Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to US Oil Refineries
Related Articles: Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to US Oil Refineries
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to US Oil Refineries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to US Oil Refineries

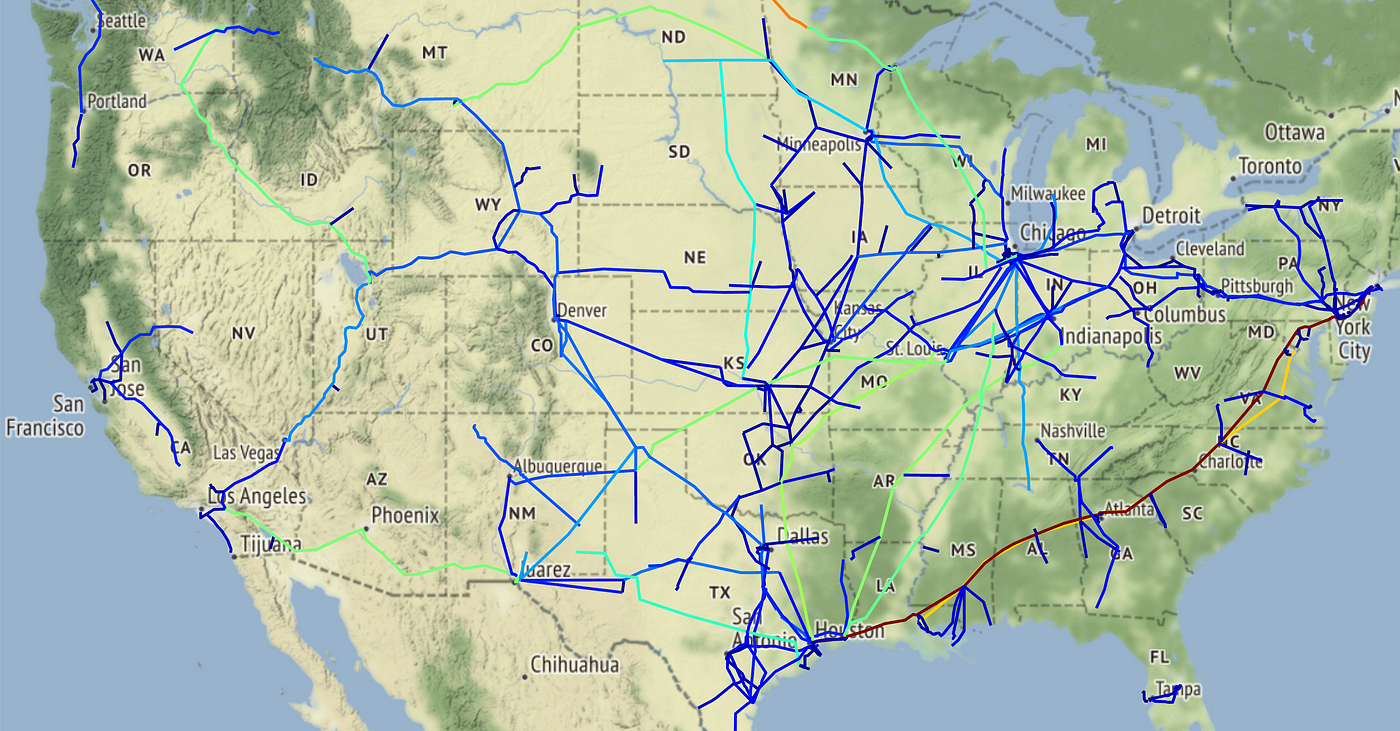
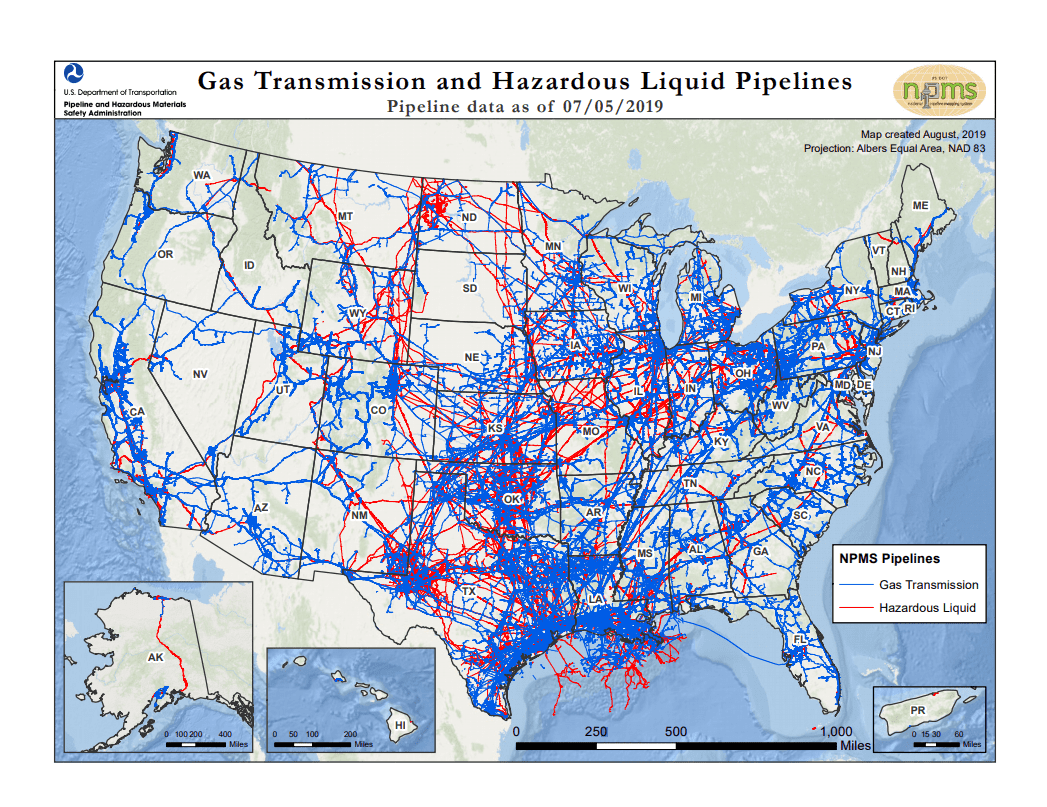
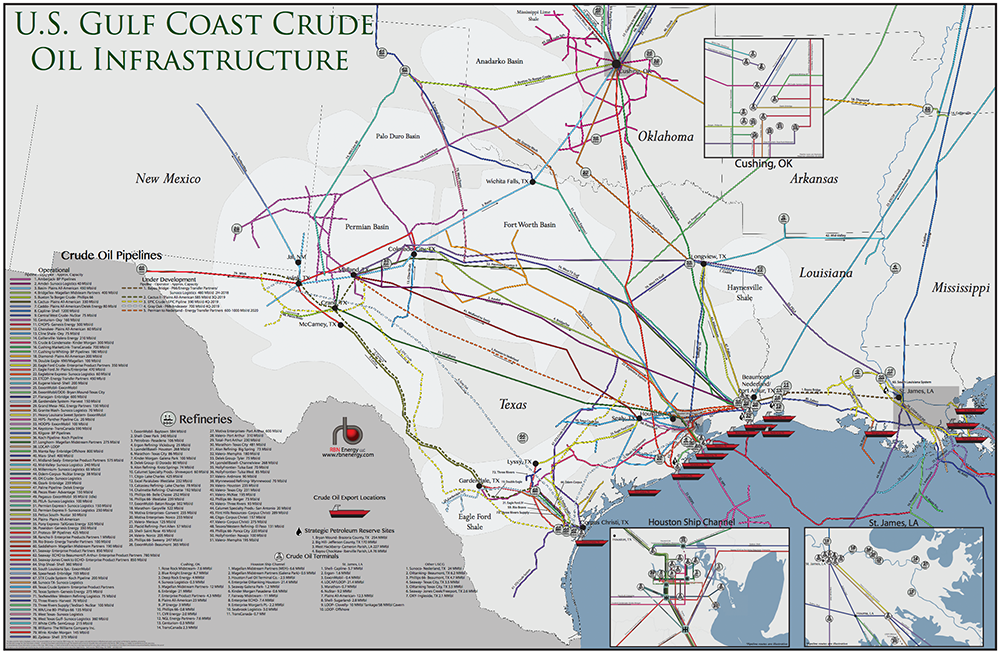
The United States is a global leader in oil production and refining, with a complex network of refineries scattered across the country. Understanding the distribution and capacity of these facilities is crucial for comprehending the nation’s energy landscape, its economic health, and its environmental impact. This comprehensive guide explores the map of US oil refineries, offering insights into their location, capacity, and significance.
