Turkey: A Bridge Between Continents on the World Map
Related Articles: Turkey: A Bridge Between Continents on the World Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Turkey: A Bridge Between Continents on the World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Turkey: A Bridge Between Continents on the World Map
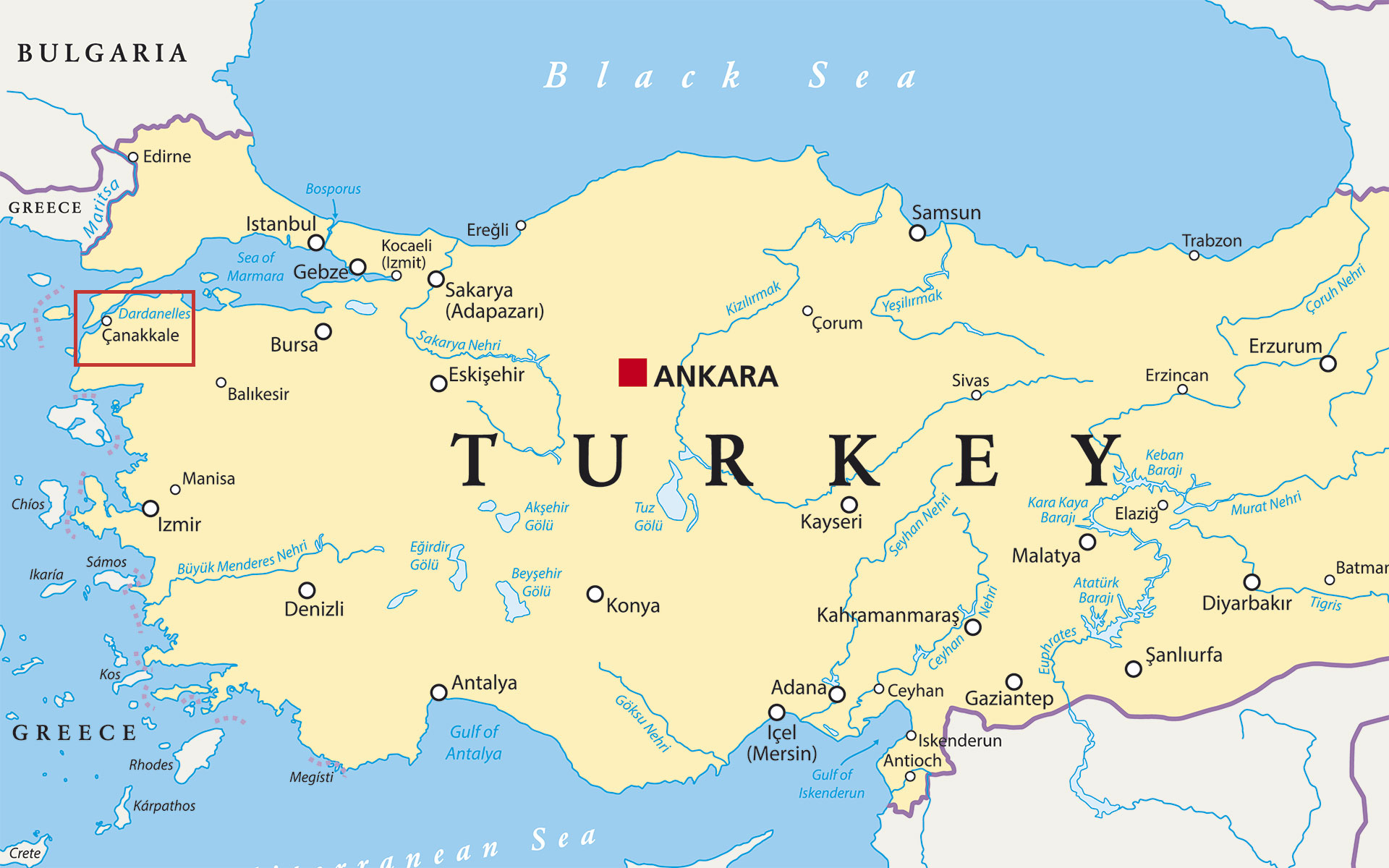
Turkey, a nation with a rich history and diverse geography, occupies a unique position on the world map, straddling the border between Europe and Asia. This strategic location has shaped its cultural identity, economic development, and global significance. Understanding Turkey’s position on the world map provides crucial insight into its history, culture, and its role in the modern world.
