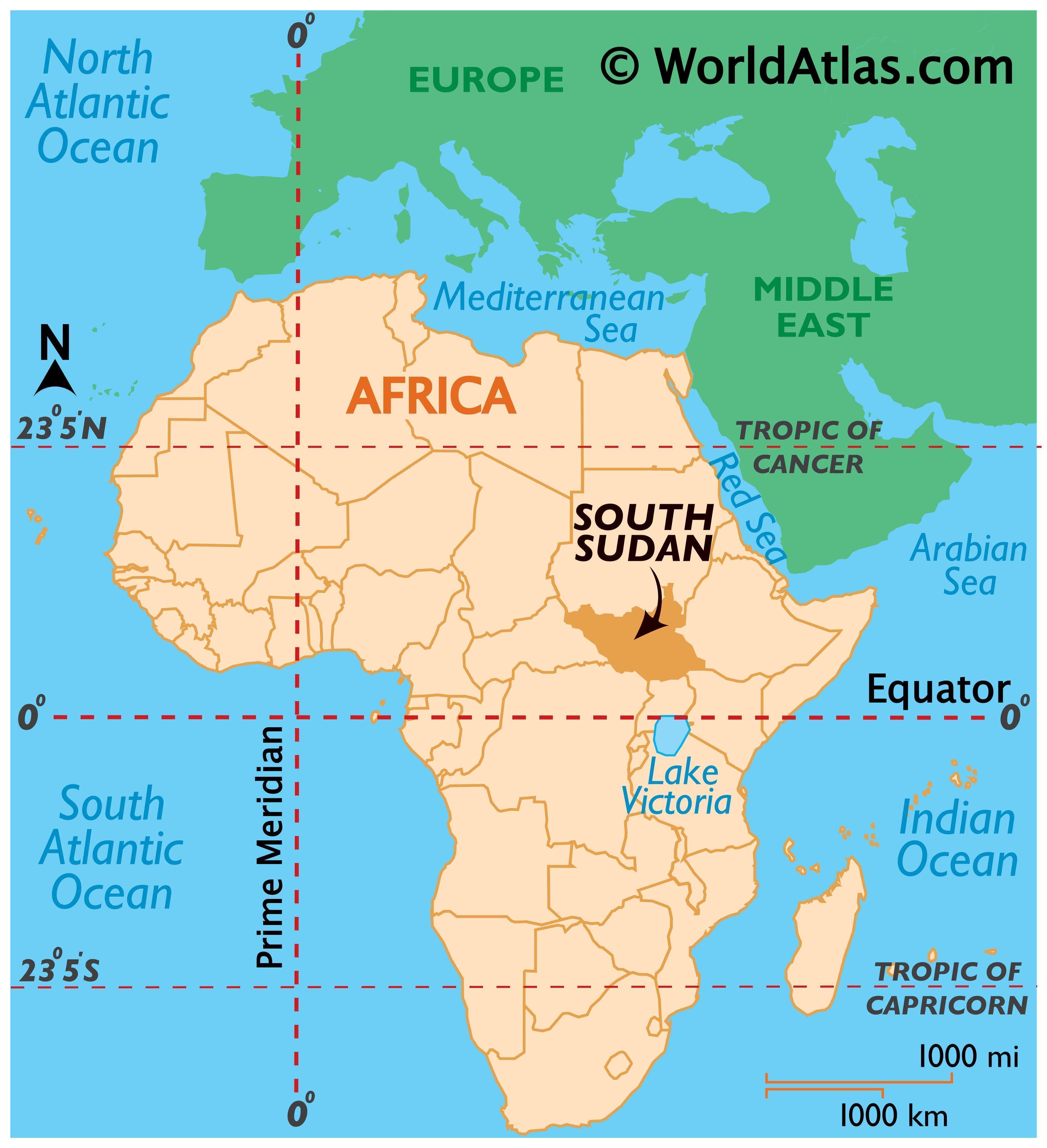
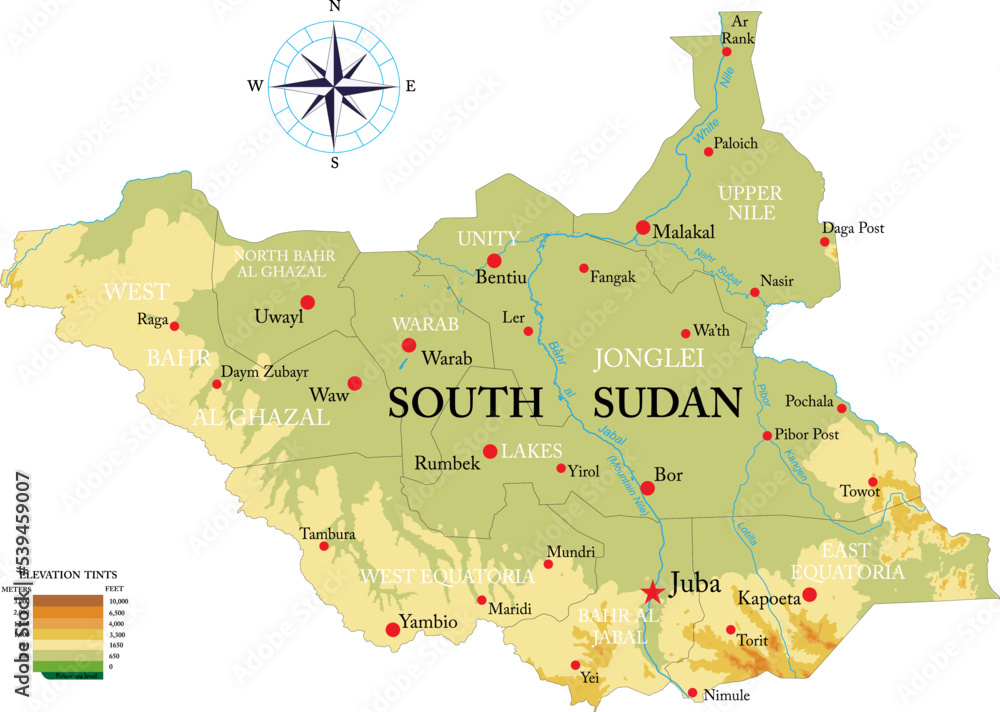
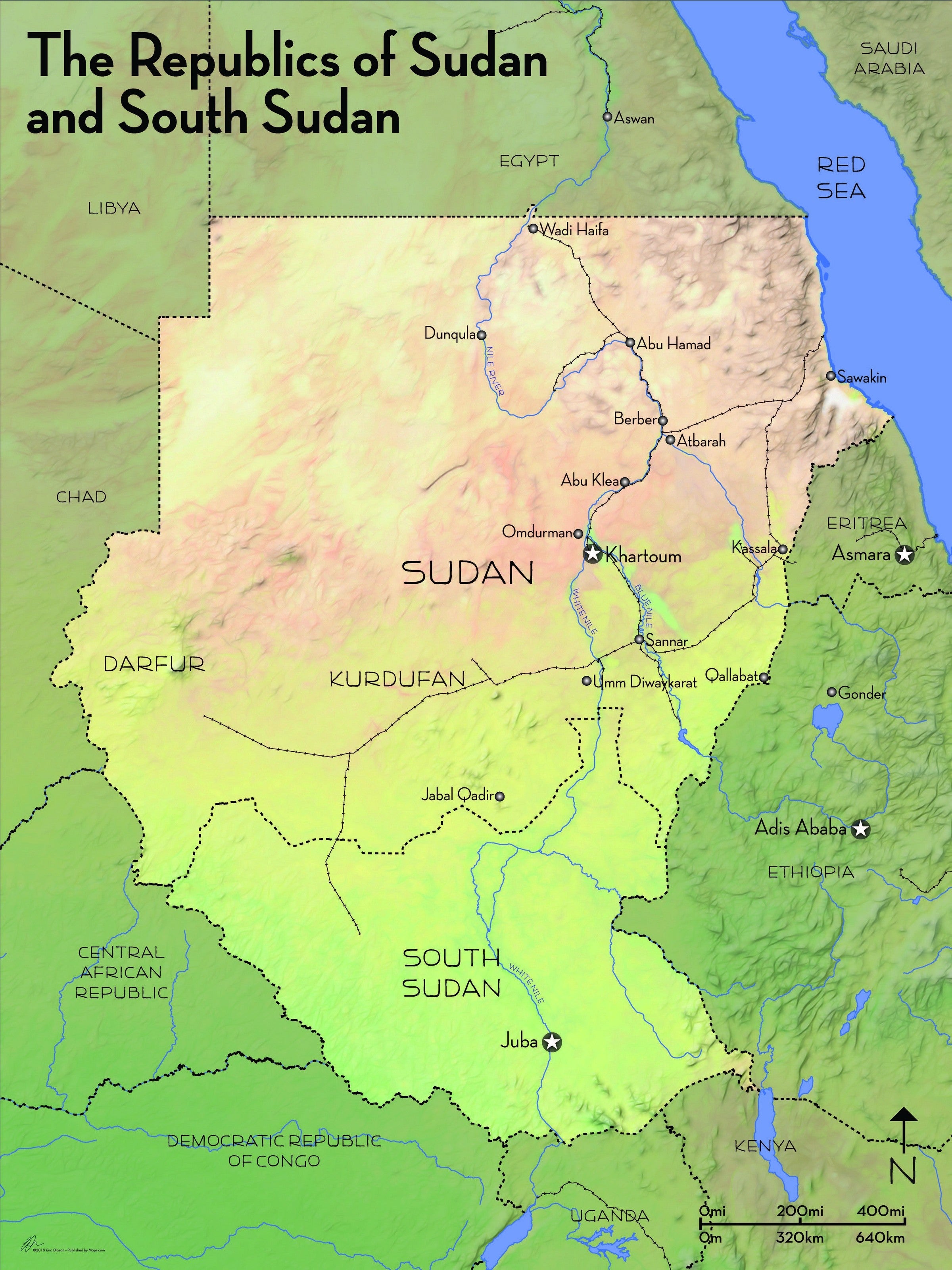
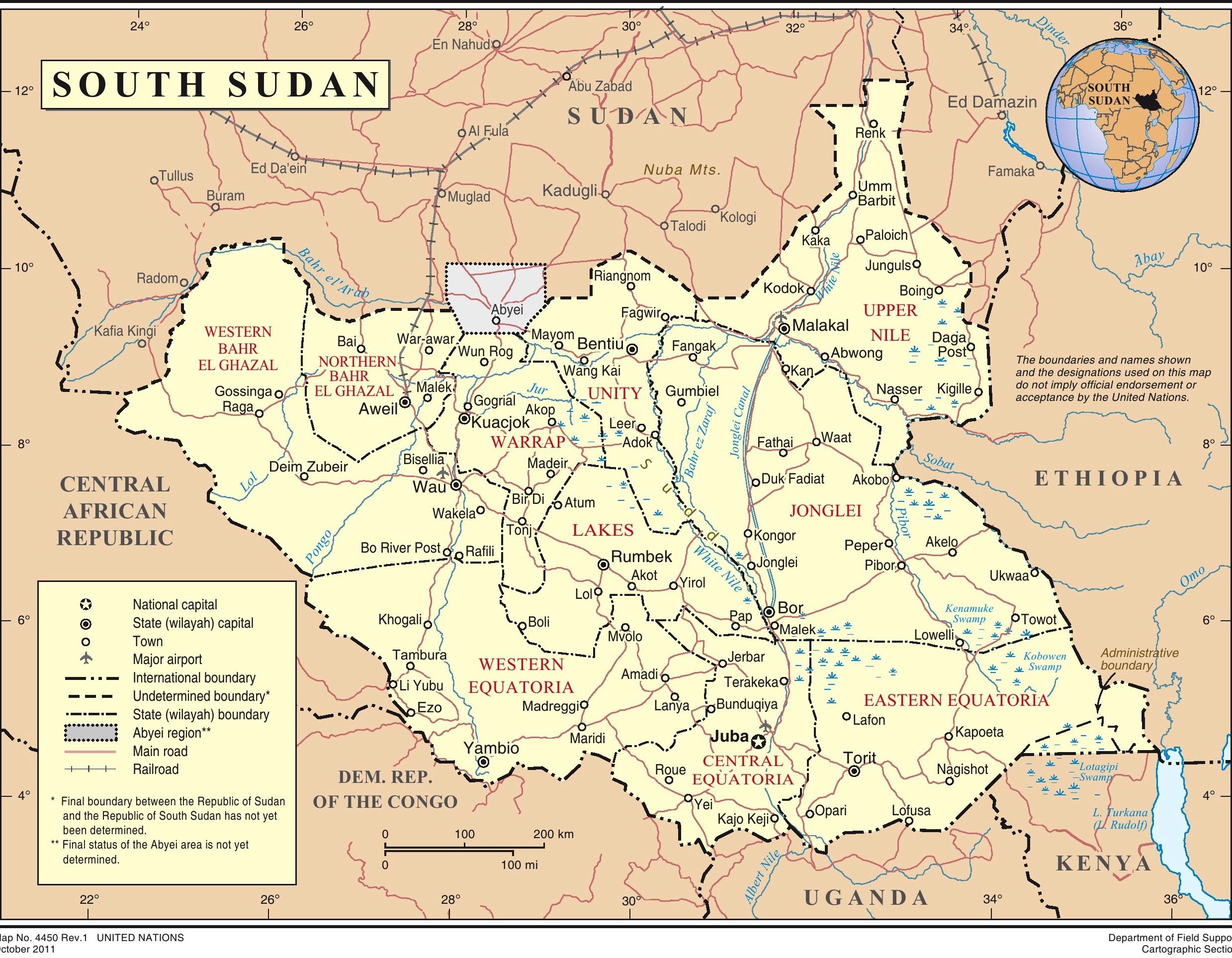
