Navigating the Red River: A Geographic Exploration of a Vital Waterway
Related Articles: Navigating the Red River: A Geographic Exploration of a Vital Waterway
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Red River: A Geographic Exploration of a Vital Waterway. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Red River: A Geographic Exploration of a Vital Waterway

The Red River, a significant waterway in the southern United States, meanders through a diverse landscape, shaping the history, culture, and economy of the region. Its journey, stretching over 1,200 miles, encompasses portions of Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, and Louisiana, leaving an indelible mark on the American map. Understanding the Red River’s geography and its historical significance is crucial for appreciating its ongoing influence on the region and its people.
A River of Many Names and Origins
The Red River, aptly named for the reddish sediment it carries, originates in the Llano Estacado, a vast plateau in western Texas. Its source lies near the town of Red River, New Mexico, before it flows eastward, carving its path through the heartland of the American Southwest. The river’s journey is marked by a series of tributaries, each contributing to its volume and influencing its course.
The Red River’s Physical Geography: A Journey Through Diverse Landscapes
The Red River traverses a diverse range of landscapes, from the arid plains of the Llano Estacado to the fertile valleys of the Ouachita Mountains. This geographic diversity contributes to the river’s rich ecosystem, supporting a vibrant array of flora and fauna.
-
Headwaters and the Llano Estacado: The Red River’s journey begins in the high plains of the Llano Estacado, where the river’s flow is relatively shallow and meandering. This section of the river is characterized by its arid climate and sparse vegetation.
-
The Rolling Plains: As the Red River descends from the Llano Estacado, it enters the Rolling Plains, a region characterized by rolling hills and fertile grasslands. This section of the river is wider and deeper than its headwaters, supporting a more diverse ecosystem.
-
The Ouachita Mountains: The Red River’s path then takes it through the Ouachita Mountains, where the river carves its way through rugged terrain. This section of the river is characterized by its scenic beauty and its importance as a source of hydroelectric power.
-
The Red River Valley: After traversing the Ouachita Mountains, the Red River enters the Red River Valley, a fertile agricultural region that stretches from Oklahoma to Louisiana. This section of the river is characterized by its rich soil and its importance as a source of irrigation.
The Red River’s Historical Significance: A Tapestry of Cultures and Conflicts
The Red River has been a vital waterway for centuries, serving as a transportation route, a source of sustenance, and a focal point for human settlement. Its history is interwoven with the stories of Native American tribes, European explorers, and American settlers.
-
Native American Cultures: The Red River was a central part of the lives of numerous Native American tribes, including the Comanche, Kiowa, and Wichita. These tribes relied on the river for food, water, and transportation, and their cultural practices were deeply intertwined with the river’s ecosystem.
-
European Exploration: European explorers, including Francisco Vásquez de Coronado and René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle, followed the Red River in the 16th and 17th centuries, seeking new trade routes and opportunities for expansion. Their explorations laid the groundwork for future European settlement in the region.
-
American Settlement and Expansion: The Red River played a significant role in the westward expansion of the United States. American settlers, drawn by the fertile land and the promise of a new life, established communities along the river’s banks. The Red River became a vital transportation route for agricultural products and other goods.
-
Conflicts and Disputes: The Red River’s history is also marked by conflict and dispute. The region witnessed numerous clashes between Native American tribes, European powers, and American settlers. The Red River served as a boundary line between competing claims, leading to wars and treaties.
The Red River Today: A Vital Resource for the Region
The Red River continues to be a vital resource for the region, providing water for irrigation, drinking, and industry. Its importance is reflected in the numerous dams and reservoirs that have been constructed along its course. The river also supports a thriving ecosystem, providing habitat for a diverse array of wildlife and serving as a popular destination for recreation.
-
Agriculture: The Red River Valley remains a major agricultural region, producing cotton, wheat, and other crops. The river’s water is vital for irrigation, ensuring the productivity of the region’s farms.
-
Industry: The Red River is also an important source of water for industry, providing water for manufacturing, power generation, and other industrial uses.
-
Recreation: The Red River is a popular destination for recreation, offering opportunities for fishing, boating, camping, and wildlife viewing. The river’s scenic beauty and its diverse ecosystem attract visitors from across the region.
