The Middle Map: Navigating the Complexities of Data Visualization
Related Articles: The Middle Map: Navigating the Complexities of Data Visualization
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Middle Map: Navigating the Complexities of Data Visualization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Middle Map: Navigating the Complexities of Data Visualization
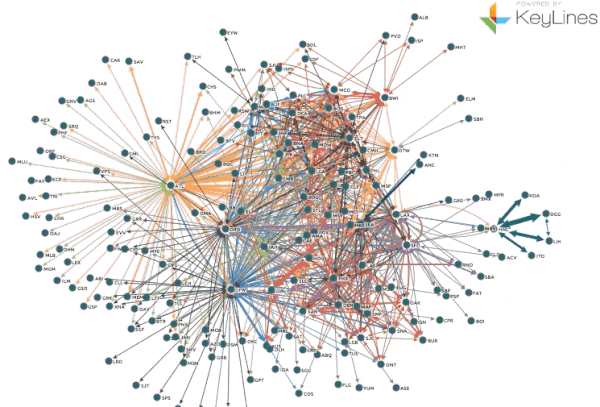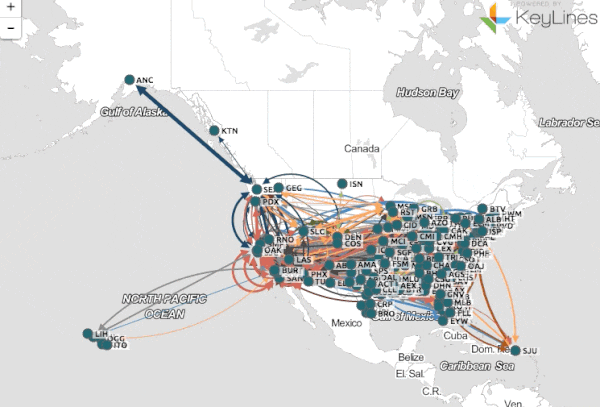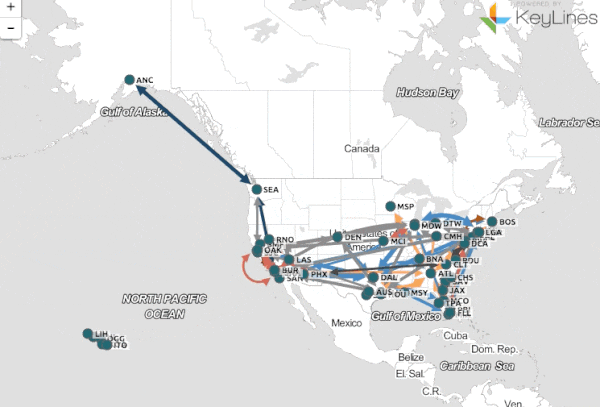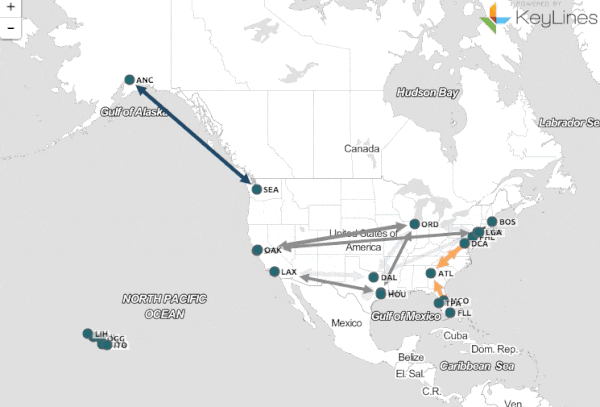
In the modern era, data visualization has become an indispensable tool for understanding complex information. From financial markets to scientific research, the ability to translate raw data into meaningful visual representations is paramount. Yet, within this landscape of data visualization, a specific type of map stands out: the middle map.
Understanding the Middle Map: Beyond the Traditional
The middle map is a unique approach to data visualization, distinct from the traditional map that primarily focuses on geographical locations. It deviates from the conventional by representing abstract concepts, relationships, and connections in a visually compelling manner. These maps are not bound by the constraints of physical space, instead, they explore the intricacies of information itself.
The Essence of Middle Maps: A Bridge Between Abstraction and Understanding
The power of the middle map lies in its ability to bridge the gap between abstract data and human comprehension. By translating complex relationships, patterns, and trends into visual forms, it facilitates a deeper understanding of the underlying information. This process is particularly valuable when dealing with data that is inherently non-spatial, such as:
- Networks and Relationships: Middle maps can effectively illustrate social networks, business relationships, or even the interconnectedness of ideas.
