Understanding Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Normal Ranges and Their Significance
Related Articles: Understanding Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Normal Ranges and Their Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Normal Ranges and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Normal Ranges and Their Significance
![Understanding Blood Pressure [Ultimate BP by Age Chart] - Vive Health](https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0763/4541/files/general_blood_pressure_ranges-min.png?v=1496246420)
Blood pressure (BP) is a fundamental measure of cardiovascular health, reflecting the force exerted by blood against the walls of arteries as the heart pumps. Maintaining a healthy blood pressure is crucial for overall well-being, as it directly impacts the function of vital organs. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of blood pressure, exploring the concept of normal ranges, their significance, and the factors influencing their variation.
Defining Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is expressed as two numbers, systolic and diastolic, measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
- Systolic pressure represents the peak pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts (beats) and pumps blood.
- Diastolic pressure indicates the pressure in the arteries when the heart relaxes between beats.
For example, a blood pressure reading of 120/80 mmHg indicates a systolic pressure of 120 mmHg and a diastolic pressure of 80 mmHg.
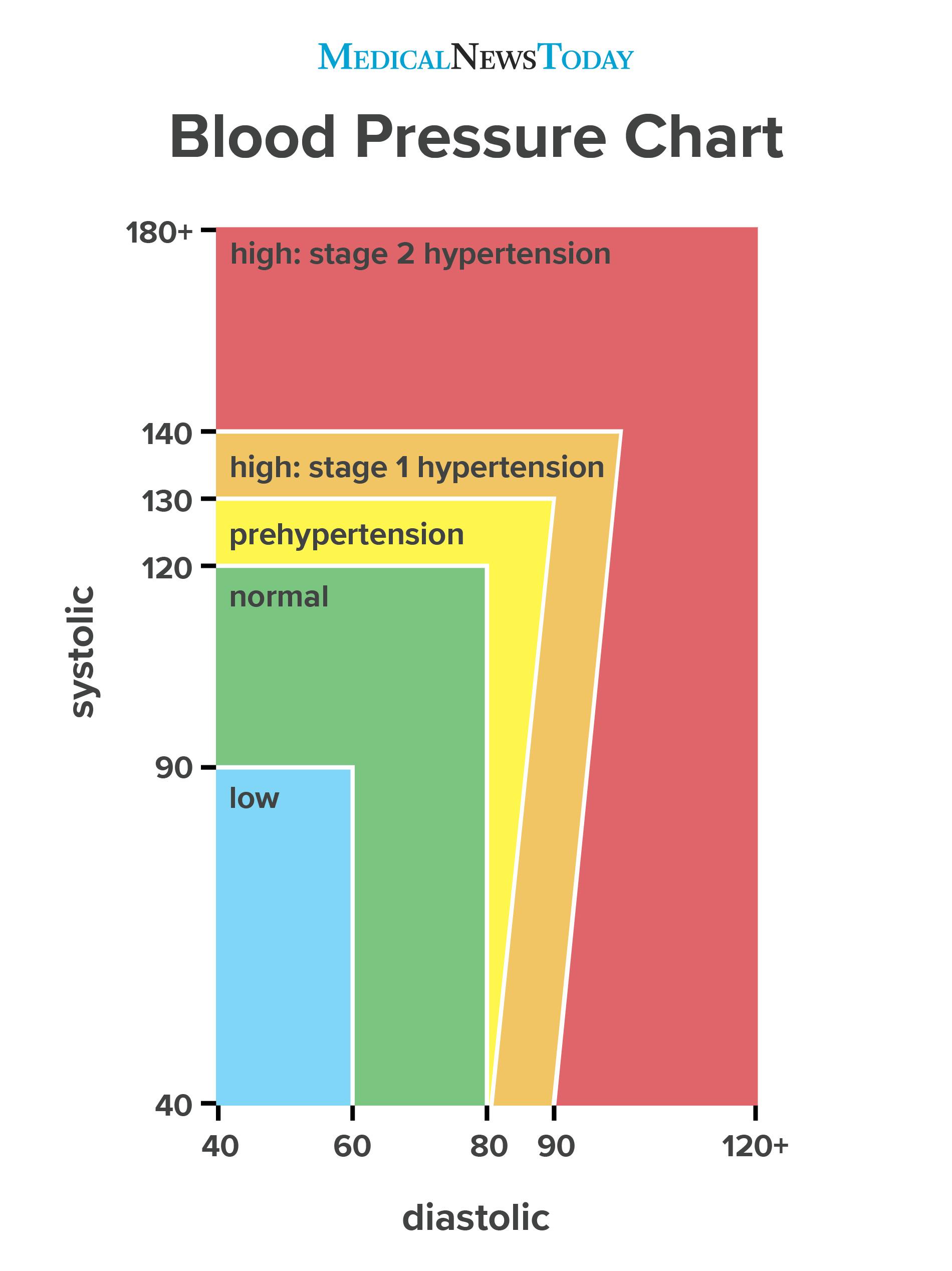
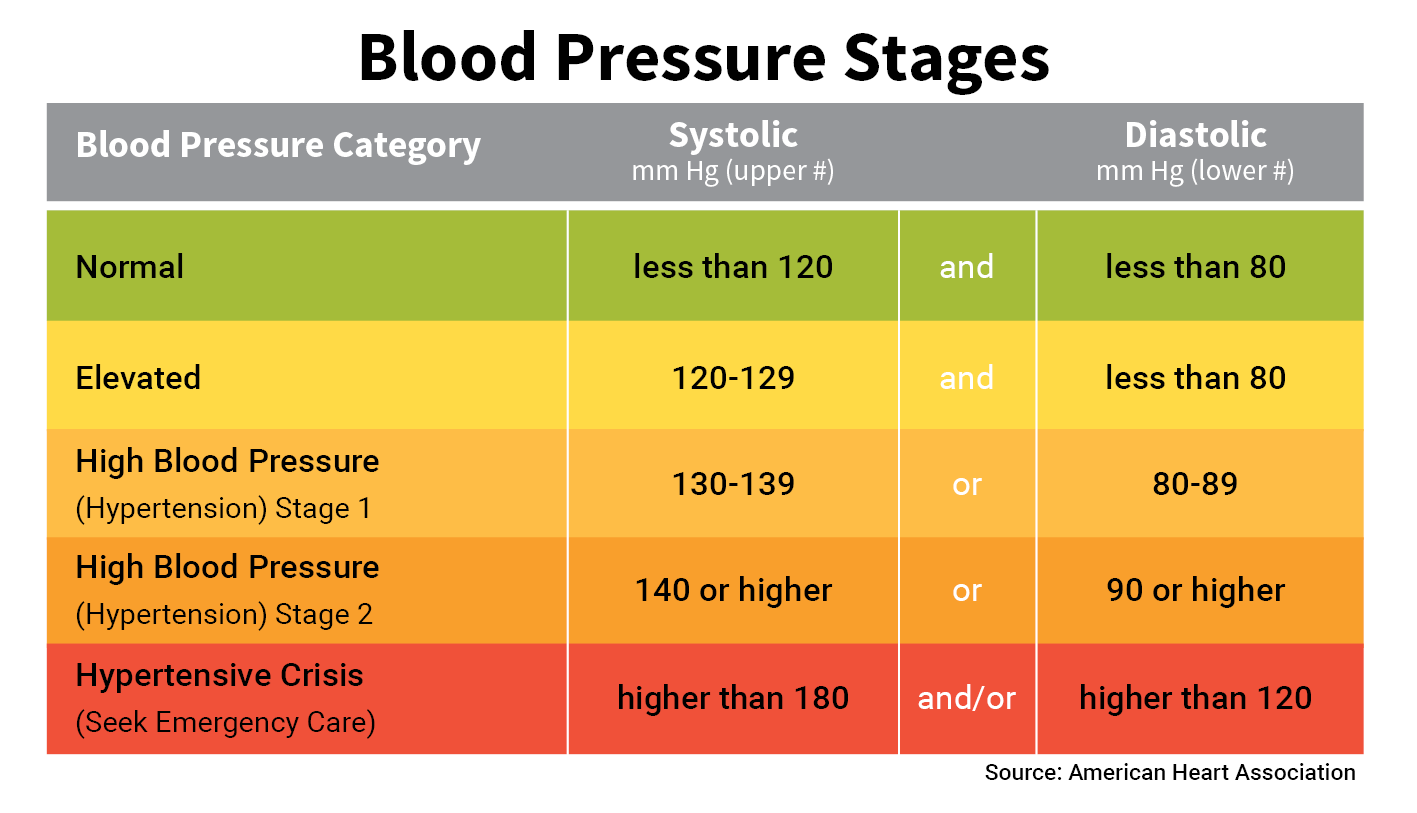
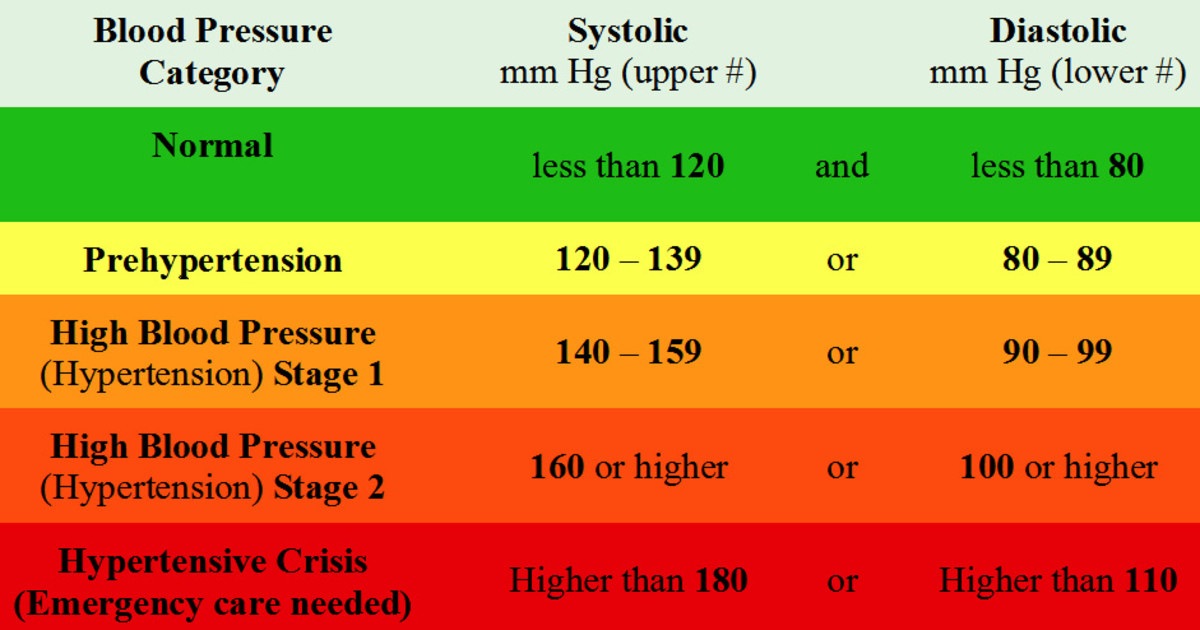
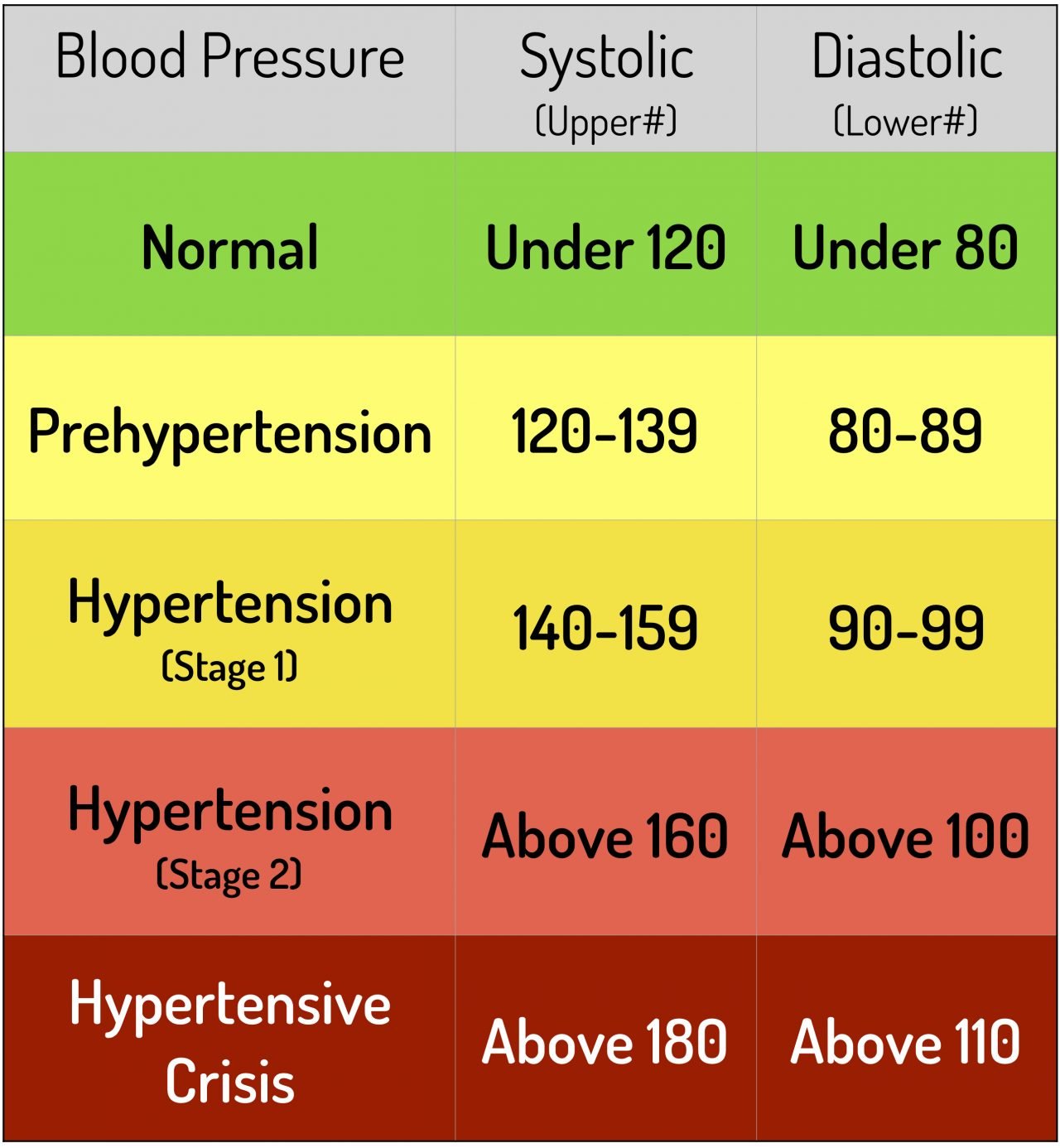
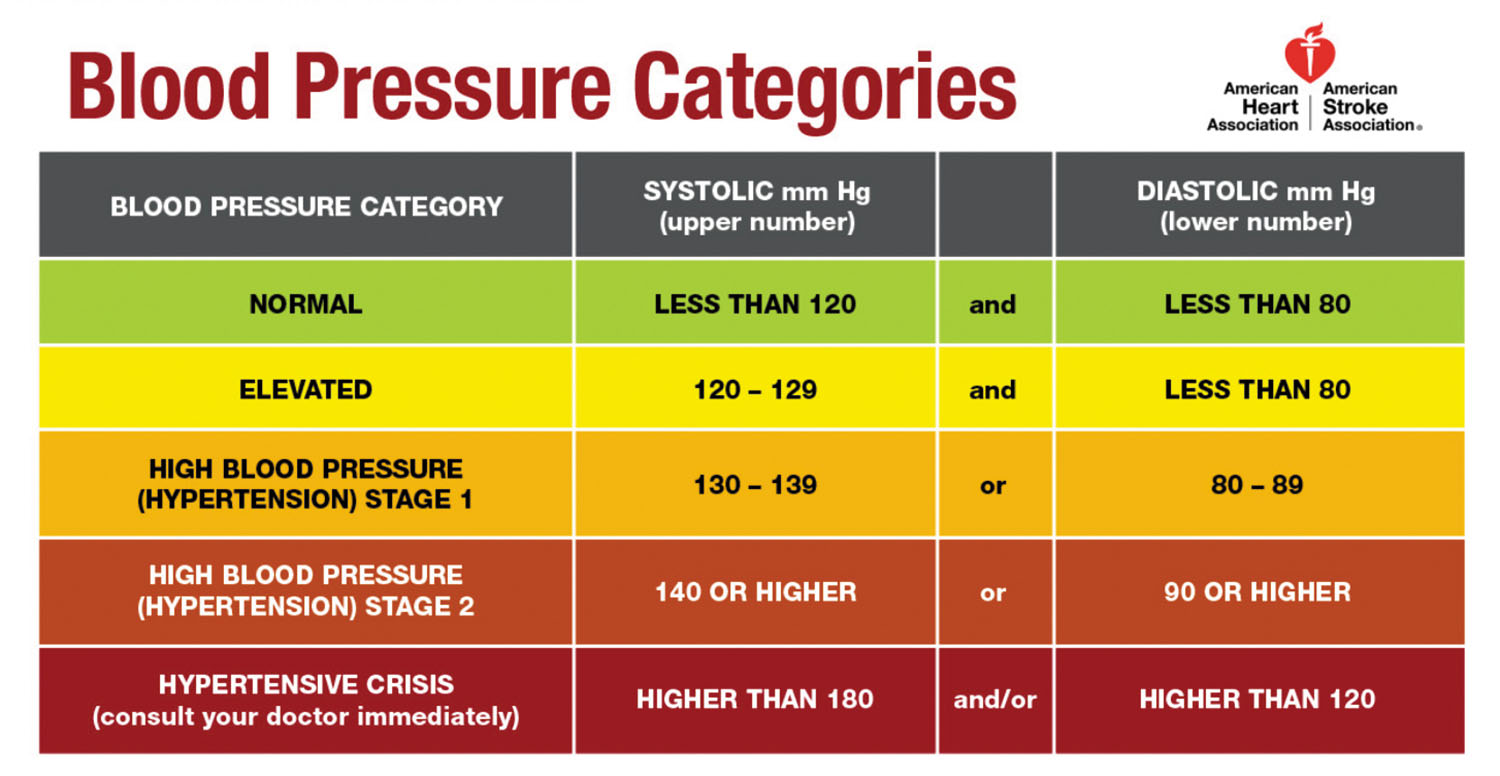
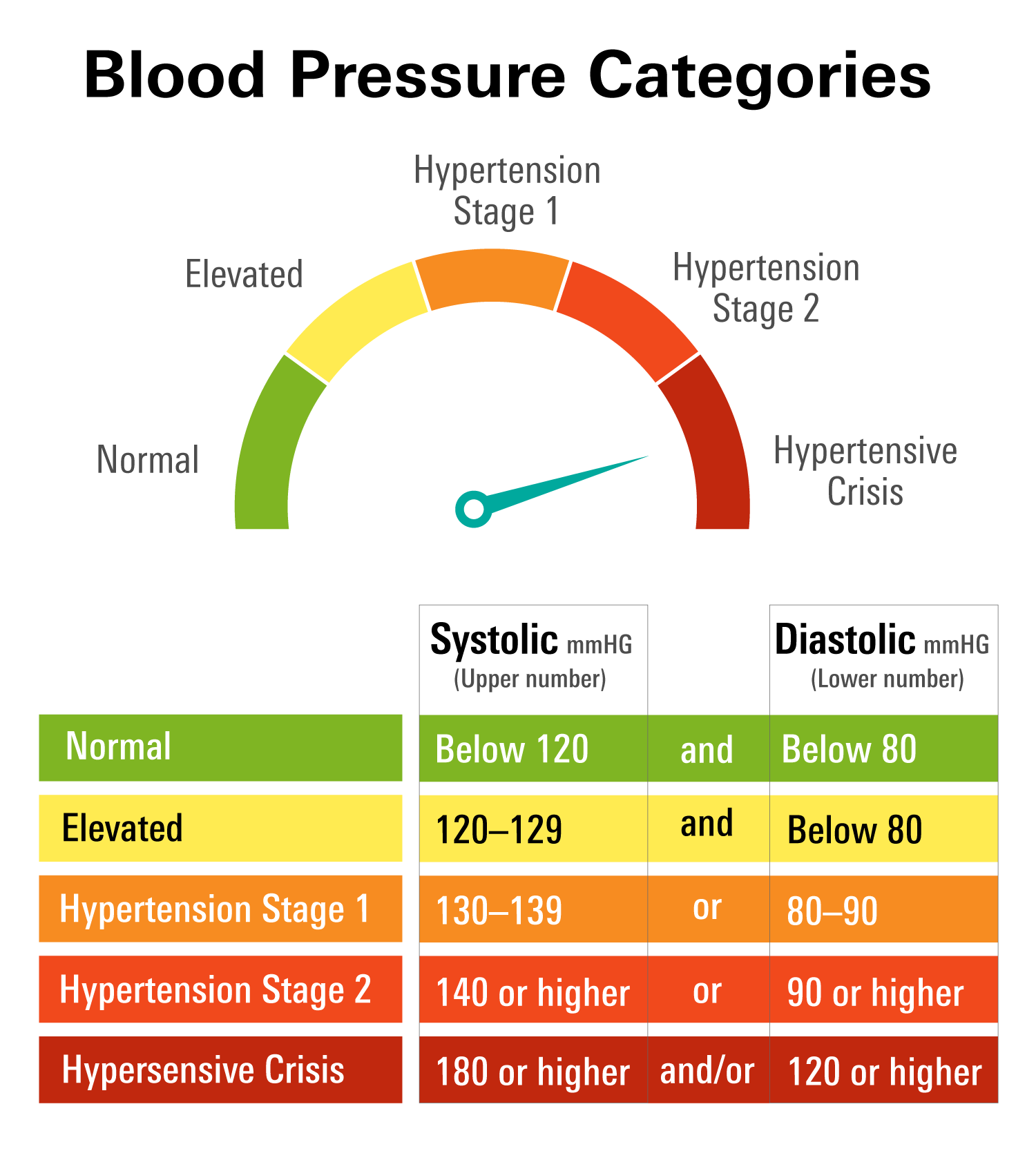
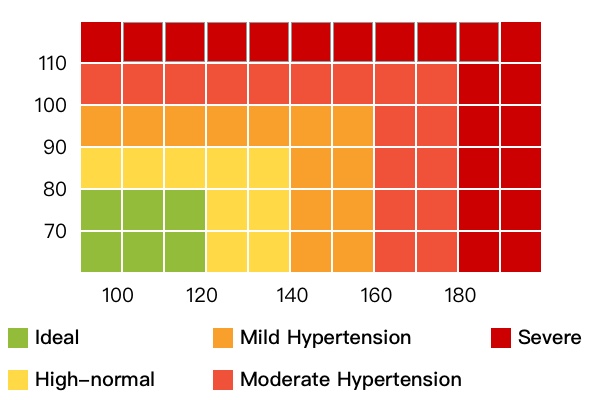
Understanding Normal Blood Pressure Ranges
The concept of "normal" blood pressure is not static, as it can fluctuate based on age, sex, and individual factors. However, a general guideline for healthy adults is:
- Normal blood pressure: Systolic pressure below 120 mmHg and diastolic pressure below 80 mmHg.
- Prehypertension: Systolic pressure between 120-129 mmHg or diastolic pressure between 80-89 mmHg.
- High blood pressure (Hypertension): Systolic pressure 130 mmHg or higher or diastolic pressure 80 mmHg or higher.
It is important to note that these are general guidelines, and individual ranges can vary based on specific health conditions and lifestyle factors.
Factors Influencing Blood Pressure
Several factors contribute to fluctuations in blood pressure, including:
- Age: Blood pressure naturally tends to increase with age due to stiffening of arteries.
- Sex: Men tend to have higher blood pressure than women until menopause, after which women’s blood pressure often surpasses men’s.
- Genetics: Family history of high blood pressure can significantly increase an individual’s risk.
- Diet: A diet high in sodium and saturated fats can contribute to elevated blood pressure.
