Navigating the Landscape of Environmental Risk: Understanding the EBR Assessor Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Environmental Risk: Understanding the EBR Assessor Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Environmental Risk: Understanding the EBR Assessor Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Environmental Risk: Understanding the EBR Assessor Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscape of Environmental Risk: Understanding the EBR Assessor Map
- 3.1 The Importance of Visual Representation
- 3.2 Key Elements of an EBR Assessor Map
- 3.3 Types of EBR Assessor Maps
- 3.4 Benefits of Using EBR Assessor Maps
- 3.5 FAQs about EBR Assessor Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Creating Effective EBR Assessor Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscape of Environmental Risk: Understanding the EBR Assessor Map
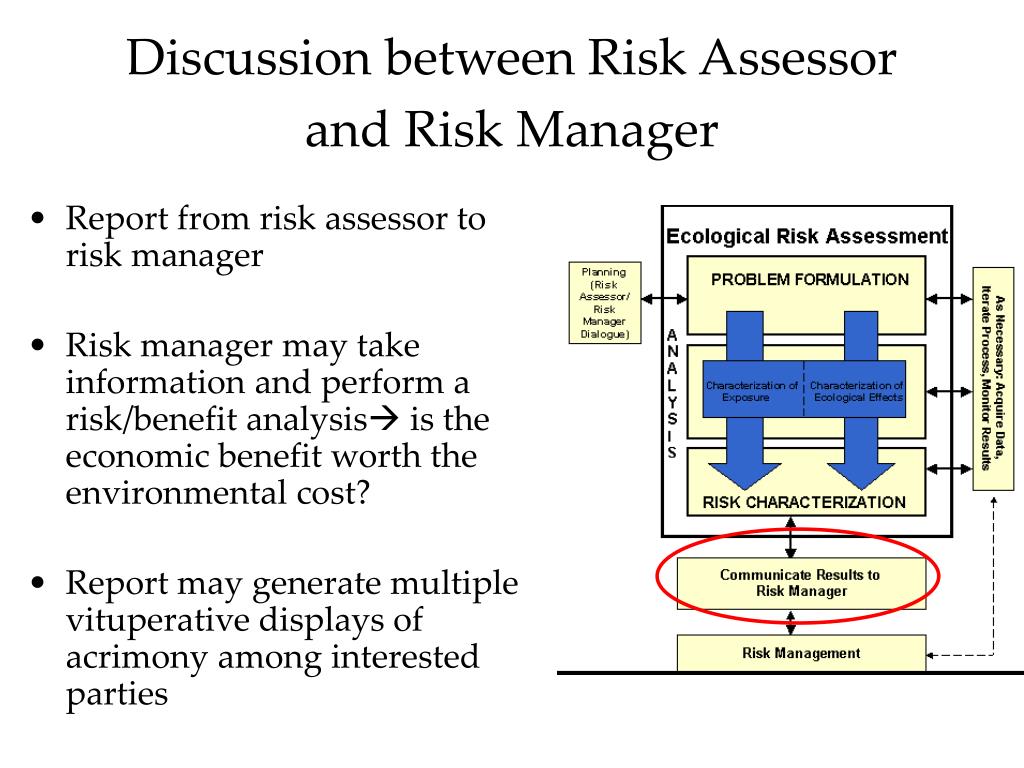
The Environmental Baseline Report (EBR) is a crucial document in environmental impact assessments, providing a comprehensive overview of the existing environmental conditions within a proposed project area. This report serves as a foundation for understanding the potential impacts of a project and for developing mitigation strategies. A key component of the EBR is the EBR Assessor Map, a visual representation of the environmental data collected and analyzed for the project.
The Importance of Visual Representation
The EBR Assessor Map plays a vital role in conveying complex environmental information in a clear and accessible manner. It serves as a visual bridge between technical data and stakeholder understanding, facilitating informed decision-making. The map acts as a powerful tool for:
- Identifying Key Environmental Features: The map highlights areas of significance, such as sensitive ecosystems, water bodies, cultural heritage sites, and areas of biodiversity. This visual representation helps stakeholders quickly grasp the environmental context of the project.
- Visualizing Potential Impacts: By overlaying project boundaries and proposed activities on the map, potential impacts on the surrounding environment can be visualized and assessed. This allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the project’s footprint and its potential consequences.
- Communicating Complex Data: The EBR Assessor Map simplifies complex environmental data, presenting it in a user-friendly format. This accessibility promotes effective communication between stakeholders, including project developers, regulatory agencies, and the local community.
- Facilitating Collaboration: The shared visual representation of environmental information fosters collaboration and open dialogue among stakeholders. It provides a common ground for understanding and discussing potential environmental risks and mitigation measures.
Key Elements of an EBR Assessor Map
An effective EBR Assessor Map typically includes:
- Base Map: A high-resolution topographic map or aerial imagery serving as the foundation for the map.
- Project Boundaries: Clear delineation of the project area, including proposed infrastructure, facilities, and activities.
-
Environmental Features: Representation of key environmental features, such as:
- Water bodies: Rivers, lakes, wetlands, and groundwater sources.
- Terrestrial ecosystems: Forests, grasslands, deserts, and agricultural lands.
- Protected areas: National parks, wildlife refuges, and other protected areas.
