Understanding the Significance of Frost-Free Zones in Florida: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Significance of Frost-Free Zones in Florida: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Significance of Frost-Free Zones in Florida: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Significance of Frost-Free Zones in Florida: A Comprehensive Guide
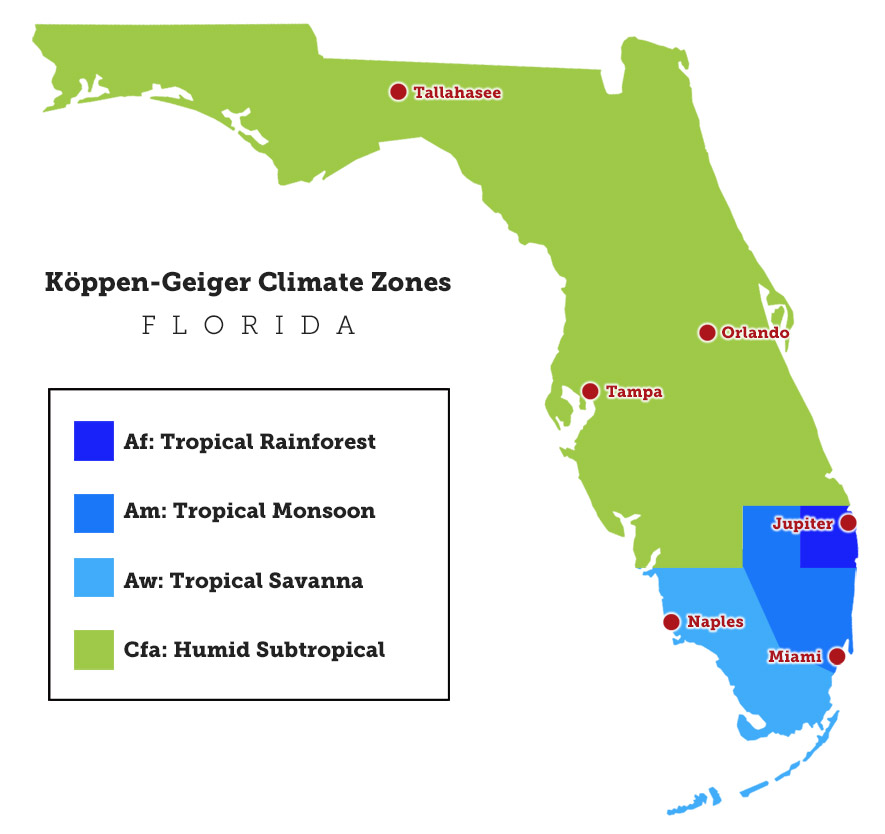
Florida, known for its subtropical climate, offers a unique advantage for agriculture and horticulture: a generally frost-free environment. While the state does experience occasional cold snaps, the vast majority of Florida remains unaffected by frost, making it an ideal location for a diverse array of crops and plants. However, understanding the nuances of frost-free zones within Florida is crucial for successful agricultural practices and informed land use decisions.
Delving into the Concept of Frost-Free Zones:
Frost, a phenomenon occurring when temperatures drop below freezing, can cause significant damage to sensitive plants and crops. Frost-free zones are geographical areas characterized by a minimal risk of frost during a specific period. This period typically corresponds to the growing season, when plants are most vulnerable to frost damage.
Florida’s Frost-Free Zones: A Detailed Exploration:
Florida’s unique geography and climate create a diverse array of frost-free zones. The southernmost regions, including the Florida Keys and the southern tip of the peninsula, experience a near-tropical climate with minimal risk of frost throughout the year. Moving north, the state gradually transitions into a subtropical climate, with varying degrees of frost risk.
Factors Influencing Frost-Free Zones in Florida:
Several factors contribute to the variation in frost-free zones across Florida:
- Latitude: The further south a location is, the lower the risk of frost.
- Elevation: Higher elevations are more susceptible to frost due to colder temperatures at greater altitudes.
- Proximity to Water Bodies: Large bodies of water, like the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico, moderate temperatures and reduce frost risk.
- Microclimates: Local topographical features, such as valleys and hills, can create localized microclimates that influence frost patterns.
