The Enduring Legacy of Hernán Cortés: Unraveling the Maps of Conquest
Related Articles: The Enduring Legacy of Hernán Cortés: Unraveling the Maps of Conquest
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Enduring Legacy of Hernán Cortés: Unraveling the Maps of Conquest. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enduring Legacy of Hernán Cortés: Unraveling the Maps of Conquest

Hernán Cortés, the Spanish conquistador renowned for his conquest of the Aztec Empire, remains a controversial figure in history. His actions, while undeniably shaping the course of the Americas, were marked by brutality and exploitation. Yet, his legacy extends beyond conquest, encompassing a fascinating aspect often overlooked: the cartographic record he left behind. These maps, meticulously crafted by Cortés and his cartographers, offer invaluable insights into the early exploration and mapping of Mexico, providing a window into a pivotal period of history.
A Journey of Discovery: The Maps of Hernán Cortés
Cortés’s maps were not merely tools for navigation; they were crucial instruments in his campaign of conquest. They served as a means of understanding the geography of the Aztec Empire, identifying strategic locations, and planning military maneuvers. These maps, often referred to as "cartas," were meticulously detailed, capturing the physical features of the land, the location of settlements, and even the social and political structures of the Aztec civilization.
The Significance of Cortés’s Cartographic Legacy
The significance of Cortés’s maps extends beyond their military utility. They represent a pivotal moment in the history of cartography, marking the beginning of a systematic mapping of the Americas. These maps provided Europeans with their first detailed glimpse of the vast and complex world that lay beyond the Atlantic Ocean. They also served as a foundation for future exploration and cartographic endeavors, paving the way for a more accurate understanding of the Americas.
Unveiling the Secrets of the Maps
Cortés’s maps were not merely representations of physical landscapes; they were intricate narratives of conquest and cultural exchange. They reveal the complex interplay between Spanish ambition and indigenous knowledge, showcasing the clash of cultures that defined the early years of Spanish colonization.
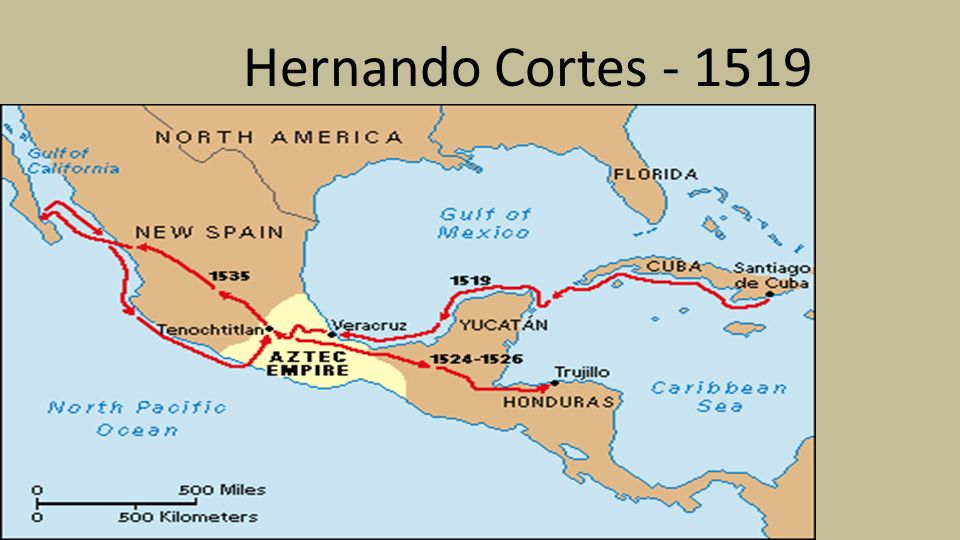
