The Foundation of Geographic Information Systems: Understanding ArcGIS Basemaps
Related Articles: The Foundation of Geographic Information Systems: Understanding ArcGIS Basemaps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Foundation of Geographic Information Systems: Understanding ArcGIS Basemaps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Foundation of Geographic Information Systems: Understanding ArcGIS Basemaps
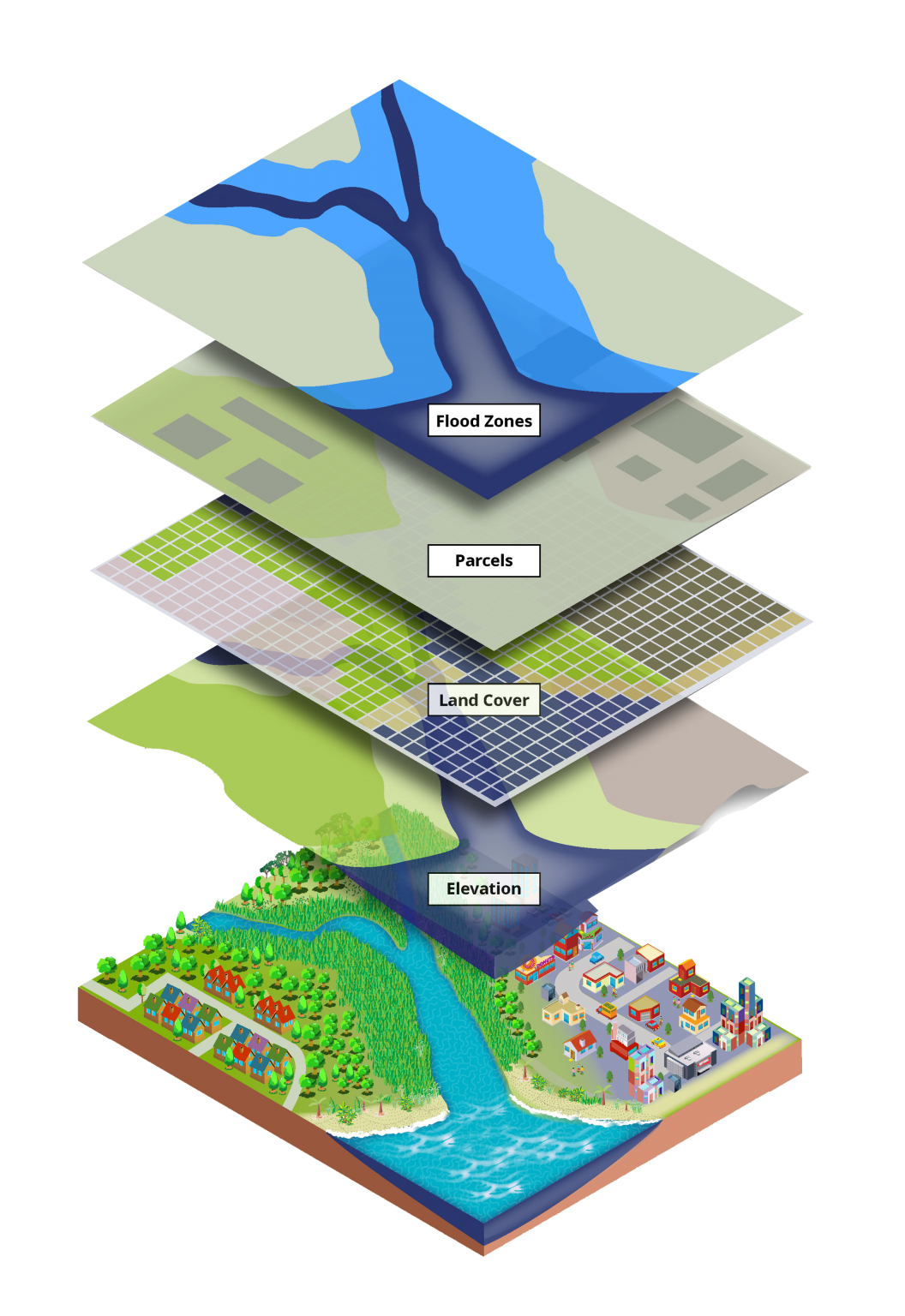
In the realm of geographic information systems (GIS), the concept of a basemap is fundamental. Basemaps serve as the foundational layer, providing a visual context for data visualization and analysis. ArcGIS, a leading GIS platform, offers a diverse array of basemaps, each tailored to specific applications and user needs. This article delves into the intricacies of ArcGIS basemaps, exploring their functionalities, benefits, and applications.
