North Africa: A Battlefield in World War II
Related Articles: North Africa: A Battlefield in World War II
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to North Africa: A Battlefield in World War II. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
North Africa: A Battlefield in World War II
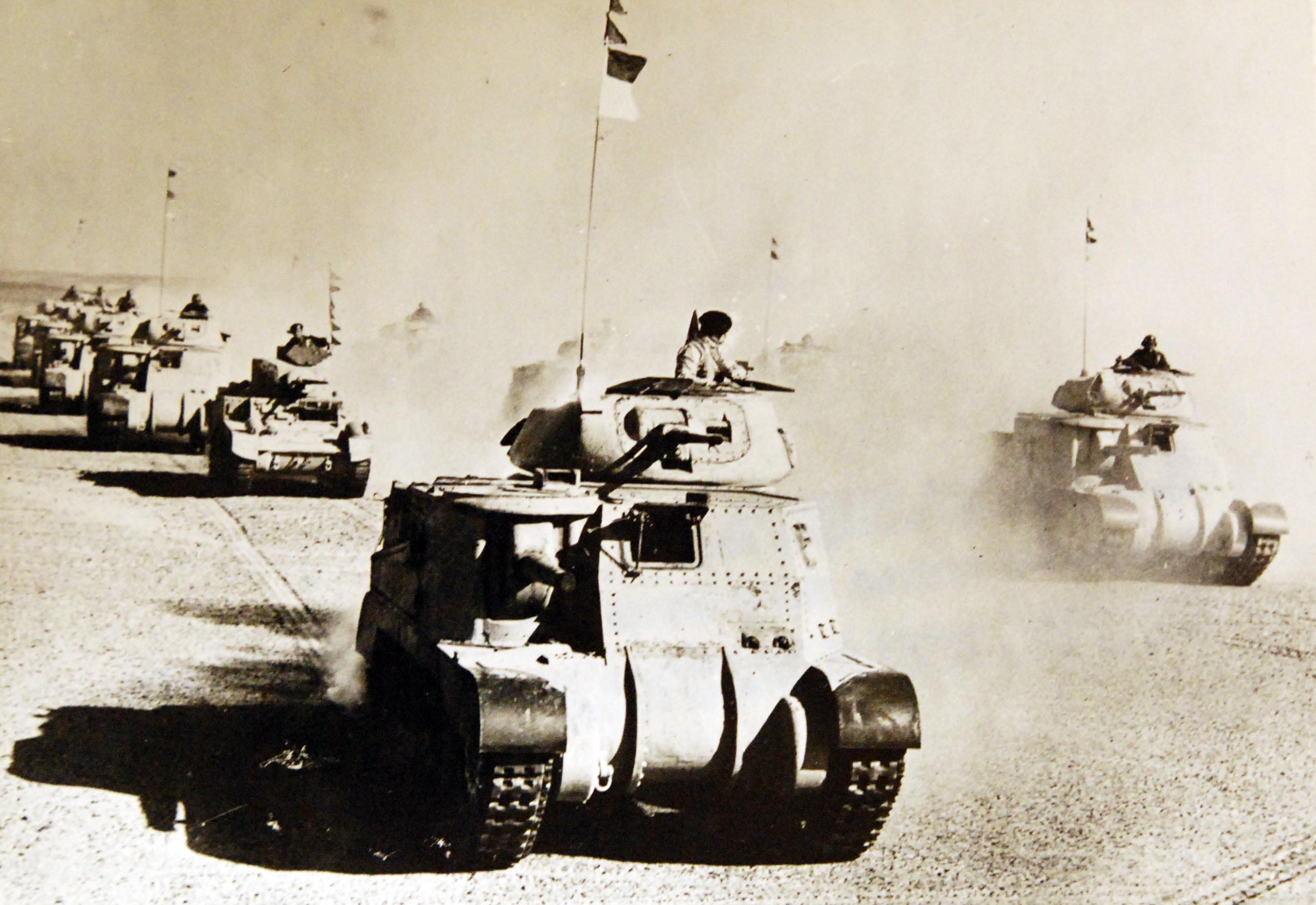

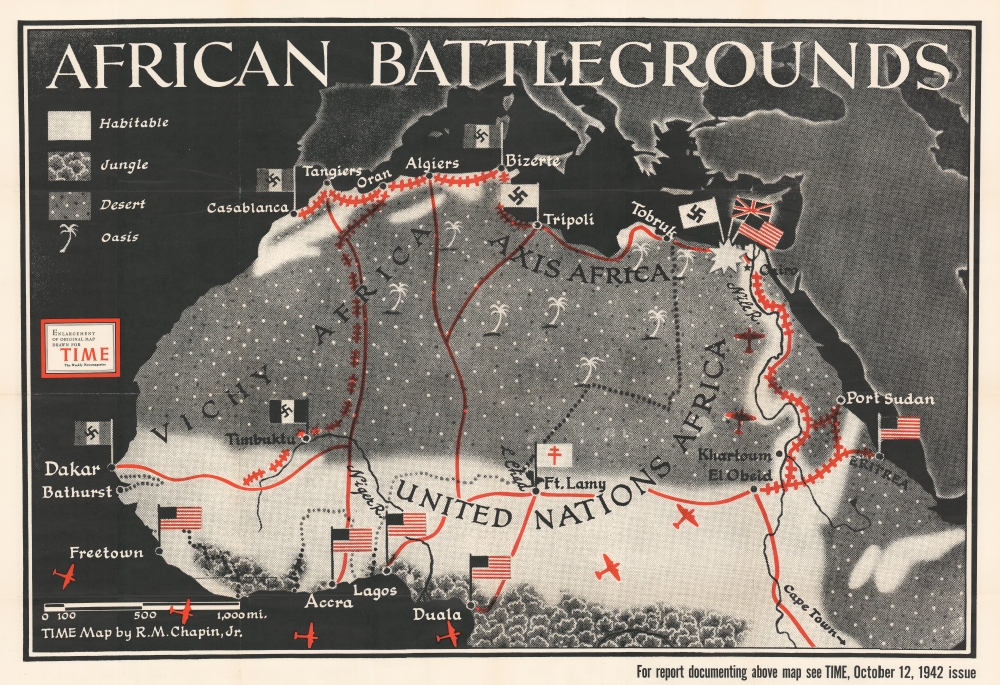
The North African campaign of World War II, spanning from 1940 to 1943, was a crucial theatre of war that saw fierce battles between the Axis and Allied powers. This region, encompassing present-day Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Egypt, became a strategic battleground for control of vital resources, trade routes, and the Suez Canal, a crucial waterway connecting Europe to Asia.
The Geographical Context
The North African landscape, characterized by vast deserts, rugged mountains, and fertile oases, posed unique challenges for both sides. The vast distances and harsh weather conditions made logistics and supply lines extremely difficult, while the terrain provided opportunities for ambushes and defensive positions.
Early Axis Victories and the Rise of Rommel
The campaign began with early Axis successes. In June 1940, Italy invaded Egypt, but was swiftly repelled by the British. However, the arrival of German General Erwin Rommel, known as the "Desert Fox," changed the tide of the war in North Africa. Rommel’s brilliant tactics and lightning-fast offensives, coupled with the superior German equipment, pushed the British forces back, leading to the capture of Tobruk in June 1942.
The Allied Counteroffensive and the Turning Point
The Allied forces, led by General Bernard Montgomery, launched a counteroffensive in October 1942, known as the Second Battle of El Alamein. This pivotal battle, fought near the Egyptian town of El Alamein, marked a turning point in the North African campaign. Montgomery’s skillful strategy, combined with the superior Allied firepower, resulted in a decisive victory for the Allies, forcing Rommel’s retreat and effectively ending the Axis threat in North Africa.
The Tunisian Campaign and the Final Victory
Following El Alamein, the Allies pursued the retreating Axis forces into Tunisia. The Tunisian Campaign, fought between January and May 1943, was a brutal and bloody conflict, involving heavy fighting in the rugged terrain of the Atlas Mountains. Despite fierce resistance, the Axis forces were eventually overwhelmed, culminating in their surrender in May 1943.