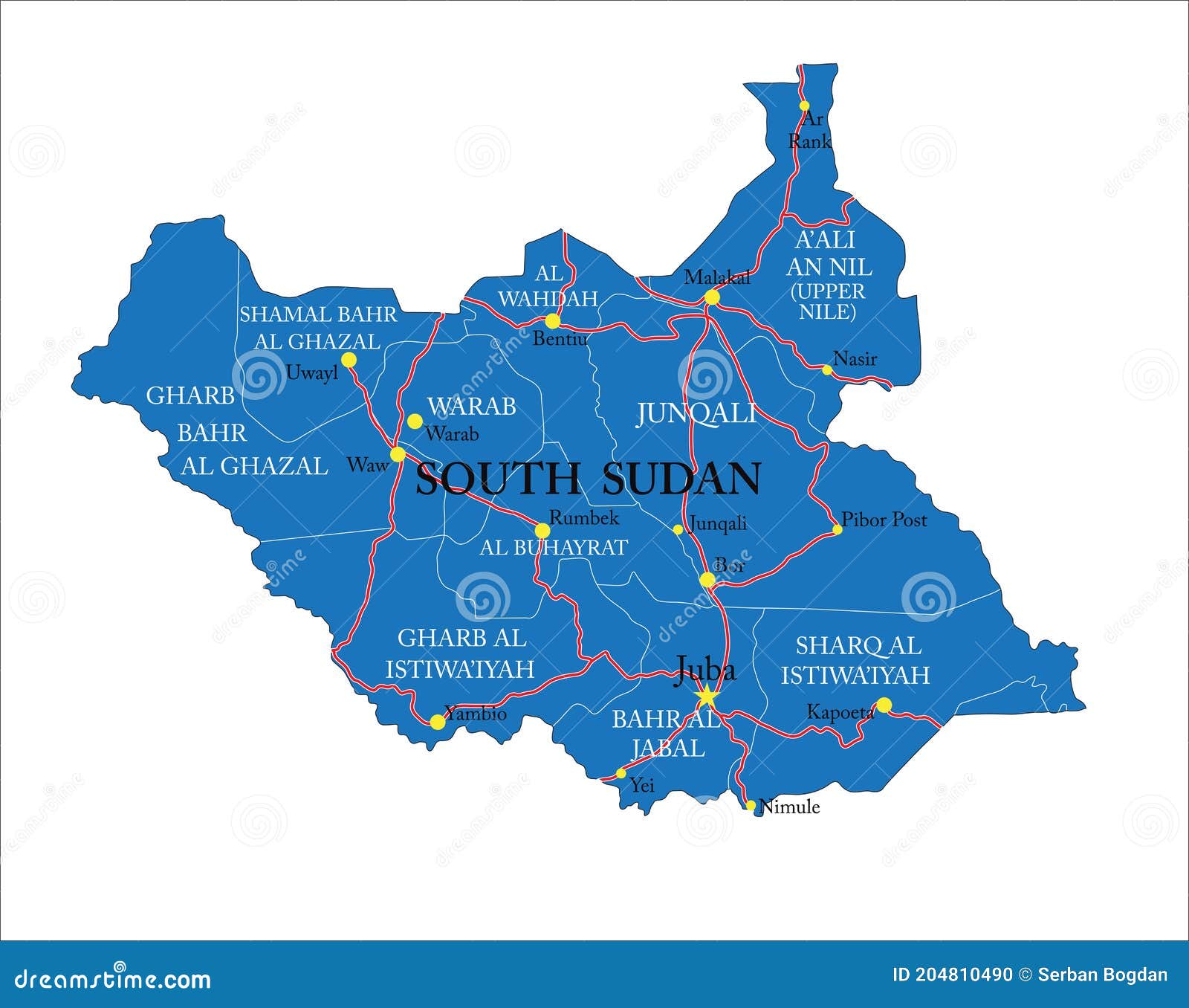
South Sudan, a relatively young nation born in 2011, holds a significant place on the world map. Situated in Northeast Africa, it shares borders with Sudan to the north, Ethiopia and Kenya to the east, Uganda to the south, and the Central African Republic to the west. Its unique geographical position and complex history have shaped its present and hold implications for its future.