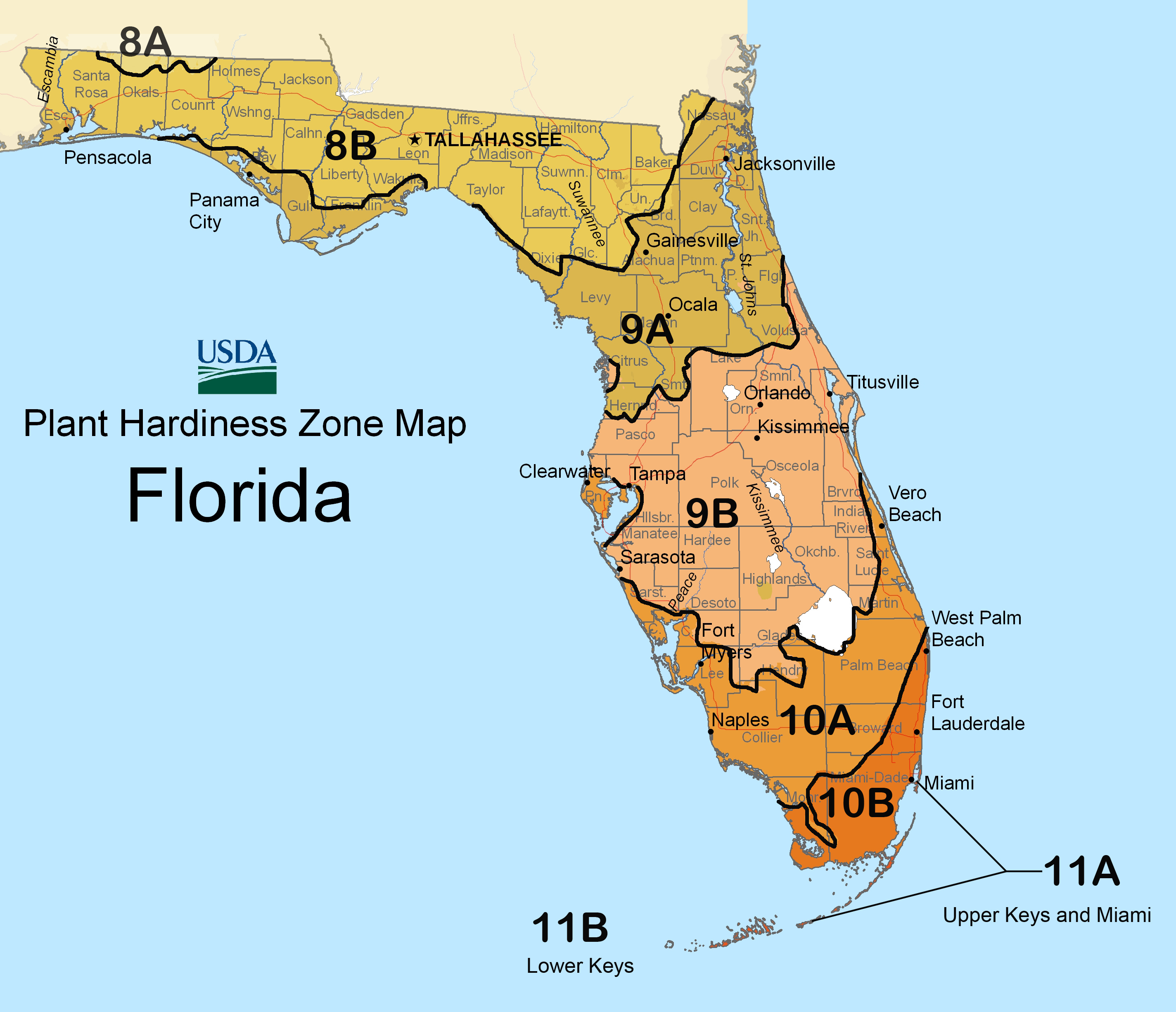
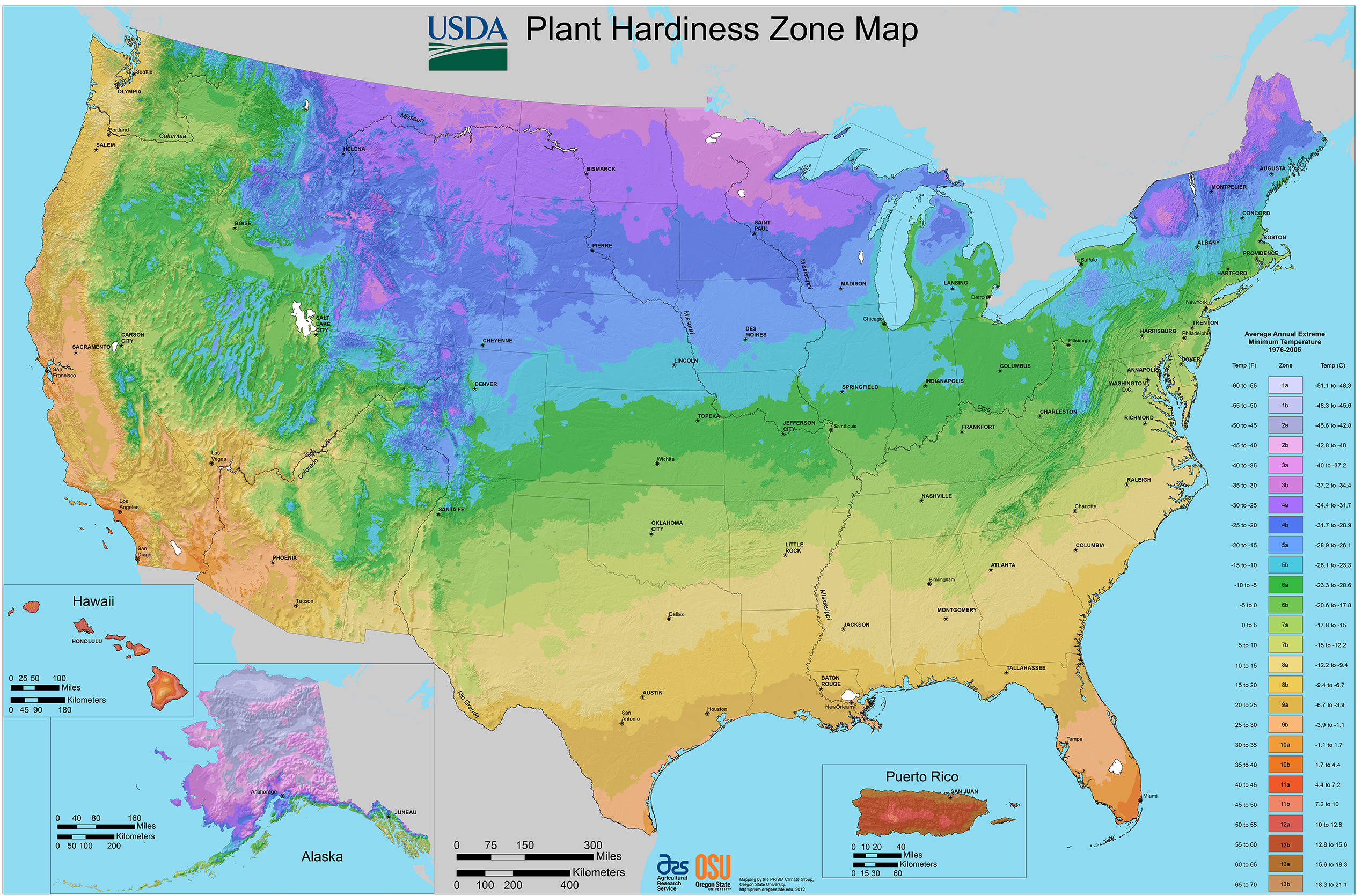
Understanding the Frost-Free Map of Florida:
The Frost-Free Map of Florida provides a visual representation of the expected number of frost-free days in different regions of the state. This map is an invaluable tool for:
- Farmers and Agriculturalists: Determining suitable crops and planting schedules based on frost risk.
- Horticulturists and Gardeners: Selecting appropriate plant species and planning planting times to minimize frost damage.
- Land Developers and Planners: Making informed decisions regarding land use and development projects, considering potential frost risks.
Benefits of Utilizing a Frost-Free Map:
- Optimized Crop Production: By understanding the frost-free period, farmers can strategically plan their planting and harvesting schedules, maximizing crop yields and minimizing losses due to frost damage.
- Enhanced Horticultural Success: Gardeners can choose plants that thrive in specific frost-free zones, ensuring their plants flourish and thrive without experiencing frost damage.
- Informed Land Use Decisions: Developers and planners can utilize the frost-free map to identify areas suitable for various land uses, considering factors like agricultural suitability and potential frost risks.
Exploring the Frost-Free Map of Florida: A Deeper Dive
The Frost-Free Map of Florida is typically divided into zones, each representing a specific range of frost-free days. For instance, Zone 1 might encompass areas with over 300 frost-free days, while Zone 8 might indicate regions with less than 100 frost-free days.
Key Considerations When Using the Frost-Free Map:
- Historical Data: The Frost-Free Map is based on historical data, and occasional variations in weather patterns can occur.
- Microclimates: Local factors can influence frost patterns, so it’s essential to consider microclimates within a specific zone.
