Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Look at GPS Map Satellites
Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Look at GPS Map Satellites
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Look at GPS Map Satellites. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Look at GPS Map Satellites

The ability to pinpoint one’s location with remarkable accuracy is a modern marvel, made possible by a network of specialized satellites orbiting Earth. These are the Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites, the backbone of navigation systems used in countless devices, from smartphones to cars to airplanes. This article delves into the intricacies of GPS map satellites, exploring their functions, benefits, and the technology that underpins their operation.
Understanding the Fundamentals of GPS Map Satellites
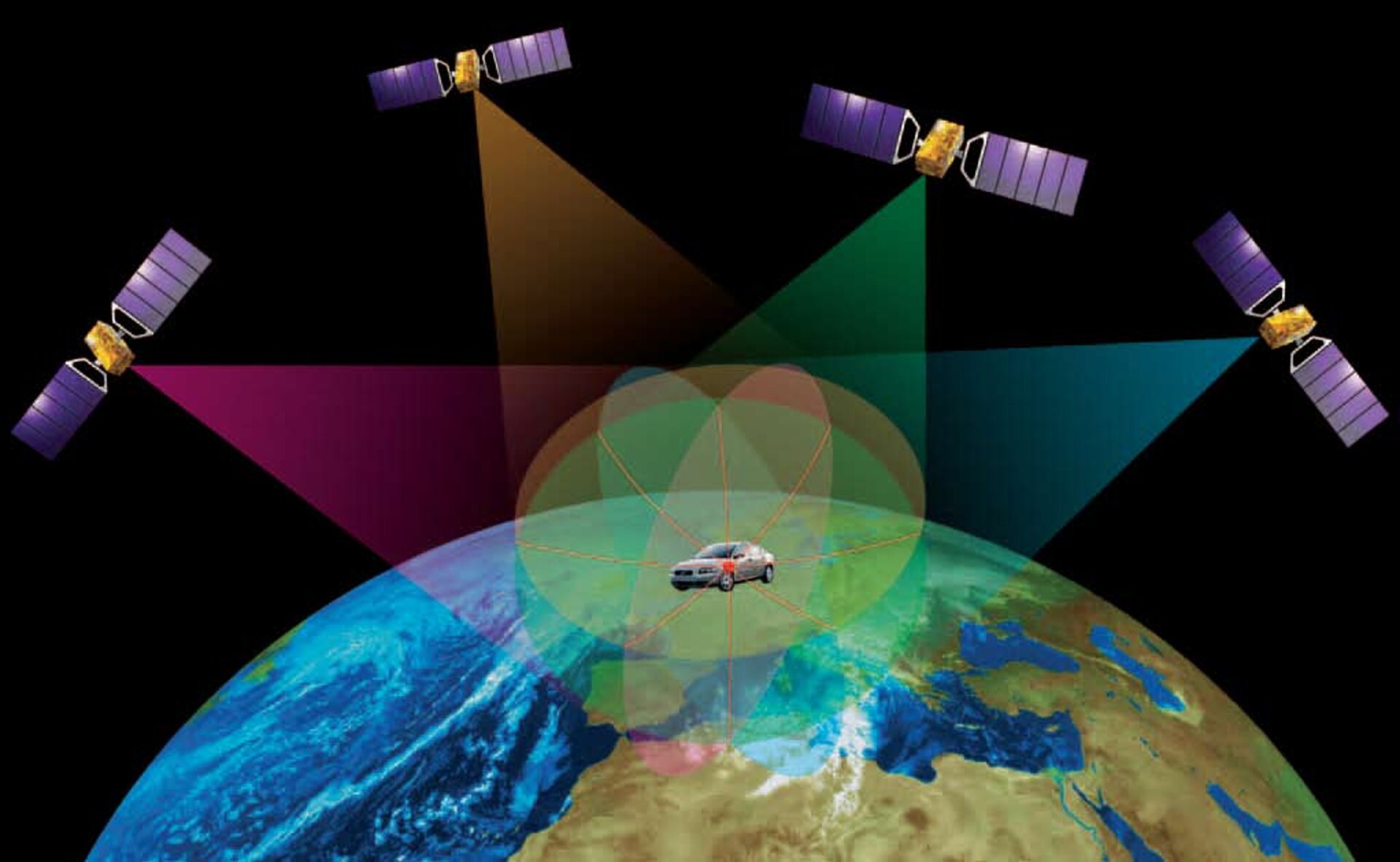
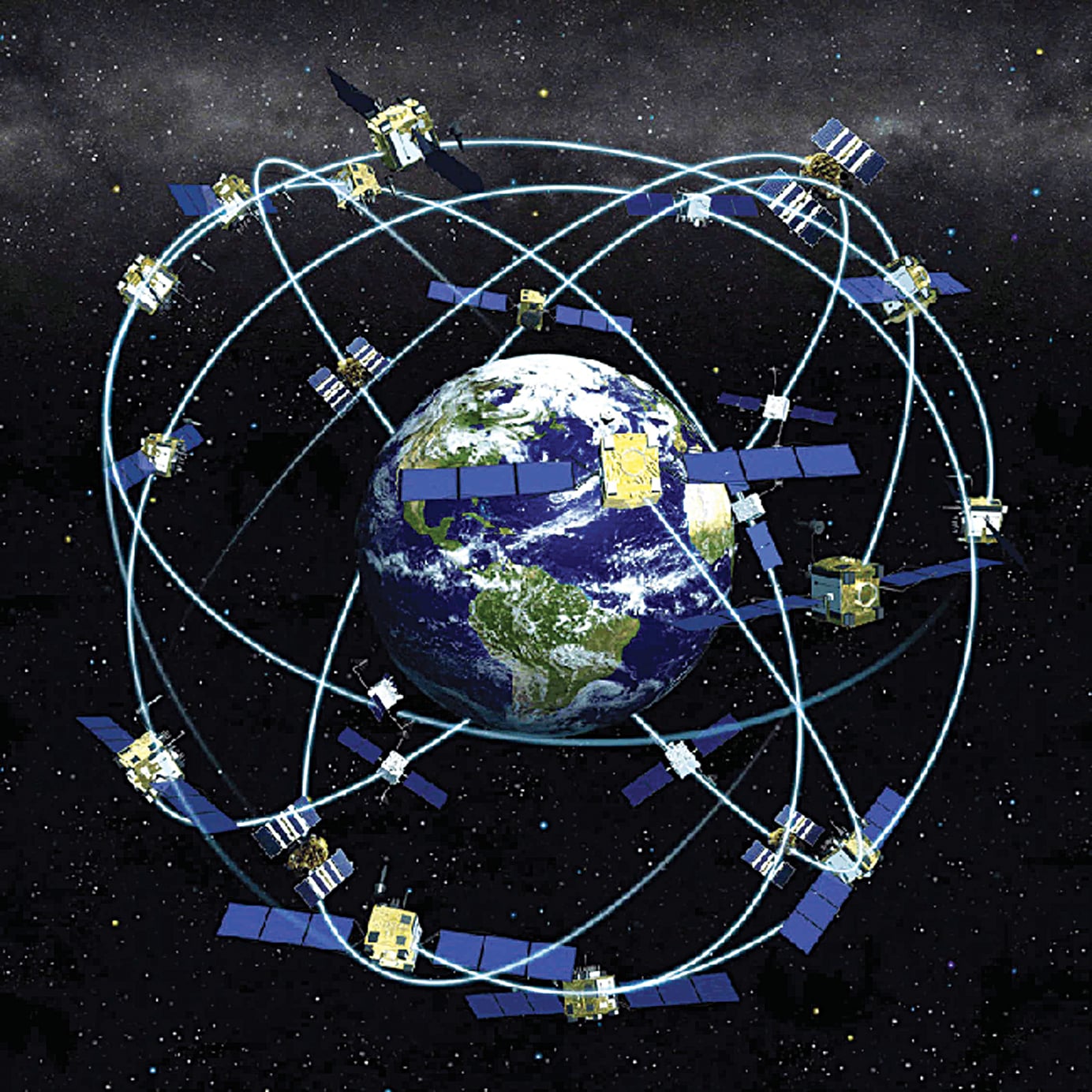
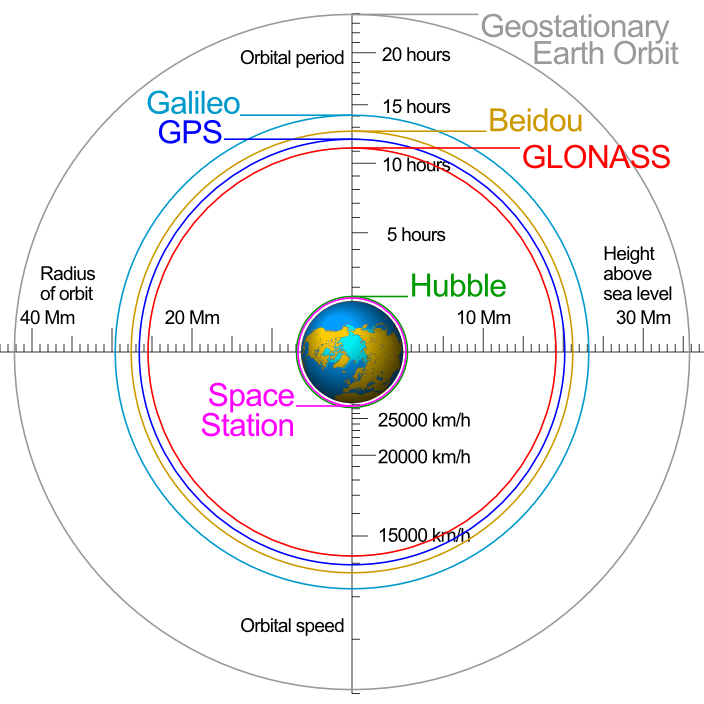