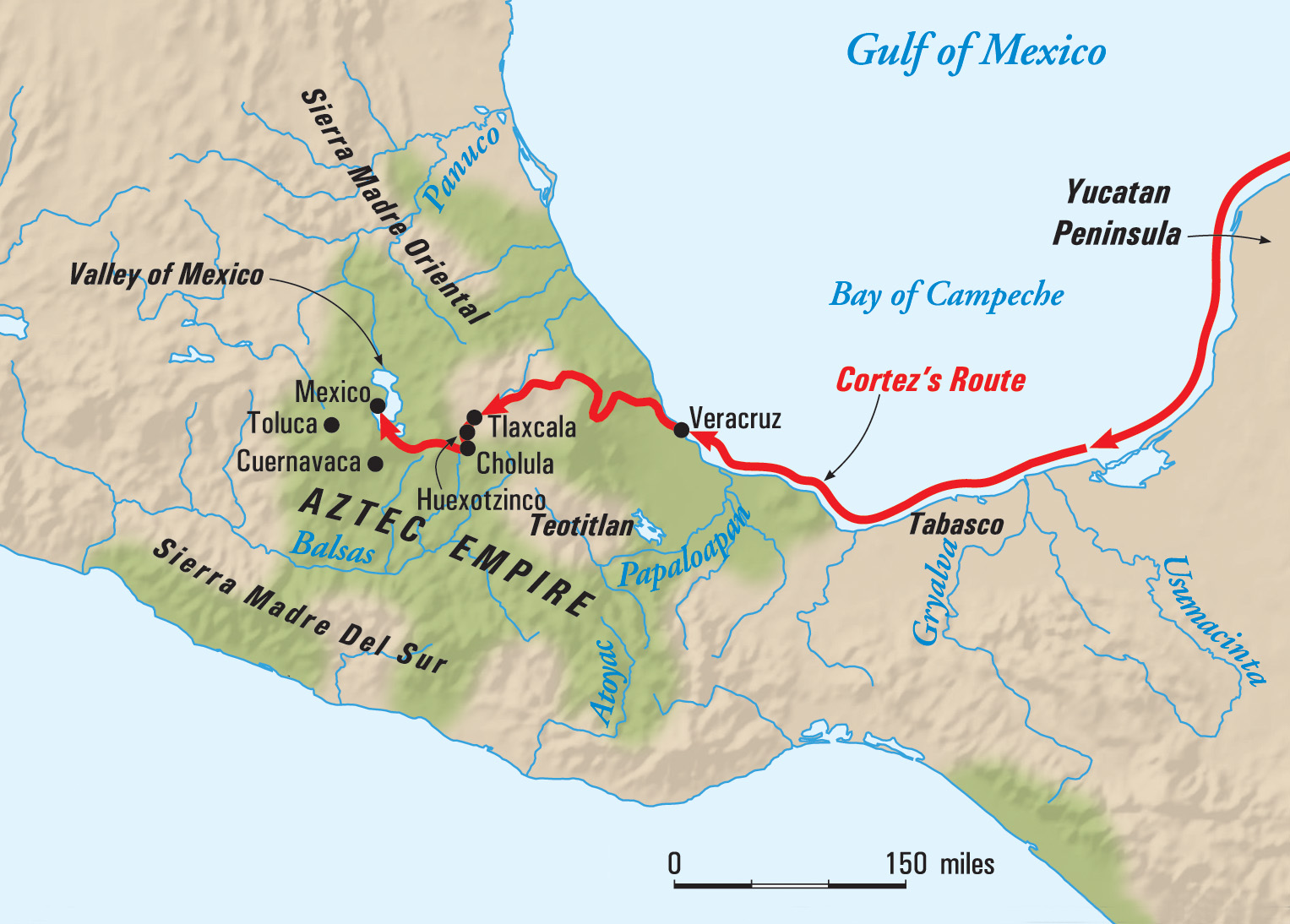
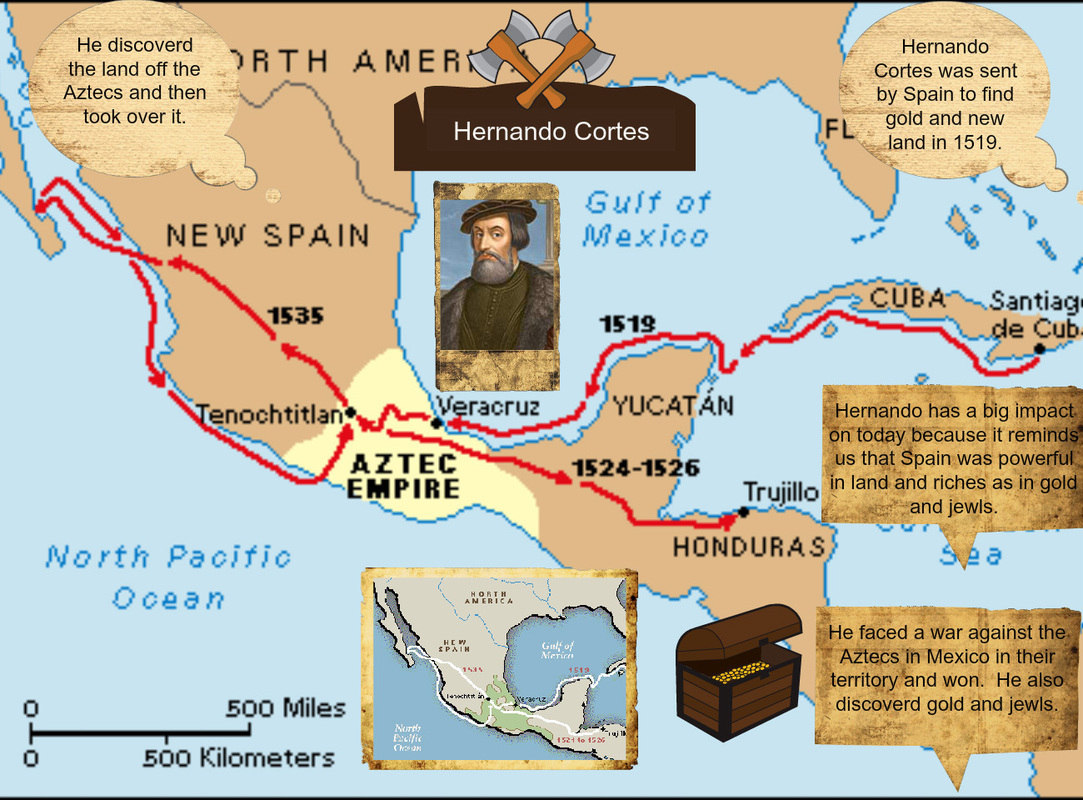
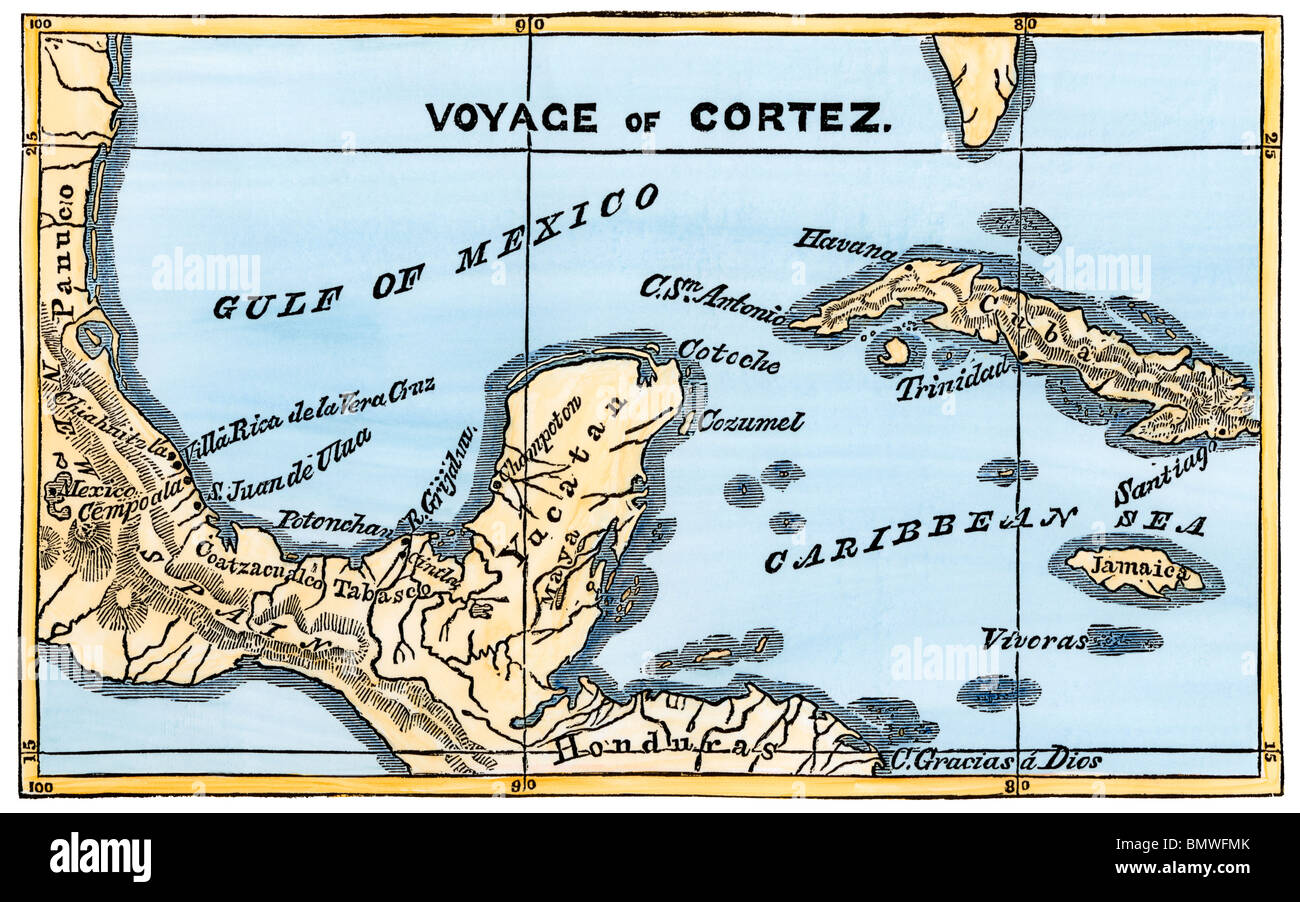
- The "Mapa de Cortés" (Cortés Map): This map, believed to have been created around 1520, is considered one of the most important cartographic documents of the early colonial period. It depicts the route Cortés took from Veracruz to Tenochtitlan, the Aztec capital. This map, meticulously detailed, includes geographical features, settlements, and even the location of battles. Its significance lies in its ability to provide a visual narrative of the conquest, capturing the strategic movements of Cortés’s forces.
- The "Mapa de Teotihuacan" (Teotihuacan Map): This map, believed to have been created in the 16th century, provides a unique glimpse into the ancient city of Teotihuacan. It depicts the layout of the city, including its pyramids, temples, and plazas. This map is particularly valuable because it offers insights into the urban planning and architectural achievements of pre-Columbian civilizations.
- The "Mapa de la Nueva España" (New Spain Map): This map, created in the 16th century, depicts the entire territory of New Spain, which encompassed present-day Mexico and parts of Central America. It provides a comprehensive overview of the region, including its geographical features, settlements, and political boundaries. This map is a testament to the ambition and reach of Spanish exploration and colonization.
Decoding the Language of the Maps
Cortés’s maps were not simply visual representations; they were imbued with a complex language of symbols and conventions. These symbols, often drawn from indigenous iconography, were used to represent various elements, including geographical features, settlements, and even cultural practices. By deciphering these symbols, historians gain a deeper understanding of the interactions between Spanish conquistadors and indigenous populations.
The Enduring Legacy of Exploration
The maps created by Hernán Cortés and his cartographers continue to hold immense historical and cultural significance. They serve as a testament to the ambition, curiosity, and ultimately, the audacity of early European exploration. These maps provide a unique window into the past, offering valuable insights into the complex relationship between Spain and the Americas, and the enduring legacy of conquest.