The Significance of the North African Campaign
The North African campaign held immense strategic importance for both sides:
- Control of the Suez Canal: The Suez Canal was a vital waterway for the British Empire, connecting Europe to Asia and its colonies. Controlling the canal would have given the Axis forces a significant advantage in the war.
- Access to Resources: North Africa was rich in oil and other resources, which were crucial for the war effort. Controlling these resources would have provided the Axis with a vital advantage.
- Strategic Location: North Africa’s strategic location, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, made it a key battleground for controlling sea lanes and air bases.
- Psychological Impact: The Allied victory in North Africa boosted morale and provided a much-needed psychological boost to the Allied war effort.
The Legacy of the North African Campaign
The North African campaign left a lasting legacy:
- Military Innovations: The campaign saw the development of new military tactics and technologies, such as the use of armored warfare and desert warfare strategies.
- Impact on the War: The Allied victory in North Africa was a crucial turning point in World War II, paving the way for the Allied invasion of Italy and the eventual defeat of the Axis powers.
- Historical Significance: The campaign remains a testament to the bravery and resilience of the soldiers who fought in the harsh conditions of the North African desert.
FAQs about the Map of North Africa in World War II
Q: What was the significance of the Suez Canal in the North African campaign?
A: The Suez Canal was a vital waterway for the British Empire, connecting Europe to Asia and its colonies. Controlling the canal would have given the Axis forces a significant advantage in the war, allowing them to disrupt Allied supply lines and potentially threaten British control of the Middle East.
Q: How did the terrain of North Africa impact the fighting?
A: The vast deserts, rugged mountains, and fertile oases of North Africa posed unique challenges for both sides. The vast distances and harsh weather conditions made logistics and supply lines extremely difficult, while the terrain provided opportunities for ambushes and defensive positions. The open desert terrain favored mobile warfare, while the rugged mountains offered opportunities for defensive positions.
Q: What were the key battles of the North African campaign?
A: The North African campaign saw several key battles, including:
- The Battle of Tobruk (1941): A crucial battle for control of the strategically important port city of Tobruk.
- The First Battle of El Alamein (1942): A major battle that resulted in a stalemate, but marked a turning point in the campaign.
- The Second Battle of El Alamein (1942): A decisive Allied victory that effectively ended the Axis threat in North Africa.
- The Tunisian Campaign (1943): A brutal and bloody conflict that resulted in the final defeat of the Axis forces in North Africa.
Q: Who were the key commanders in the North African campaign?
A: Some of the key commanders in the North African campaign included:
- Erwin Rommel (Axis): Known as the "Desert Fox," Rommel’s brilliant tactics and lightning-fast offensives posed a significant threat to the Allied forces.
- Bernard Montgomery (Allied): Montgomery’s skillful strategy and leadership were instrumental in the Allied victory at El Alamein.
- Harold Alexander (Allied): Alexander commanded the Allied forces in North Africa after Montgomery’s victory at El Alamein.
- Umberto II of Italy (Axis): The Italian King who was in charge of the Italian forces in North Africa.
Tips for Understanding the Map of North Africa in World War II
- Study the key geographical features: Understanding the terrain, including the deserts, mountains, and oases, is crucial for understanding the course of the campaign.
- Focus on the key battles: Studying the key battles, such as El Alamein and Tobruk, will provide insights into the strategic importance of different locations and the tactics used by both sides.
- Learn about the key commanders: Understanding the strategies and leadership styles of key commanders, such as Rommel and Montgomery, can provide a deeper understanding of the campaign.
- Consider the logistical challenges: The vast distances and harsh conditions of North Africa made logistics and supply lines extremely difficult. Understanding these challenges can help explain the course of the campaign.
Conclusion
The North African campaign was a pivotal theatre of World War II, characterized by fierce battles, strategic maneuvering, and immense logistical challenges. The campaign was a testament to the bravery and resilience of the soldiers who fought in the harsh conditions of the North African desert. The Allied victory in North Africa had a significant impact on the course of the war, paving the way for the Allied invasion of Italy and the eventual defeat of the Axis powers. Studying the map of North Africa in World War II provides valuable insights into the strategic importance of this region, the challenges faced by both sides, and the impact of the campaign on the course of the war.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into North Africa: A Battlefield in World War II. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!