The GPS system relies on a constellation of 31 operational satellites, strategically positioned in six orbital planes around Earth. These satellites constantly transmit radio signals, containing information about their location and the precise time of transmission. Receivers on Earth, such as GPS-enabled devices, pick up these signals and use them to calculate their own position.
How GPS Map Satellites Work: A Breakdown
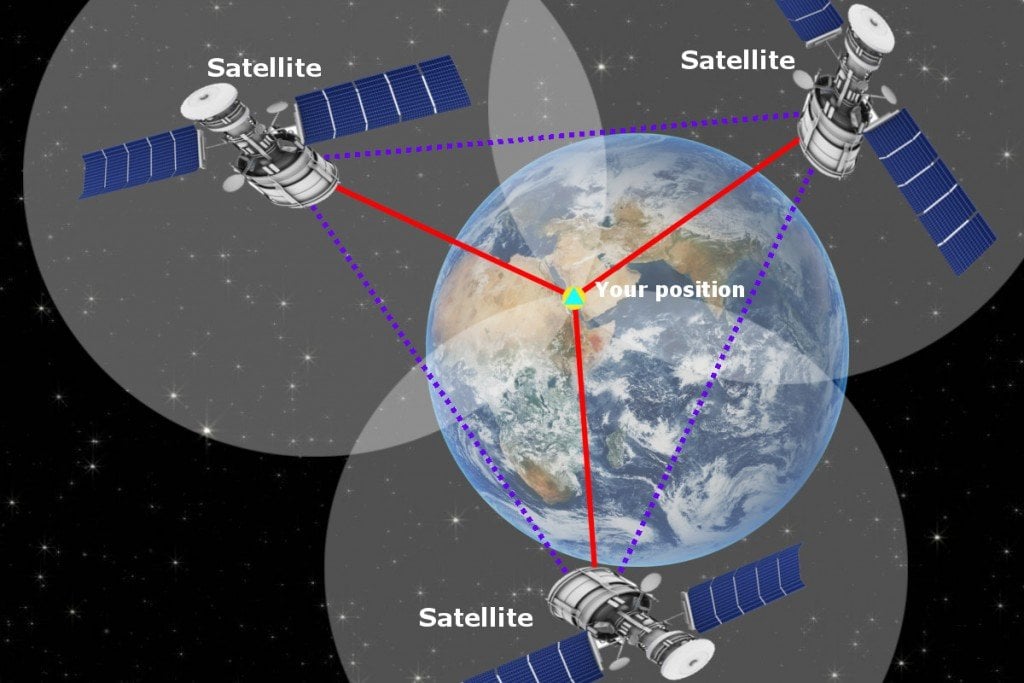
The process of determining location using GPS satellites involves a series of calculations