- Cultural heritage sites: Archaeological sites, historical landmarks, and traditional cultural areas.
- Biodiversity hotspots: Areas with high concentrations of endemic species or unique ecosystems.
- Sensitive areas: Areas vulnerable to environmental degradation, such as floodplains, coastal zones, and areas with sensitive species.
-
Environmental Data Overlays: Visual representation of environmental data, such as:
- Soil types: Mapping different soil types and their associated characteristics.
- Vegetation: Mapping vegetation types and their distribution.
- Wildlife habitat: Mapping known or potential habitats for various species.
- Air quality: Mapping air quality data, including pollutants and their sources.
- Noise levels: Mapping noise levels and potential sources of noise pollution.
- Legend and Scale: A clear and concise legend explaining the symbols and colors used on the map, along with a scale bar for accurate spatial reference.
Types of EBR Assessor Maps
EBR Assessor Maps can be tailored to specific project needs and environmental contexts. Common types include:
- Base Map with Overlays: A simple map displaying the project area and key environmental features, with overlays showing potential impacts or environmental data.
- Thematic Maps: Maps focusing on specific environmental aspects, such as soil types, vegetation, or wildlife habitat.
- Interactive Maps: Digital maps that allow users to zoom, pan, and explore different layers of information.
- 3D Models: Three-dimensional representations of the project area and its surrounding environment, providing a more immersive understanding of the landscape.
Benefits of Using EBR Assessor Maps
The use of EBR Assessor Maps offers numerous benefits for environmental impact assessments:
- Improved Decision-Making: Visualizing environmental data helps stakeholders make informed decisions about project design, mitigation measures, and potential risks.
- Enhanced Communication: The map serves as a common language for communicating environmental information to diverse audiences, including project developers, regulators, and the public.
- Increased Transparency: The visual representation of environmental data promotes transparency and accountability in the environmental impact assessment process.
- Early Identification of Risks: The map helps identify potential environmental risks and conflicts early in the project development phase, allowing for proactive mitigation strategies.
- Effective Stakeholder Engagement: The map facilitates meaningful stakeholder engagement by providing a visual platform for discussions and collaboration.
FAQs about EBR Assessor Maps
Q: What is the purpose of an EBR Assessor Map?
A: The EBR Assessor Map provides a visual representation of the environmental data collected for an Environmental Baseline Report (EBR). It helps stakeholders understand the existing environmental conditions within a proposed project area, identify potential impacts, and develop mitigation strategies.
Q: Who uses EBR Assessor Maps?
A: EBR Assessor Maps are used by a wide range of stakeholders involved in environmental impact assessments, including:
- Project developers: To understand the environmental context of their projects and identify potential risks.
- Regulatory agencies: To review project proposals and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
- Environmental consultants: To analyze environmental data and develop mitigation strategies.
- Local communities: To understand the potential impacts of projects on their environment and health.
Q: What are the key elements of an EBR Assessor Map?
A: Key elements include a base map, project boundaries, environmental features, data overlays, a legend, and a scale.
Q: How are EBR Assessor Maps created?
A: EBR Assessor Maps are created using geographic information systems (GIS) software. Data collected during environmental surveys, field investigations, and remote sensing is used to create layers of information that are then combined to form the map.
Q: What are the benefits of using EBR Assessor Maps?
A: Benefits include improved decision-making, enhanced communication, increased transparency, early risk identification, and effective stakeholder engagement.
Q: How can EBR Assessor Maps be used to improve environmental impact assessments?
A: By providing a clear and accessible visual representation of environmental data, EBR Assessor Maps can help improve the quality and effectiveness of environmental impact assessments. They facilitate better understanding of the project’s potential impacts, promote collaboration among stakeholders, and contribute to more informed decision-making.
Tips for Creating Effective EBR Assessor Maps
- Use high-resolution base maps: Ensure that the base map is accurate and detailed enough to support the overlay of environmental data.
- Clearly define project boundaries: Use distinct colors or lines to delineate the project area and proposed activities.
- Represent environmental features accurately: Use appropriate symbols and colors to represent key environmental features and data.
- Include a comprehensive legend: Provide a clear and concise legend explaining the symbols and colors used on the map.
- Use a consistent scale: Maintain a consistent scale throughout the map to ensure accurate spatial reference.
- Consider using interactive maps: Interactive maps allow users to zoom, pan, and explore different layers of information, enhancing user engagement and understanding.
- Incorporate 3D models: For complex projects, consider using 3D models to provide a more immersive understanding of the landscape and potential impacts.
- Involve stakeholders in the map development process: Engage stakeholders in the map development process to ensure that the map meets their needs and reflects their perspectives.
Conclusion
The EBR Assessor Map is an essential tool for environmental impact assessments, serving as a visual bridge between technical data and stakeholder understanding. By effectively communicating complex environmental information, the map facilitates informed decision-making, promotes collaboration, and contributes to more sustainable project development. As environmental regulations and public awareness of environmental issues continue to evolve, the use of EBR Assessor Maps will become increasingly crucial for ensuring environmentally responsible development and protecting the natural world.



![Environmental Risk Assessor Job Description [Updated for 2024]](https://interviewguy.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/environmental-risk-assessor-job-description.webp)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Environmental Risk: Understanding the EBR Assessor Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!