Geographical Significance:
Turkey’s geographical position is pivotal. It bridges the continents of Europe and Asia, connecting the Black Sea to the Mediterranean Sea and the Aegean Sea to the Caspian Sea. This strategic location has historically made Turkey a crossroads for trade and cultural exchange.
- Landmass: Turkey occupies a landmass of 783,562 square kilometers, making it the 37th largest country in the world.
- Borders: It shares land borders with eight countries: Greece, Bulgaria, Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Iran, Iraq, and Syria.
- Seas: Turkey has coastlines on the Black Sea, the Aegean Sea, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Sea of Marmara.
- Peninsulas: Turkey encompasses the Anatolian Peninsula (also known as Asia Minor), the Balkan Peninsula, and the Thrace region.
Historical Context:
Turkey’s location has played a crucial role in shaping its history. The country has been a center of civilizations for millennia, with empires such as the Hittites, Romans, Byzantines, and Ottomans leaving their mark on its landscape and culture.
- Ancient Civilizations: The Anatolian Peninsula was home to several ancient civilizations, including the Hittites, Phrygians, and Lydians.
- Roman Empire: Turkey was a vital part of the Roman Empire, with cities like Ephesus, Pergamum, and Antioch flourishing as major centers of trade and culture.
- Byzantine Empire: After the fall of the Roman Empire, the Byzantine Empire emerged, with Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) serving as its capital.
- Ottoman Empire: The Ottoman Empire, which rose to prominence in the 13th century, controlled a vast territory spanning three continents, including significant parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Modern Turkey:
Modern Turkey, founded in 1923, is a republic with a diverse population and a vibrant culture. Its strategic location continues to be a source of both opportunity and challenge.
- Economic Hub: Turkey’s location makes it a natural hub for trade and investment, connecting Europe to Asia and the Middle East.
- Cultural Crossroads: Turkey’s diverse cultural heritage, influenced by its history as a crossroads of civilizations, is evident in its architecture, cuisine, and art.
- Geopolitical Significance: Turkey’s strategic location places it at the center of important geopolitical issues, including regional security, energy resources, and migration.
Understanding Turkey’s Importance:
- Trade and Commerce: Turkey’s strategic location has made it a key player in international trade, serving as a bridge between Europe and Asia.
- Cultural Exchange: Turkey’s diverse cultural heritage, shaped by its history as a crossroads of civilizations, has enriched its art, music, cuisine, and architecture.
- Global Security: Turkey’s location at the intersection of Europe, Asia, and the Middle East makes it a crucial player in global security issues, particularly in relation to terrorism, migration, and energy security.
FAQs about Turkey’s Position on the World Map:
-
Q: What is the significance of Turkey’s location between Europe and Asia?
- A: Turkey’s location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia has made it a vital center for trade, cultural exchange, and geopolitical influence throughout history.
-
Q: Why is Turkey considered a strategic location?
- A: Turkey’s location connects the Black Sea to the Mediterranean Sea and the Aegean Sea to the Caspian Sea, making it a critical route for trade and transportation.
-
Q: What are some of the historical empires that have controlled Turkey?
- A: Turkey has been ruled by various empires throughout history, including the Hittites, Romans, Byzantines, and Ottomans, each leaving a lasting impact on its culture and landscape.
-
Q: What are some of the challenges Turkey faces due to its location?
- A: Turkey’s strategic location also presents challenges, including geopolitical tensions, regional conflicts, and the influx of refugees.
Tips for Understanding Turkey’s Position on the World Map:
- Use a World Map: Refer to a world map to visualize Turkey’s location in relation to other countries and continents.
- Research Historical Maps: Examine historical maps to understand how Turkey’s borders and geopolitical significance have evolved over time.
- Explore Geographical Features: Identify Turkey’s major geographical features, such as the Anatolian Peninsula, the Black Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea, to gain a better understanding of its landscape and resources.
- Study Turkish History: Learn about the major empires and civilizations that have ruled Turkey, as this will provide context for its cultural and political development.
Conclusion:
Turkey’s position on the world map is a testament to its rich history, diverse culture, and strategic importance. Its location as a bridge between continents has made it a crossroads for trade, cultural exchange, and geopolitical influence for millennia. Understanding Turkey’s unique geographical location is crucial for appreciating its role in the global landscape, both historically and in the present day.