based on the principles of triangulation and time measurement. Here’s a simplified explanation:
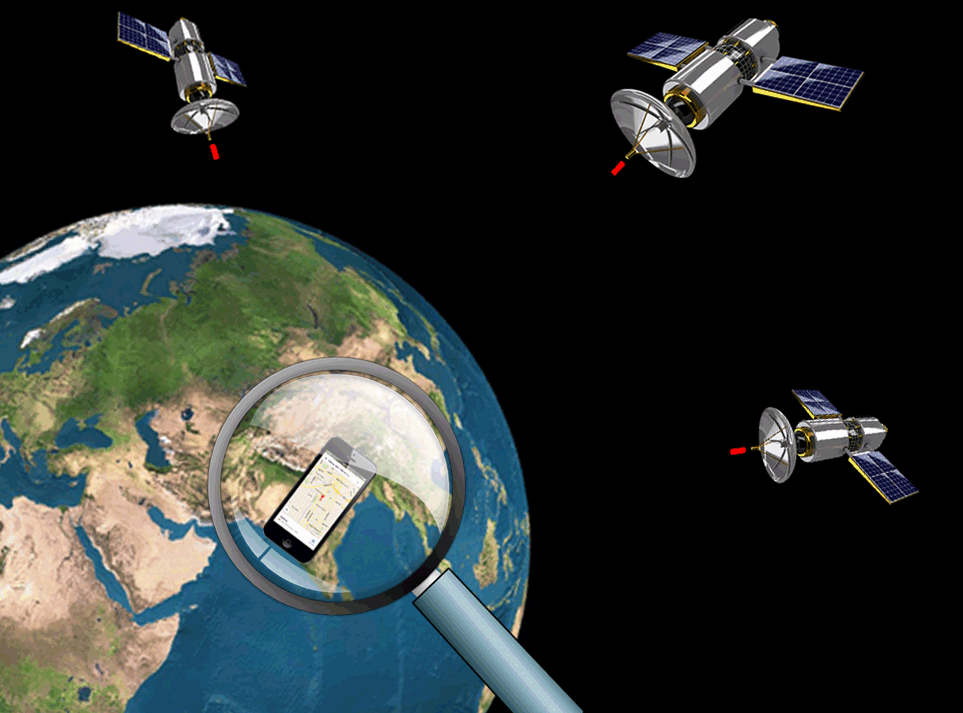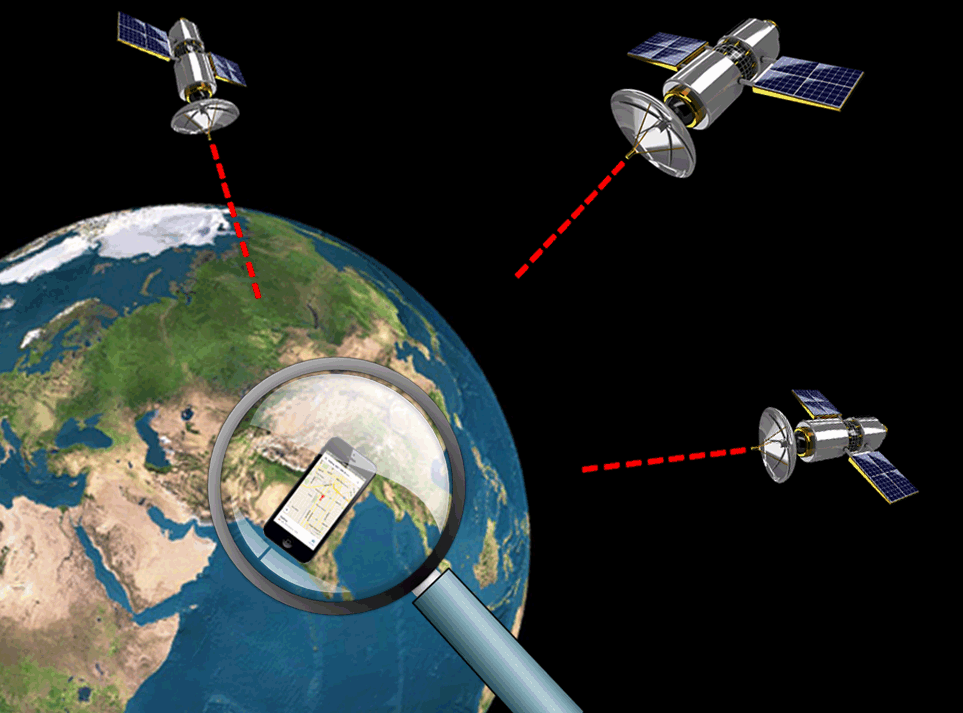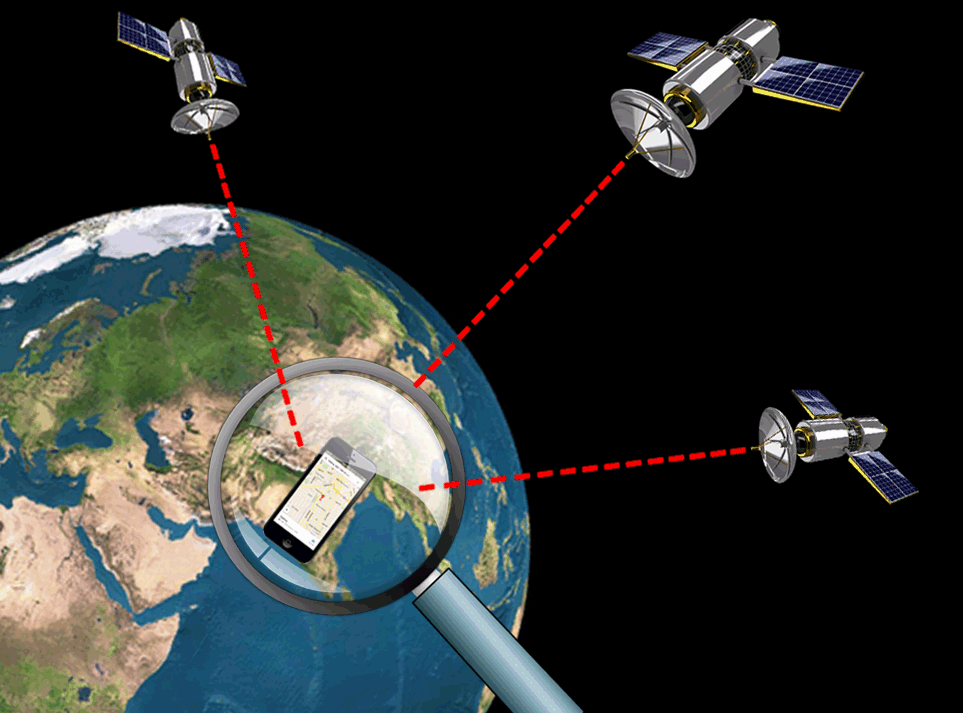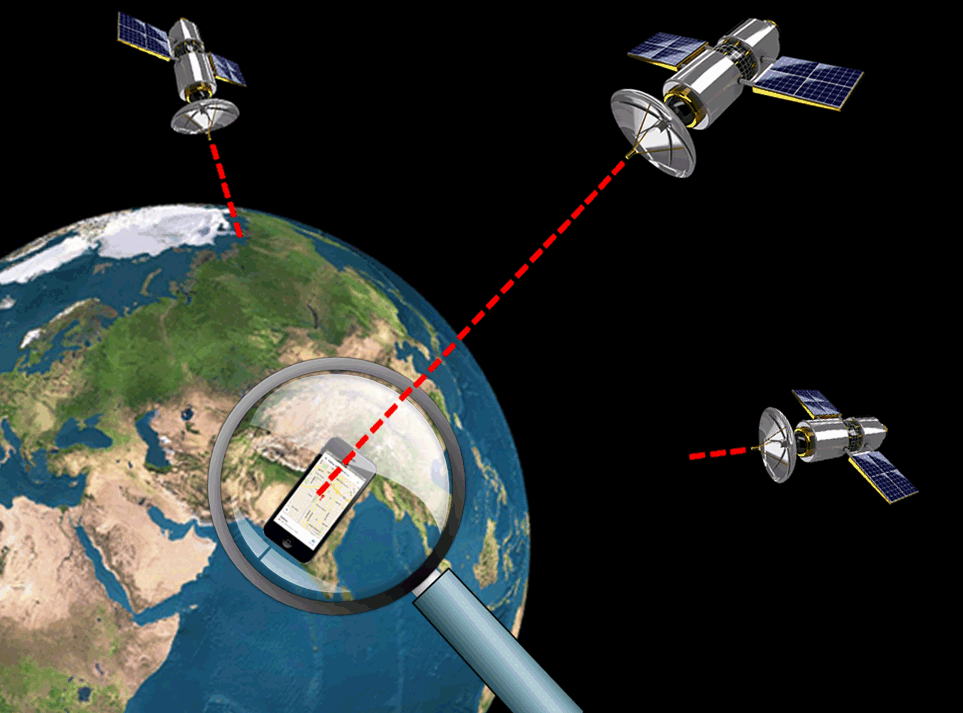
- Signal Reception: A GPS receiver picks up signals from at least four GPS satellites.
- Time Measurement: The receiver measures the time it takes for each signal to reach it.
- Distance Calculation: Knowing the speed of light, the receiver calculates the distance between itself and each satellite.