What are ArcGIS Basemaps?
ArcGIS basemaps are pre-constructed maps that serve as the visual foundation for geospatial data. They provide a comprehensive geographical framework, encompassing various elements such as:
- Geographic Features: These include roads, rivers, lakes, land cover, and political boundaries, offering a visual representation of the Earth’s surface.
- Cartographic Styles: Basemaps employ distinct color schemes, symbols, and fonts to enhance readability and visual appeal.
- Reference Information: Basemaps integrate crucial reference data, such as latitude and longitude grids, ensuring accurate spatial orientation.
- Projection Systems: Each basemap adheres to a specific projection system, ensuring consistent data representation across different geographic areas.
The Significance of ArcGIS Basemaps:
ArcGIS basemaps are integral to GIS workflows, offering numerous benefits:
- Visual Context: Basemaps provide a clear visual context for geospatial data, enabling users to understand the spatial relationships between different features and layers.
- Data Exploration: Basemaps facilitate data exploration by providing a visual foundation for analyzing and interpreting spatial patterns.
- Communication and Collaboration: Basemaps enhance communication and collaboration by providing a shared visual language for presenting and discussing geospatial information.
- Time and Resource Efficiency: Pre-built basemaps save significant time and resources by eliminating the need to create maps from scratch.
- Customizability: ArcGIS basemaps offer various customization options, allowing users to tailor them to their specific needs and preferences.
Types of ArcGIS Basemaps:
ArcGIS offers a wide array of basemaps categorized into distinct types:
- World Basemaps: These provide a global perspective, encompassing the entire Earth’s surface. Examples include the "World Topographic Map" and "World Imagery" basemaps.
- Regional Basemaps: These focus on specific geographic regions, offering detailed information about particular areas. Examples include "North America Topographic" and "Europe Street Map" basemaps.
- Specialty Basemaps: These cater to specialized applications, such as "Ocean Basemap" for marine research and "Terrain Basemap" for elevation analysis.
- Custom Basemaps: Users can create custom basemaps by combining different data layers and applying unique styles to meet specific requirements.
Understanding Basemap Properties:
Each ArcGIS basemap possesses specific properties that influence its appearance and functionality:
- Projection: Basemaps employ different projection systems, affecting the way geographic features are displayed on the map.
- Scale: The scale of a basemap determines the level of detail displayed. Larger-scale basemaps provide more detail, while smaller-scale basemaps offer a broader view.
- Data Sources: Basemaps are built using various data sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photographs, and geospatial databases.
- Style: Basemaps utilize distinct cartographic styles, influencing the color schemes, symbols, and fonts used to represent geographic features.
Applications of ArcGIS Basemaps:
ArcGIS basemaps find widespread applications across various fields, including:
- Environmental Monitoring: Basemaps are crucial for visualizing and analyzing environmental data, such as deforestation patterns, air pollution levels, and water quality.
- Urban Planning: Basemaps assist in urban planning by providing a visual framework for understanding city infrastructure, population distribution, and land use patterns.
- Emergency Management: Basemaps facilitate emergency response efforts by providing real-time information on disaster zones, evacuation routes, and resource availability.
- Business Intelligence: Basemaps enable businesses to visualize customer demographics, market trends, and supply chain logistics.
- Education and Research: Basemaps are essential tools for teaching geography, conducting spatial analysis, and exploring various geographic phenomena.
FAQs about ArcGIS Basemaps:
1. How do I choose the right basemap for my project?
The selection of an appropriate basemap depends on the specific project objectives, data type, and intended audience. Consider factors like:
- Scale: Choose a basemap with a scale that matches the level of detail required for your project.
- Projection: Ensure the basemap’s projection aligns with the data you are working with.
- Data Sources: Select a basemap that utilizes data sources relevant to your project.
