The Crimea: A Complex Landscape of History, Politics, and Geography
Related Articles: The Crimea: A Complex Landscape of History, Politics, and Geography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Crimea: A Complex Landscape of History, Politics, and Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Crimea: A Complex Landscape of History, Politics, and Geography
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-135291171-5c8d65f746e0fb00016ee0b7.jpg)
The Crimean Peninsula, a geographically and historically significant region on the northern coast of the Black Sea, has been a focal point of geopolitical tension for centuries. Its strategic location, diverse landscape, and rich cultural heritage have interwoven its fate with the destinies of neighboring empires and nations. Understanding the Crimean Peninsula’s geography, history, and current political status requires navigating a complex web of influences and perspectives.
A Geographic Overview:
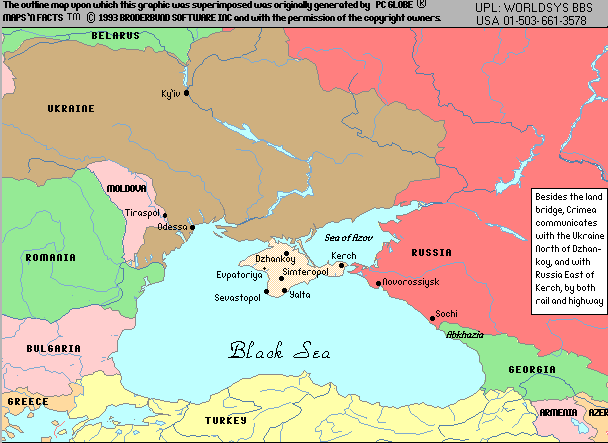
The Crimea, measuring roughly 26,000 square kilometers, protrudes into the Black Sea from the Ukrainian mainland, forming a natural bridge between Europe and Asia. Its diverse landscape encompasses:
- The Crimean Mountains: A range of low mountains, reaching a maximum elevation of 1,545 meters at Mount Roman-Kosh, traverses the southern portion of the peninsula. These mountains are home to diverse flora and fauna, including the endemic Crimean pine and the rare Crimean deer.
- The Crimean Steppe: A vast, flat expanse of fertile land stretches across the northern part of the peninsula. This region has historically been crucial for agriculture, particularly for the cultivation of wheat and sunflowers.
- The Black Sea Coast: With its stunning beaches, picturesque coves, and rich marine life, the Black Sea coast attracts tourists from around the world. The coastal cities of Sevastopol and Yalta are renowned for their historical significance and scenic beauty.
Historical Tapestry:
The Crimea has witnessed the rise and fall of numerous civilizations, each leaving its mark on the peninsula’s cultural and architectural landscape.
- Ancient Greek Colonies: As early as the 6th century BCE, Greek colonists established settlements on the Crimean coast. These settlements, including Chersonesus, played a vital role in trade and cultural exchange between the Greek world and the Black Sea region.
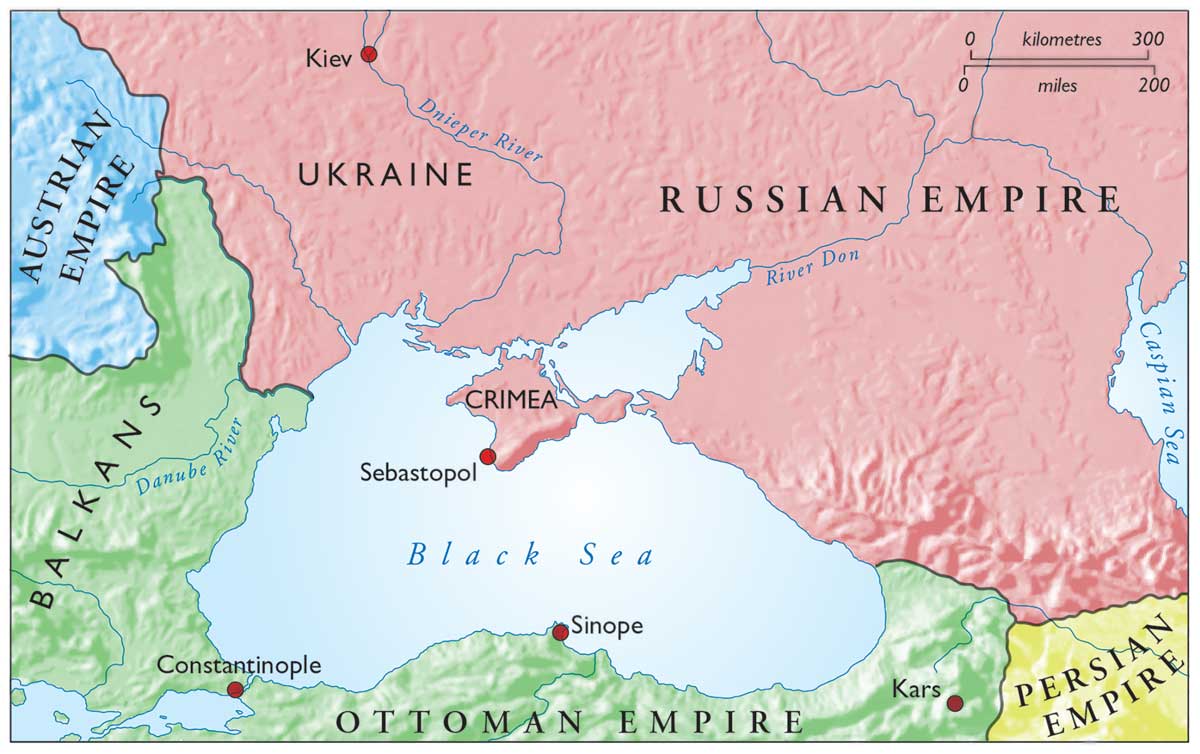
- The Golden Horde: During the Middle Ages, the Crimean Peninsula was ruled by the Golden Horde, a successor state to the Mongol Empire. This period witnessed the establishment of the Crimean Khanate, a powerful and independent state that controlled a significant portion of the Black Sea trade.
- The Ottoman Empire: In the 15th century, the Crimean Khanate became a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire. This period marked a significant cultural and religious transformation, with the majority of the Crimean population converting to Islam.