- Triangulation: The receiver uses the distances to each satellite to pinpoint its location in three dimensions (latitude, longitude, and altitude).
Key Components of the GPS System:
- Space Segment: This comprises the constellation of GPS satellites, responsible for transmitting signals.
- Control Segment: Ground stations monitor and control the satellites, ensuring their accurate positioning and signal transmission.
- User Segment: This encompasses all GPS receivers, ranging from smartphones to specialized navigation systems.
Benefits of GPS Map Satellites: A Transformative Impact
GPS map satellites have revolutionized navigation and location-based services, offering numerous benefits across diverse sectors:
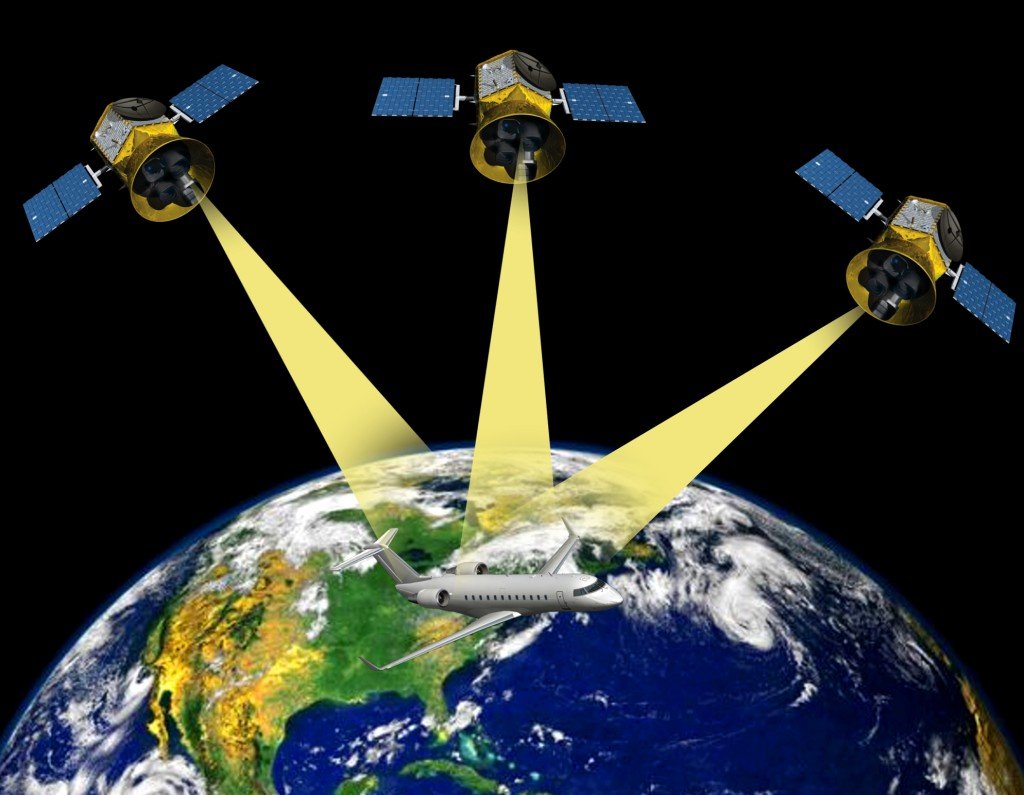
- Navigation: The most prominent application of GPS is in navigation. Drivers, hikers, sailors, and pilots rely on GPS devices to find their way, offering real-time directions and accurate location tracking.