- Flows and Processes: They can visualize complex processes, such as supply chains, information flows, or even the movement of capital.
- Hierarchical Structures: Middle maps are adept at representing hierarchical structures, such as organizational charts, decision trees, or family lineages.
- Data Clusters and Patterns: They can highlight clusters of data points, identify trends, and reveal hidden patterns within datasets.
The Benefits of Middle Maps: A Powerful Tool for Insight and Communication
The use of middle maps offers a myriad of advantages, making them an invaluable tool for various applications:
- Enhanced Comprehension: By transforming abstract data into visual representations, middle maps enable a more intuitive and accessible understanding of complex information.
- Effective Communication: They provide a clear and concise way to communicate complex ideas, making them ideal for presentations, reports, and educational materials.
- Identification of Patterns and Trends: Middle maps facilitate the identification of patterns, trends, and anomalies within data, leading to valuable insights.
- Problem Solving and Decision Making: By visualizing relationships and dependencies, middle maps aid in problem-solving and decision-making processes.
- Innovation and Exploration: The visual nature of middle maps encourages exploration and discovery, fostering creativity and innovation.
Types of Middle Maps: A Diverse Landscape of Visual Representations
The realm of middle maps encompasses a diverse range of visual representations, each tailored to specific data types and communication goals. Some prominent types include:
- Network Maps: These maps depict relationships and connections between entities, often using nodes and edges to represent individuals, organizations, or ideas.
- Tree Maps: They visualize hierarchical structures, using nested rectangles to represent different levels of organization, with size and color representing data values.
- Flow Maps: These maps illustrate the movement of data, resources, or processes, using arrows and lines to depict direction and volume.
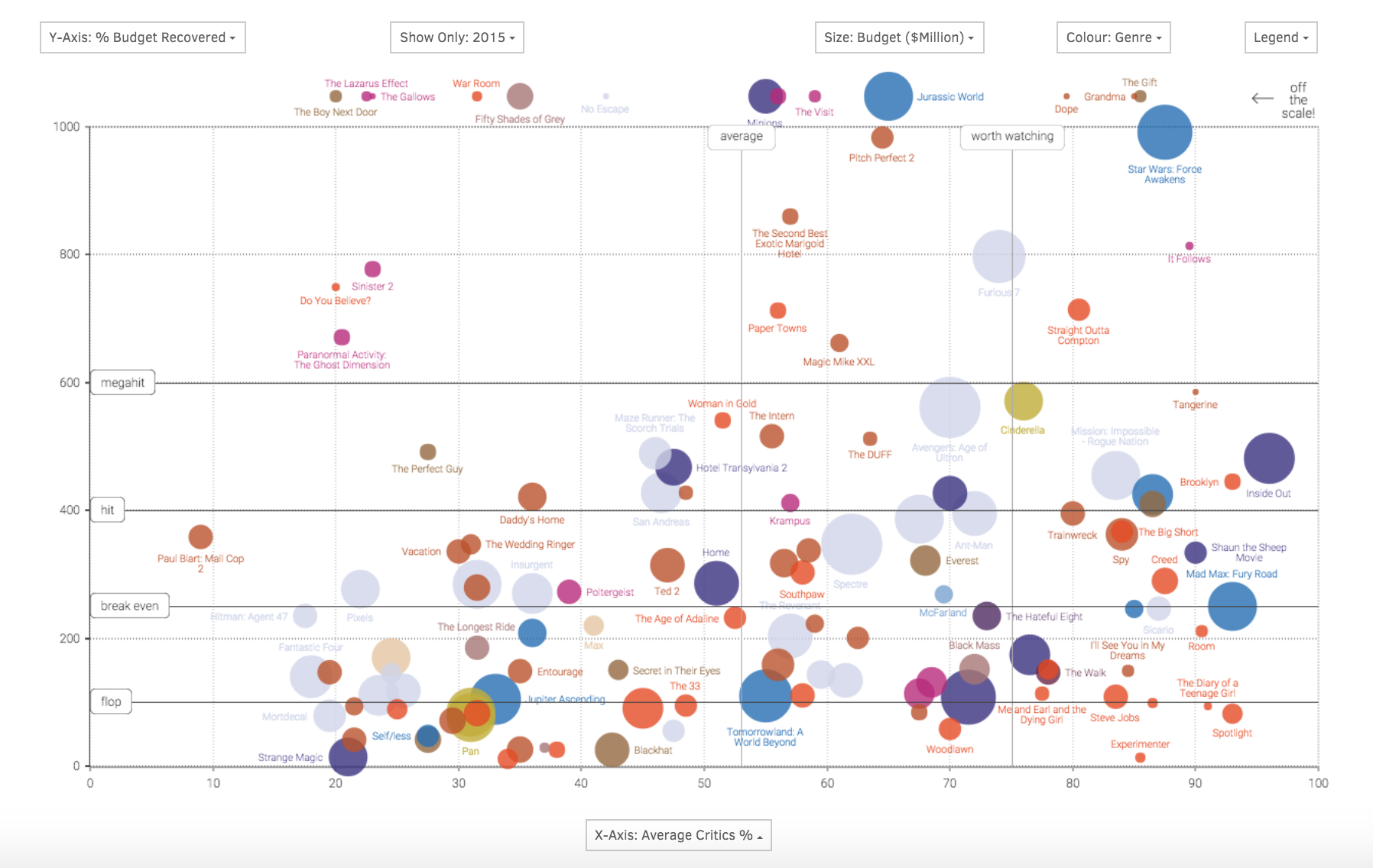
- Scatterplots and Bubble Charts: These maps use points or bubbles to represent data points, with size, color, and position conveying different data values.