FAQs
1. What is the significance of Hernán Cortés’s maps?
Cortés’s maps are significant for several reasons:
- Early Mapping of the Americas: They represent the beginning of a systematic mapping of the Americas, providing Europeans with their first detailed glimpse of this new world.
- Military Strategy: They were crucial instruments in Cortés’s campaign of conquest, allowing him to understand the geography of the Aztec Empire and plan strategic maneuvers.
- Cultural Exchange: They reveal the complex interplay between Spanish ambition and indigenous knowledge, showcasing the clash of cultures that defined the early years of Spanish colonization.
2. What types of information do Cortés’s maps contain?
Cortés’s maps contain a wide range of information, including:
- Geographical Features: Mountains, rivers, forests, and other natural features of the landscape.
- Settlements: The location and size of towns, villages, and cities.
- Political Boundaries: The borders between different regions and empires.
- Social and Political Structures: Information about the organization and governance of indigenous societies.
- Military Movements: The routes taken by Cortés’s forces and the locations of battles.
3. How did Cortés’s maps contribute to the Spanish conquest of Mexico?
Cortés’s maps played a crucial role in the Spanish conquest of Mexico:
- Strategic Planning: They provided Cortés with detailed knowledge of the Aztec Empire, enabling him to plan his campaigns and exploit weaknesses in the Aztec defenses.
- Communication: They allowed Cortés to communicate effectively with his forces and coordinate his movements.
- Navigation: They guided Cortés and his troops through unfamiliar territory, helping them to avoid ambushes and navigate complex terrain.
4. What are the challenges in interpreting Cortés’s maps?
Interpreting Cortés’s maps presents several challenges:
- Cultural Differences: The maps were created by Europeans using symbols and conventions that were unfamiliar to indigenous populations.
- Lack of Context: The maps often lack specific details about the social and political context of the regions they depict.
- Bias: The maps may reflect the biases of the Spanish conquistadors, presenting a skewed perspective on the events of the conquest.
5. What is the legacy of Cortés’s maps?
Cortés’s maps have left a lasting legacy:
- Foundation for Future Exploration: They provided a foundation for future exploration and cartographic endeavors, paving the way for a more accurate understanding of the Americas.
- Historical Insights: They offer valuable insights into the early exploration and mapping of Mexico, providing a window into a pivotal period of history.
- Cultural Exchange: They showcase the complex interplay between Spanish ambition and indigenous knowledge, highlighting the impact of the conquest on both cultures.
Tips for Understanding Cortés’s Maps
- Context is Key: It is essential to consider the historical context in which the maps were created. Understanding the motivations of the Spanish conquistadors and the social and political structures of the indigenous populations is crucial for interpreting the maps.
- Decipher the Symbols: The maps use a variety of symbols, many of which are drawn from indigenous iconography. Understanding these symbols is essential for interpreting the information contained in the maps.
- Compare and Contrast: Comparing Cortés’s maps with other cartographic sources from the same period can provide valuable insights into the evolution of cartography and the changing perspectives on the Americas.
- Consider the Bias: It is important to recognize that the maps were created by Europeans with a specific agenda. The maps may reflect biases and prejudices that should be considered when interpreting the information they contain.
Conclusion
Hernán Cortés’s maps, though often overshadowed by his controversial actions, represent a significant contribution to the history of cartography and exploration. They provide a unique glimpse into the early years of Spanish colonization and the complex relationship between European ambition and indigenous knowledge. By studying these maps, we can gain a deeper understanding of the impact of the conquest on the Americas and the enduring legacy of exploration. The maps, meticulously crafted with a blend of European and indigenous influences, offer a fascinating window into the past, reminding us of the intricate tapestry of history and the enduring power of cartography to illuminate our understanding of the world.
![]()

![]()
_during_the_conquest_of_-_(MeisterDrucke-36067).jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enduring Legacy of Hernán Cortés: Unraveling the Maps of Conquest. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!