- Specific Plant Needs: The map provides general guidance, but individual plant species have unique frost tolerance levels.
FAQs Regarding Frost-Free Zones in Florida:
Q: What is the difference between a frost-free zone and a hardiness zone?
A: Frost-free zones indicate the number of days without frost, while hardiness zones define the minimum winter temperature a plant can tolerate. While related, they address different aspects of climate.
Q: How can I find the frost-free zone for my specific location in Florida?
A: Various resources, including online maps, agricultural extension services, and local nurseries, can provide information about frost-free zones for specific locations in Florida.
Q: What are some tips for protecting plants from frost in Florida?
A: Several strategies can help protect plants from frost, including:
- Mulching: Applying a layer of mulch around plants can insulate the soil and protect roots from frost.
- Covering Plants: Using blankets or sheets to cover plants can create a microclimate that reduces frost damage.
- Watering Plants: Deeply watering plants before a potential frost event can help protect them from freezing temperatures.
Conclusion:
The Frost-Free Map of Florida is a valuable tool for understanding the unique climate of the state and making informed decisions related to agriculture, horticulture, and land use. By considering the frost-free zones, individuals and organizations can optimize their activities, minimizing potential damage and maximizing success. As Florida continues to grow and evolve, understanding the nuances of frost-free zones will remain essential for sustainable development and thriving ecosystems.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Significance of Frost-Free Zones in Florida: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!