-
Environmental Challenges: The Red River faces a number of environmental challenges, including pollution, water scarcity, and habitat loss. These challenges threaten the river’s ecosystem and its ability to support human activities.
FAQs about the Red River
1. What is the length of the Red River?
The Red River is approximately 1,200 miles long, making it one of the longest rivers in the United States.
2. What states does the Red River flow through?
The Red River flows through the states of Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, and Louisiana.
3. What are the major tributaries of the Red River?
The Red River has numerous tributaries, including the Washita River, the Little River, the Kiamichi River, and the Wichita River.
4. What is the Red River’s importance to the region?
The Red River is a vital resource for the region, providing water for irrigation, drinking, and industry. It also supports a thriving ecosystem and is a popular destination for recreation.
5. What are some of the environmental challenges facing the Red River?
The Red River faces a number of environmental challenges, including pollution, water scarcity, and habitat loss.
Tips for Exploring the Red River
-
Visit the Red River National Wildlife Refuge: This refuge provides a sanctuary for a diverse array of wildlife, including migratory birds, waterfowl, and mammals.
-
Explore the Wichita Mountains Wildlife Refuge: This refuge offers scenic hiking trails, opportunities for wildlife viewing, and a glimpse into the region’s history.
-
Take a scenic drive along the Red River: The Red River Scenic Byway offers stunning views of the river and its surrounding landscapes.
-
Visit the Red River Museum: This museum showcases the history, culture, and natural history of the Red River region.
-
Attend a Red River Festival: These festivals celebrate the river’s cultural significance and provide opportunities for entertainment and community engagement.
Conclusion
The Red River, a vital waterway in the southern United States, is a testament to the power and beauty of nature. Its journey through diverse landscapes and its rich history have shaped the region’s identity and continue to influence its future. Understanding the Red River’s geography, history, and importance is crucial for appreciating its ongoing influence on the lives of the people who call this region home. As we navigate the challenges facing the Red River, we must strive to protect this vital resource for future generations.
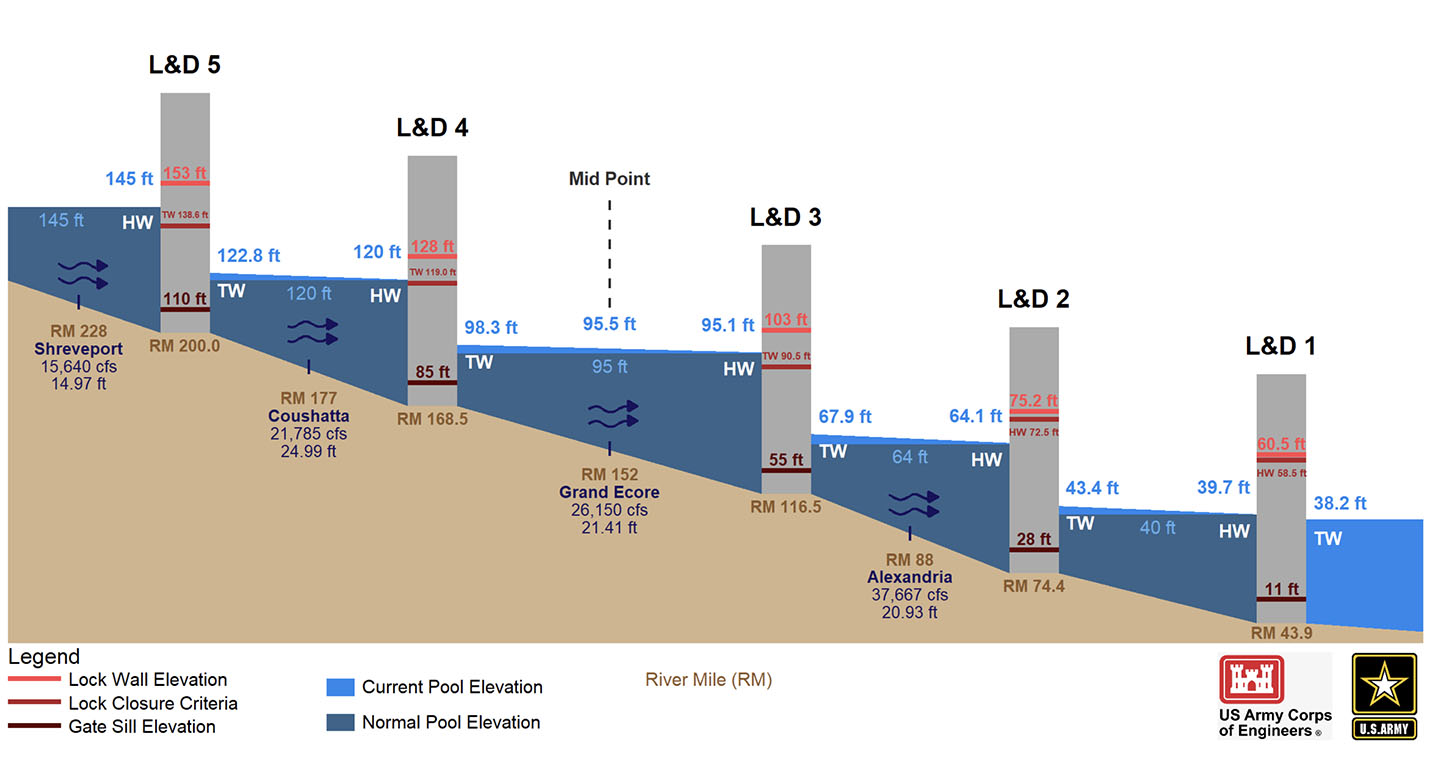


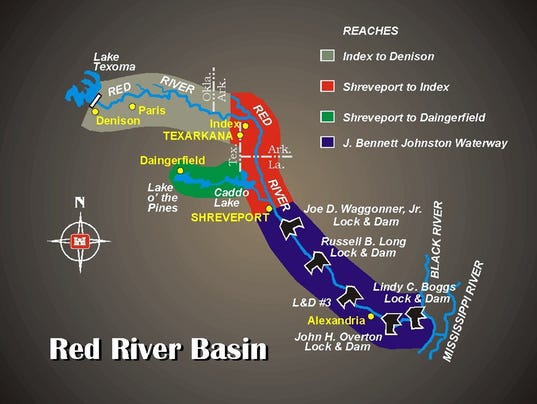
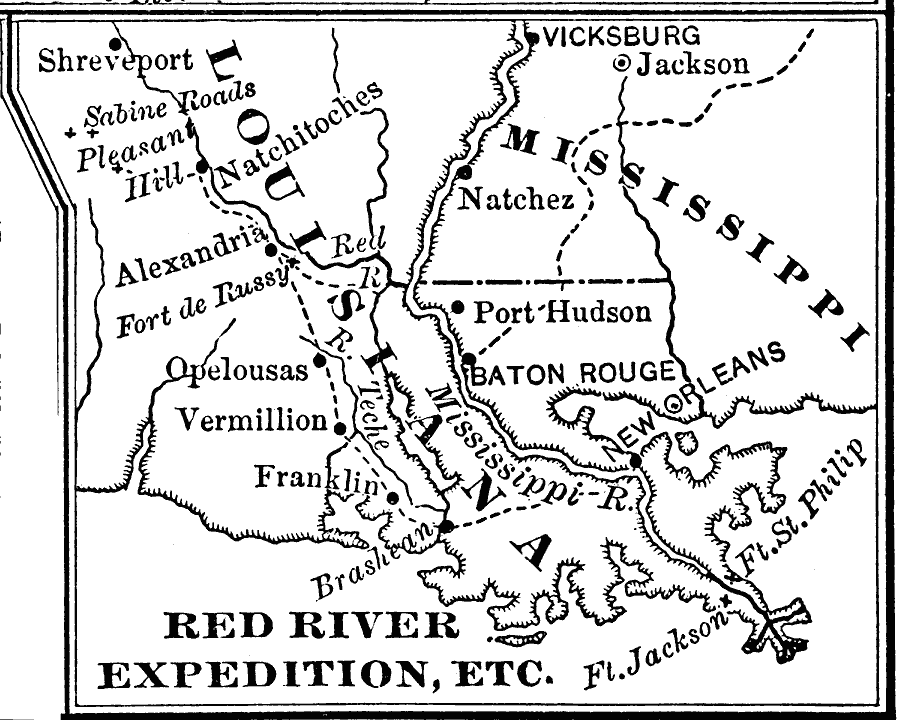



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Red River: A Geographic Exploration of a Vital Waterway. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!