- Lifestyle: Factors like smoking, lack of physical activity, and excessive alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure.
- Stress: Chronic stress can lead to elevated blood pressure.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as birth control pills and decongestants, can raise blood pressure.
- Underlying medical conditions: Conditions like kidney disease, thyroid problems, and sleep apnea can affect blood pressure.
The Importance of Maintaining Healthy Blood Pressure
Maintaining healthy blood pressure is paramount for overall health and longevity. Uncontrolled high blood pressure, also known as hypertension, can lead to a range of serious health complications, including:
- Heart disease: High blood pressure puts significant strain on the heart, increasing the risk of heart attacks, stroke, and heart failure.
- Stroke: High blood pressure weakens blood vessels, making them more susceptible to rupture, leading to stroke.
- Kidney disease: High blood pressure damages the delicate blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to kidney failure.
- Eye problems: High blood pressure can damage blood vessels in the eyes, causing vision loss and blindness.
- Aneurysm: High blood pressure weakens blood vessel walls, increasing the risk of aneurysms, which are bulges in the blood vessels that can rupture.
Monitoring Blood Pressure: A Crucial Step Towards Health
Regular blood pressure monitoring is essential for managing and preventing health complications. Home blood pressure monitors provide a convenient and cost-effective way to track blood pressure readings.
- Regular monitoring: Aim to check your blood pressure at least once a day, preferably at the same time each day.
- Keeping a log: Record your readings in a logbook or use a blood pressure monitoring app to track trends and identify potential issues.
- Seeking professional advice: If you notice significant fluctuations or consistently elevated blood pressure, consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
Lifestyle Modifications for Healthy Blood Pressure
Implementing lifestyle modifications can significantly contribute to maintaining healthy blood pressure. These include:
- Diet: Adopt a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Limit saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium intake.
- Physical activity: Engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Weight management: Maintain a healthy weight or lose weight if overweight or obese.
- Stress management: Practice stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Smoking cessation: Quit smoking to improve cardiovascular health and reduce blood pressure.
- Alcohol moderation: Limit alcohol consumption to recommended guidelines.
FAQs about Blood Pressure
1. What is considered high blood pressure in pregnancy?
Blood pressure guidelines for pregnant women differ from those for non-pregnant individuals. A systolic pressure of 140 mmHg or higher or a diastolic pressure of 90 mmHg or higher is considered high during pregnancy.
2. Can blood pressure fluctuate throughout the day?
Yes, blood pressure naturally fluctuates throughout the day, often increasing during periods of stress or physical activity.
3. What are the symptoms of high blood pressure?
High blood pressure often has no noticeable symptoms in the early stages. However, as it progresses, it can lead to headaches, fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, and nosebleeds.
4. What medications are used to treat high blood pressure?
Various medications are available to treat high blood pressure, including diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, and angiotensin II receptor blockers. The specific medication prescribed will depend on individual factors and health conditions.
5. Can high blood pressure be cured?
High blood pressure cannot be cured, but it can be effectively managed through lifestyle modifications, medication, or a combination of both.
6. What are the long-term effects of high blood pressure?
Uncontrolled high blood pressure can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, eye problems, and aneurysm.
7. How often should I get my blood pressure checked?
It is recommended to have your blood pressure checked at least once a year. If you have high blood pressure or other risk factors, your healthcare provider may recommend more frequent monitoring.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Blood Pressure
- Regular checkups: Schedule regular visits with your healthcare provider for blood pressure monitoring and overall health assessments.
- Know your numbers: Understand your blood pressure readings and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
- Follow a healthy diet: Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein while limiting saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
- Stay active: Engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Manage stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Quit smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease.
- Moderate alcohol consumption: Limit alcohol intake to recommended guidelines.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy blood pressure is essential for overall health and well-being. Understanding normal blood pressure ranges, identifying factors influencing blood pressure, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits are crucial steps towards preventing and managing high blood pressure. Regular monitoring, prompt medical attention, and adherence to prescribed treatment plans are paramount for managing hypertension and minimizing its potential complications. By taking proactive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing high blood pressure and its associated health issues, paving the way for a healthier and more fulfilling life.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Normal Ranges and Their Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!