- Style: Choose a basemap with a style that effectively communicates your data and appeals to your target audience.
2. Can I customize ArcGIS basemaps?
Yes, ArcGIS basemaps are highly customizable. Users can modify various aspects, including:
- Data Layers: Add or remove data layers to tailor the basemap to specific needs.
- Styles: Change the color schemes, symbols, and fonts to create a unique visual appearance.
- Labels: Customize the labels for geographic features to enhance clarity and readability.
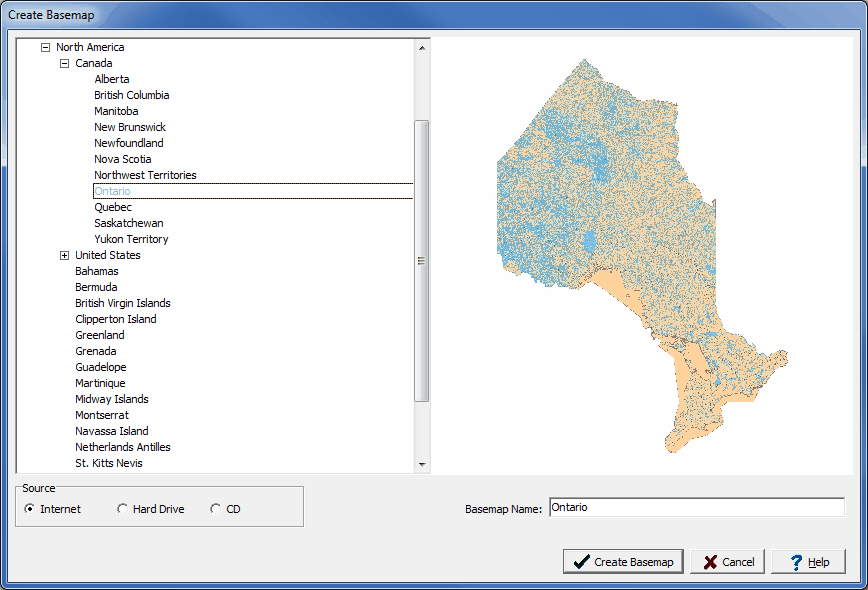
3. How do I access ArcGIS basemaps?
ArcGIS basemaps are readily available within the ArcGIS platform, including:
- ArcGIS Online: A web-based platform offering a vast library of basemaps.
- ArcGIS Pro: A desktop GIS application providing access to a comprehensive suite of basemaps.
- ArcGIS Desktop: A traditional GIS software suite offering a range of basemap options.
4. Are ArcGIS basemaps free to use?
The availability of ArcGIS basemaps depends on the specific licensing model. Some basemaps are free to use, while others require a subscription to ArcGIS Online or ArcGIS Pro.
5. What are the limitations of ArcGIS basemaps?
While ArcGIS basemaps offer numerous benefits, they also have some limitations:
- Data Accuracy: Basemap data may not always be completely accurate, especially for older data sources.
- Data Updates: Basemap data may not be updated regularly, potentially leading to outdated information.
- Customization Limitations: Customizing basemaps within ArcGIS can be complex and may require advanced GIS skills.
Tips for Using ArcGIS Basemaps Effectively:
- Understand the Purpose: Clearly define the project objectives and select a basemap that aligns with the intended purpose.
- Consider Data Type: Choose a basemap that complements the type of data being visualized.
- Explore Customization Options: Utilize customization features to tailor the basemap to specific requirements.
- Evaluate Data Sources: Be aware of the data sources used in the basemap and assess their accuracy and relevance.
- Stay Updated: Regularly check for updates to basemap data and incorporate new information into your projects.
Conclusion:
ArcGIS basemaps are essential components of GIS workflows, providing a visual foundation for data visualization, analysis, and communication. By understanding the various types, properties, and applications of basemaps, users can leverage their capabilities to enhance their geospatial projects. The ability to customize basemaps and access a diverse library of pre-built options empowers users to create insightful and engaging visualizations that effectively convey geographic information. As GIS continues to evolve, ArcGIS basemaps will remain integral tools for unlocking the power of geospatial data and driving informed decision-making.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Foundation of Geographic Information Systems: Understanding ArcGIS Basemaps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
%20Components.PNG)