- Mapping and Surveying: GPS technology enables precise mapping and surveying, crucial for infrastructure development, land management, and disaster response.
- Time Synchronization: GPS satellites provide highly accurate time synchronization, essential for financial transactions, telecommunications, and scientific research.
- Emergency Services: GPS plays a vital role in emergency response, enabling first responders to locate victims quickly and efficiently.
- Fleet Management: GPS tracking systems are used to monitor vehicle movement, optimize routes, and improve fleet efficiency.
- Agriculture: GPS-guided farming techniques enhance precision in planting, fertilization, and crop monitoring, leading to higher yields and reduced resource consumption.
- Scientific Research: GPS data is used in various scientific disciplines, including geology, meteorology, and oceanography, to study Earth’s dynamics and climate change.
Challenges and Limitations of GPS Map Satellites:
While GPS technology offers significant advantages, it also faces certain challenges and limitations:
- Signal Blockage: Buildings, dense foliage, and tunnels can block GPS signals, hindering accuracy in urban environments and enclosed spaces.
- Atmospheric Interference: The atmosphere can distort GPS signals, leading to minor inaccuracies.
- Satellite Availability: The number of visible satellites can vary depending on location and time, potentially affecting accuracy.
- Security Concerns: GPS signals are susceptible to spoofing and jamming, posing security risks in sensitive applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About GPS Map Satellites
1. What is the difference between GPS and GNSS?
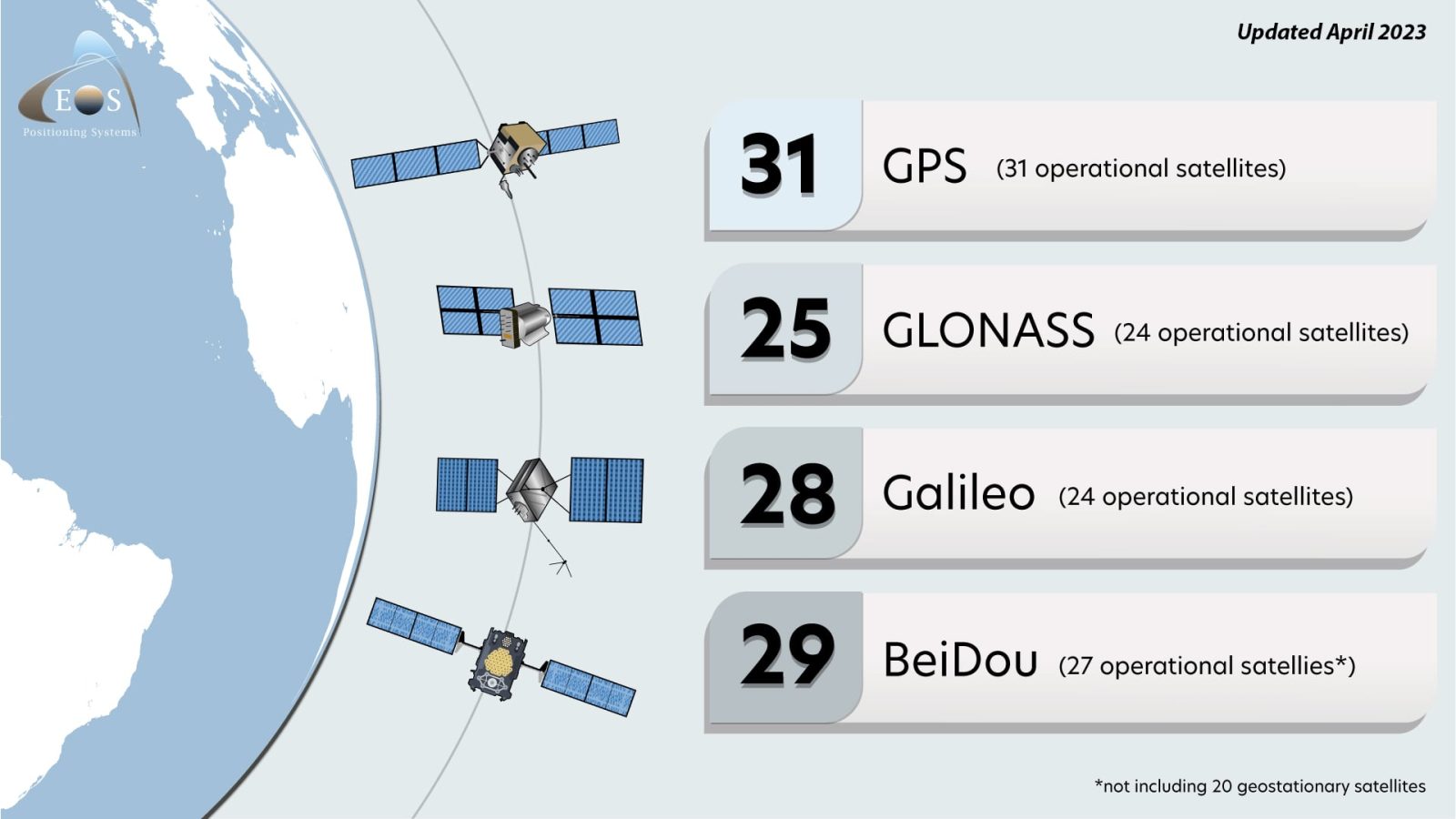
GPS refers specifically to the American satellite navigation system. GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) is a broader term encompassing all satellite navigation systems, including GPS, GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (Europe), and Beidou (China).
2. How accurate is GPS?