A Landlocked Nation: South Sudan is entirely landlocked, meaning it lacks a coastline and access to the open sea. This geographical characteristic presents challenges in terms of trade and transportation, making it reliant on neighboring countries for access to international markets. The lack of coastal access also limits the country’s potential for fishing and other maritime industries.
Diverse Topography: South Sudan’s landscape is characterized by a diverse array of geographical features. The country encompasses vast plains, fertile valleys, rolling hills, and rugged mountains. The majority of the land lies within the Sudd, a massive wetland system considered the largest in the world. The Sudd’s unique ecosystem, with its intricate network of swamps and waterways, plays a vital role in the country’s ecology and hydrology.
Rich Natural Resources: South Sudan is endowed with abundant natural resources, including oil, gold, diamonds, and timber. These resources hold significant potential for economic development and prosperity. However, their exploitation has been hampered by ongoing conflict and political instability, hindering the country’s progress towards sustainable growth.
Historical Context: The region now known as South Sudan has a long and intricate history. It was historically part of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, a colonial entity ruled by Britain and Egypt. After gaining independence from colonial rule in 1956, Sudan remained a unified state. However, tensions between the predominantly Arab north and the predominantly African south escalated, leading to decades of civil war.
The Birth of a Nation: In 2011, after a prolonged and bloody struggle for independence, South Sudan finally achieved its sovereign status. The referendum that paved the way for secession was overwhelmingly supported by the Southern Sudanese population, reflecting their desire for self-determination and a separate identity.
Challenges and Opportunities: South Sudan’s journey towards stability and prosperity has been fraught with challenges. The country has faced ongoing conflict, political instability, and humanitarian crises. However, it also possesses immense potential for growth and development. Its abundant natural resources, fertile land, and young population present opportunities for economic diversification and social progress.
Navigating the Future: Addressing the challenges and harnessing the opportunities will require a multifaceted approach. This includes prioritizing peace and security, fostering good governance, promoting economic diversification, investing in education and healthcare, and strengthening regional partnerships.
Importance and Benefits: Understanding South Sudan’s position on the world map is crucial for comprehending the complexities of the region and its impact on global affairs. Its strategic location, diverse resources, and unresolved conflicts make it a focal point for international diplomacy, humanitarian aid, and development efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- What is the capital city of South Sudan? The capital city of South Sudan is Juba.
- What is the official language of South Sudan? The official language of South Sudan is English.
- What are the major ethnic groups in South Sudan? The major ethnic groups in South Sudan include Dinka, Nuer, Bari, and Azande.
- What are the main religions practiced in South Sudan? The main religions practiced in South Sudan are Christianity, Islam, and traditional African religions.
- What are the major economic activities in South Sudan? The major economic activities in South Sudan include oil production, agriculture, and livestock raising.
Tips for Studying South Sudan:
- Consult reliable maps and atlases: Utilize detailed maps and atlases to gain a comprehensive understanding of South Sudan’s geographical features, major cities, and bordering countries.
- Explore online resources: Explore websites of reputable organizations like the United Nations, the World Bank, and the International Crisis Group for in-depth information on South Sudan’s history, politics, economy, and current affairs.
- Read books and articles: Engage with scholarly works and journalistic articles by experts on South Sudan to gain diverse perspectives on its challenges and opportunities.
- Watch documentaries and films: Explore documentaries and films that shed light on South Sudan’s culture, history, and contemporary issues.
Conclusion:
South Sudan’s journey on the world map is a testament to the resilience and aspirations of its people. Despite its challenges, the country holds immense potential for a brighter future. By fostering peace, good governance, and sustainable development, South Sudan can unlock its vast potential and secure a place of stability and prosperity within the global community. As the world continues to watch, South Sudan’s story serves as a poignant reminder of the complexities and possibilities of nation-building in the 21st century.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to South Sudan on the World Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!