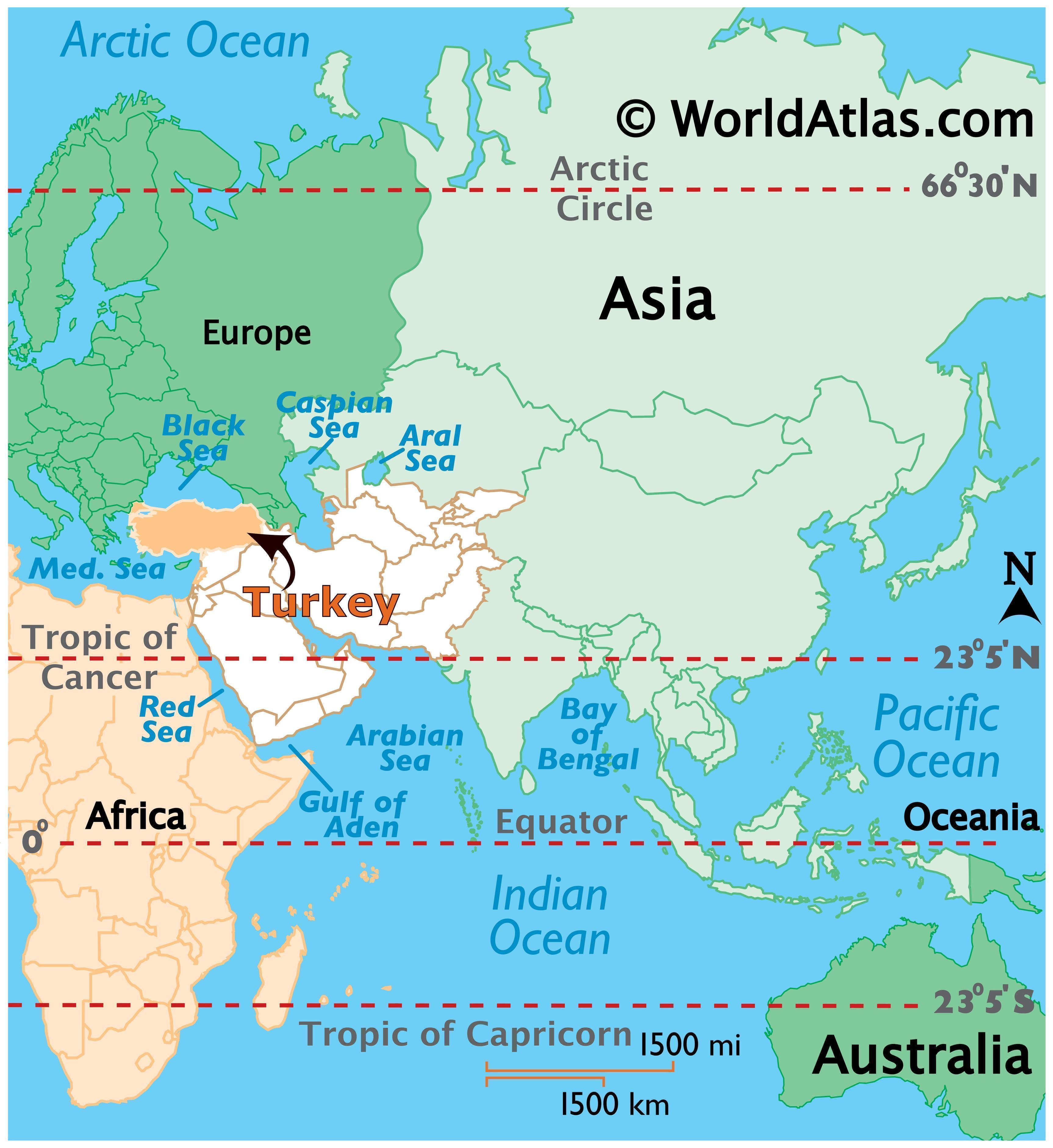
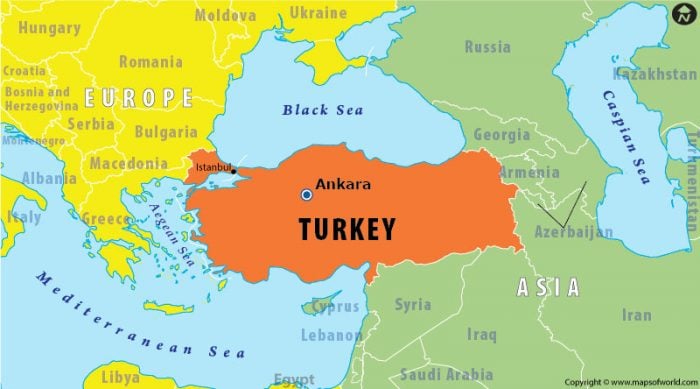





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Turkey: A Bridge Between Continents on the World Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!