GPS accuracy can vary depending on factors like atmospheric conditions, signal blockage, and the number of visible satellites. Under ideal conditions, accuracy can reach sub-meter levels.
3. Can GPS be used underwater or in space?
GPS signals do not penetrate water or the Earth’s atmosphere effectively. Therefore, GPS is not typically used underwater or in space.
4. Is GPS free to use?
GPS technology is publicly available and free to use. However, certain commercial services that rely on GPS, like mapping apps, may require subscriptions or in-app purchases.
5. How can I improve GPS accuracy?
To improve GPS accuracy, ensure you have a clear view of the sky, use a high-quality GPS receiver, and consider using assisted GPS (A-GPS) technology, which utilizes cellular networks to improve signal acquisition.
Tips for Using GPS Map Satellites Effectively
- Ensure a Clear View of the Sky: Position your GPS receiver in an open area with minimal obstruction.
- Use a High-Quality Receiver: Invest in a GPS receiver with a strong antenna and reliable software.
- Calibrate Regularly: Regularly calibrate your GPS receiver to maintain accuracy.
- Consider A-GPS Technology: A-GPS can significantly improve signal acquisition, especially in urban areas.
- Be Aware of Signal Blockage: Recognize areas where GPS signals may be blocked and plan accordingly.
- Use Multiple Navigation Sources: Combine GPS with other navigation tools, such as maps and compasses, for redundancy.
Conclusion: The Enduring Impact of GPS Map Satellites
GPS map satellites have become an integral part of modern life, revolutionizing navigation, communication, and countless other applications. Their ability to provide accurate location information has transformed industries, empowered individuals, and shaped our understanding of the world. As technology continues to advance, GPS is poised to play an even greater role in shaping our future, enabling new innovations and enhancing our understanding of our planet.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Look at GPS Map Satellites. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!