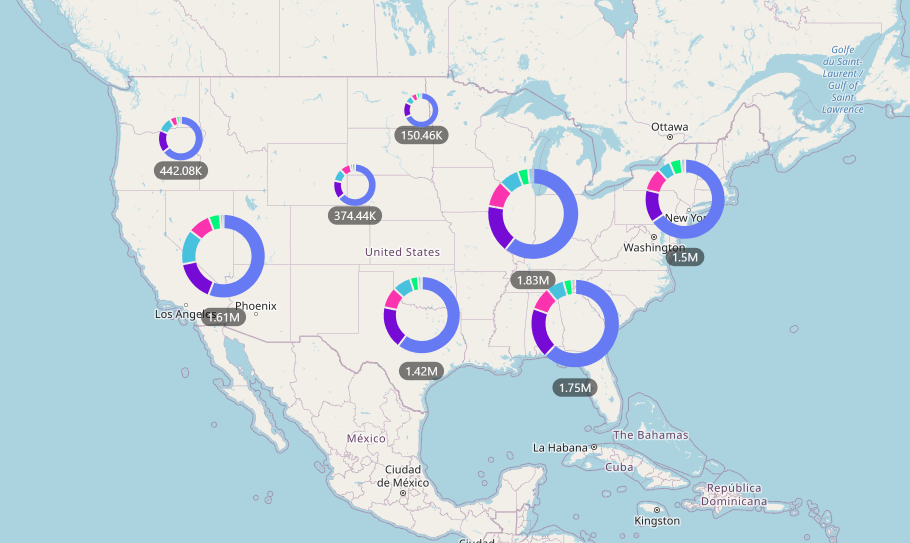
- Heat Maps: They use color gradients to represent data values, highlighting areas of high or low concentration.
FAQs on Middle Maps: Addressing Common Queries
Q: What software can be used to create middle maps?
A: Various software tools are available for creating middle maps, ranging from general-purpose data visualization tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik Sense, to specialized software for specific types of maps, such as Gephi for network maps and Cytoscape for biological networks.
Q: How do I choose the right type of middle map for my data?
A: The choice of map type depends on the nature of the data and the communication goal. Consider the type of relationships you want to represent, the level of detail required, and the target audience.
Q: What are some best practices for designing effective middle maps?
A: Effective middle map design requires clarity, simplicity, and visual coherence. Use clear labels, consistent color schemes, and avoid visual clutter. Consider using interactive features to enhance user engagement and exploration.
Tips for Creating Effective Middle Maps
- Start with a clear goal: Define the purpose of the middle map and the key insights you want to convey.
- Choose the right type of map: Select a map type that best suits the nature of your data and the communication goal.
- Simplify and prioritize: Focus on the most important information and avoid visual clutter.
- Use clear and consistent labels: Ensure that all elements are clearly labeled and use consistent font styles and sizes.
- Employ color effectively: Use a color scheme that enhances readability and highlights key information.
- Consider interactivity: Interactive features can enhance user engagement and exploration.
Conclusion: The Middle Map – A Powerful Tool for Data Exploration and Communication
The middle map represents a powerful and versatile tool for data visualization, offering a unique approach to understanding and communicating complex information. By bridging the gap between abstract data and human comprehension, it empowers users to identify patterns, trends, and insights that might otherwise remain hidden. As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, the middle map will play an increasingly vital role in navigating the information landscape, facilitating informed decision-making and fostering a deeper understanding of the world around us.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Middle Map: Navigating the Complexities of Data Visualization. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!