The Geography of Refining:
The map of US oil refineries reveals a geographically diverse landscape. While some regions, like the Gulf Coast, boast a high concentration of refineries, others have a more limited presence. This distribution is influenced by several factors:
- Proximity to Crude Oil Sources: Refineries are often located near major oil-producing regions, minimizing transportation costs and maximizing efficiency. The Gulf Coast, with its vast offshore oil reserves, serves as a prime example.
- Access to Transportation Infrastructure: Refineries rely on robust transportation networks, including pipelines, railroads, and waterways, to transport crude oil and refined products. Coastal locations with access to ports and shipping lanes offer significant advantages.
- Market Demand: The location of refineries is also influenced by the demand for refined products in specific regions. Areas with high population density and industrial activity tend to have a higher concentration of refineries.
Types of Refineries:
US refineries can be categorized based on their complexity and the types of products they produce:
- Complex Refineries: These facilities are equipped to process a wide range of crude oil types, producing a diverse array of refined products, including gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, and petrochemicals. They are typically located in areas with high demand for a variety of products.
- Simple Refineries: These facilities are designed to process specific types of crude oil, primarily producing a limited range of products, often focused on gasoline or diesel. They are often located in areas with less diverse demand or limited access to complex processing technologies.
Capacity and Production:
The capacity of US refineries varies significantly, with some facilities capable of processing millions of barrels of crude oil per day, while others operate at a smaller scale. This capacity plays a crucial role in determining the overall refining capacity of the nation and its ability to meet domestic and international demand for refined products.
Environmental Considerations:
While refineries are essential for meeting energy demands, they also generate significant environmental impacts, including air and water pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. The map of US oil refineries highlights the need for responsible environmental practices, including:
- Modernization and Upgrades: Investing in advanced technologies to minimize emissions and improve efficiency.
- Stricter Environmental Regulations: Implementing robust regulations to limit pollution and ensure responsible waste management.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Exploring the integration of renewable energy sources to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Economic Importance:
The oil refining industry is a significant contributor to the US economy, providing employment opportunities and generating revenue through taxes and royalties. The map of US oil refineries highlights the economic interdependence of different regions, as refineries create jobs and stimulate economic activity in their surrounding communities.
Strategic Significance:
The map of US oil refineries also reveals the strategic importance of these facilities in ensuring national energy security. They provide a critical source of fuel for transportation, industry, and households, ensuring the nation’s economic and military resilience.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The future of the US oil refining industry is shaped by several challenges and opportunities:
- Shifting Energy Demand: The growing adoption of electric vehicles and renewable energy sources is likely to reduce demand for gasoline and diesel, potentially impacting the future of some refineries.
- Environmental Regulations: Increasingly stringent environmental regulations are likely to drive investments in cleaner technologies and processes.
- Technological Advancements: Emerging technologies, such as biofuels and carbon capture, could offer new opportunities for the refining industry.
FAQs:
Q: What are the largest oil refineries in the US?
A: Some of the largest refineries in the US include:
- Valero Energy Corp. – Corpus Christi, Texas: With a capacity of over 600,000 barrels per day.
- Marathon Petroleum Corp. – Garyville, Louisiana: With a capacity of over 585,000 barrels per day.
- ExxonMobil Corp. – Baytown, Texas: With a capacity of over 560,000 barrels per day.
Q: How does the map of US oil refineries help understand the energy landscape?
A: The map reveals the distribution of refining capacity across the country, providing insights into the location of major oil production and consumption centers. It also highlights the interdependence of different regions and the role of transportation infrastructure in moving crude oil and refined products.
Q: What are the environmental concerns associated with oil refineries?
A: Refineries generate air and water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and waste products. These concerns necessitate responsible environmental practices and technological advancements to minimize environmental impact.
Tips:
- Explore online mapping tools: Several websites offer interactive maps of US oil refineries, providing detailed information about their location, capacity, and ownership.
- Follow industry news: Stay informed about the latest developments in the oil refining industry, including new technologies, environmental regulations, and market trends.
- Engage in community discussions: Participate in local discussions about the environmental and economic impacts of refineries in your community.
Conclusion:
The map of US oil refineries provides a valuable tool for understanding the nation’s energy landscape, its economic health, and its environmental impact. By understanding the location, capacity, and significance of these facilities, we can better appreciate the complex interplay between energy production, consumption, and environmental sustainability. As the energy landscape continues to evolve, the map of US oil refineries will remain a critical resource for navigating the future of the nation’s energy sector.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to US Oil Refineries. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!