- The Russian Empire: In the 18th century, the Russian Empire began to exert its influence over the Crimean Peninsula, culminating in its annexation in 1783. This event marked the beginning of a period of Russian dominance, which lasted until the collapse of the Soviet Union.
- The Soviet Era: Under Soviet rule, the Crimean Peninsula became an integral part of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic. The region experienced significant industrial development, with the construction of large-scale factories and infrastructure projects.
The 2014 Annexation and Its Aftermath:
The Crimean Peninsula’s history took a dramatic turn in 2014 with Russia’s annexation of the region. This event, triggered by the Euromaidan Revolution in Ukraine and the subsequent political instability, sparked international condemnation and sanctions against Russia.
- Referendum and International Response: A referendum held in Crimea on March 16, 2014, resulted in a majority vote in favor of joining Russia. However, the international community, including the United States, the European Union, and the United Nations, condemned the referendum as illegal and illegitimate.
- International Sanctions and Diplomatic Tensions: The annexation led to the imposition of economic sanctions against Russia by Western countries. These sanctions have significantly impacted Russia’s economy and have strained relations between Russia and the West.
- Ongoing Political and Military Tensions: The annexation of Crimea has created a volatile geopolitical situation in the Black Sea region. Russia’s military presence in Crimea has increased significantly, leading to concerns about potential military conflict.
The Current Status of Crimea:
The Crimean Peninsula is currently administered by Russia as a federal subject, known as the Republic of Crimea. However, the international community, with the exception of a handful of countries, does not recognize the annexation and continues to consider Crimea as part of Ukraine.
The Importance of the Crimean Peninsula:
The Crimean Peninsula’s strategic location, rich history, and diverse landscape have made it a subject of intense geopolitical interest. The peninsula holds significant importance for:
- Security: The Crimean Peninsula is strategically located on the Black Sea, controlling access to the Sea of Azov and the Donbas region. Its military significance has been highlighted by Russia’s deployment of naval and air bases in Sevastopol.
- Economy: The peninsula possesses significant economic potential, particularly in tourism, agriculture, and energy resources. The development of the Kerch Strait Bridge, connecting Crimea to mainland Russia, has been touted as a key infrastructure project to boost the region’s economy.
- Culture: The Crimean Peninsula boasts a rich and diverse cultural heritage, blending influences from various civilizations throughout history. The region is home to numerous historical sites, museums, and cultural institutions, attracting tourists and scholars alike.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The Crimean Peninsula faces a number of challenges, including:
- Political Instability: The annexation of Crimea has created a volatile political situation, with ongoing tensions between Russia and Ukraine. The future of the peninsula remains uncertain, with the possibility of further conflict or political instability.
- Economic Challenges: The annexation and subsequent international sanctions have had a significant impact on the Crimean economy. The region faces challenges in attracting investment and developing its economic potential.
- Environmental Concerns: The peninsula’s unique ecosystem is facing increasing environmental pressures, including pollution from industrial activities and tourism. The preservation of the Crimean environment is a critical challenge.
Despite these challenges, the Crimean Peninsula also presents opportunities for:
- Economic Development: The peninsula has the potential to become a significant economic hub in the Black Sea region. The development of tourism, agriculture, and energy resources could contribute to economic growth.
- Cultural Exchange: The peninsula’s rich cultural heritage can be a source of pride and a platform for cultural exchange between Russia, Ukraine, and the international community.
- Peace and Stability: The Crimean Peninsula has the potential to become a bridge for dialogue and cooperation between Russia and Ukraine. The promotion of peace and stability in the region is essential for regional security and prosperity.
FAQs:
1. Why is the Crimea important?
The Crimean Peninsula is strategically located on the Black Sea, controlling access to the Sea of Azov and the Donbas region. It also possesses significant economic potential, particularly in tourism, agriculture, and energy resources. Additionally, the peninsula boasts a rich cultural heritage, blending influences from various civilizations throughout history.
2. What is the current political status of Crimea?
The Crimean Peninsula is currently administered by Russia as a federal subject, known as the Republic of Crimea. However, the international community, with the exception of a handful of countries, does not recognize the annexation and continues to consider Crimea as part of Ukraine.
3. What are the main challenges facing Crimea?
The Crimean Peninsula faces a number of challenges, including political instability, economic challenges, and environmental concerns. The annexation of Crimea has created a volatile political situation, with ongoing tensions between Russia and Ukraine. The region also faces challenges in attracting investment and developing its economic potential. Additionally, the peninsula’s unique ecosystem is facing increasing environmental pressures.
4. What are the opportunities for Crimea?
Despite the challenges, the Crimean Peninsula also presents opportunities for economic development, cultural exchange, and peace and stability. The peninsula has the potential to become a significant economic hub in the Black Sea region. The development of tourism, agriculture, and energy resources could contribute to economic growth. Additionally, the peninsula’s rich cultural heritage can be a source of pride and a platform for cultural exchange.
5. What is the future of Crimea?
The future of the Crimean Peninsula remains uncertain. The ongoing tensions between Russia and Ukraine, the lack of international recognition for the annexation, and the economic challenges facing the region all contribute to a volatile situation. The future of Crimea will depend on the outcome of negotiations between Russia and Ukraine and the international community’s response to the annexation.
Tips:
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date on developments in the Crimean Peninsula by following reputable news sources and academic research.
- Engage in Dialogue: Participate in discussions about the Crimean Peninsula with an open mind and a willingness to consider different perspectives.
- Support Peace and Stability: Advocate for peaceful resolution of the conflict and for the promotion of peace and stability in the region.
- Respect Cultural Diversity: Appreciate the rich cultural heritage of the Crimean Peninsula and respect the diversity of perspectives on its history and current situation.
Conclusion:
The Crimean Peninsula stands as a testament to the complexities of history, politics, and geography. Its strategic location, diverse landscape, and rich cultural heritage have intertwined its fate with the destinies of neighboring empires and nations. The annexation of Crimea in 2014 has created a volatile geopolitical situation, with ongoing tensions between Russia and Ukraine. The future of the peninsula remains uncertain, with the potential for further conflict or political instability. However, the peninsula also presents opportunities for economic development, cultural exchange, and peace and stability. Understanding the complexities of the Crimean Peninsula is crucial for navigating the geopolitical landscape of the Black Sea region and for promoting peace and stability in the region.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Crimea: A Complex Landscape of History, Politics, and Geography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!