Unlocking Efficiency and Clarity: A Comprehensive Guide to Process Mapping
Related Articles: Unlocking Efficiency and Clarity: A Comprehensive Guide to Process Mapping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking Efficiency and Clarity: A Comprehensive Guide to Process Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking Efficiency and Clarity: A Comprehensive Guide to Process Mapping
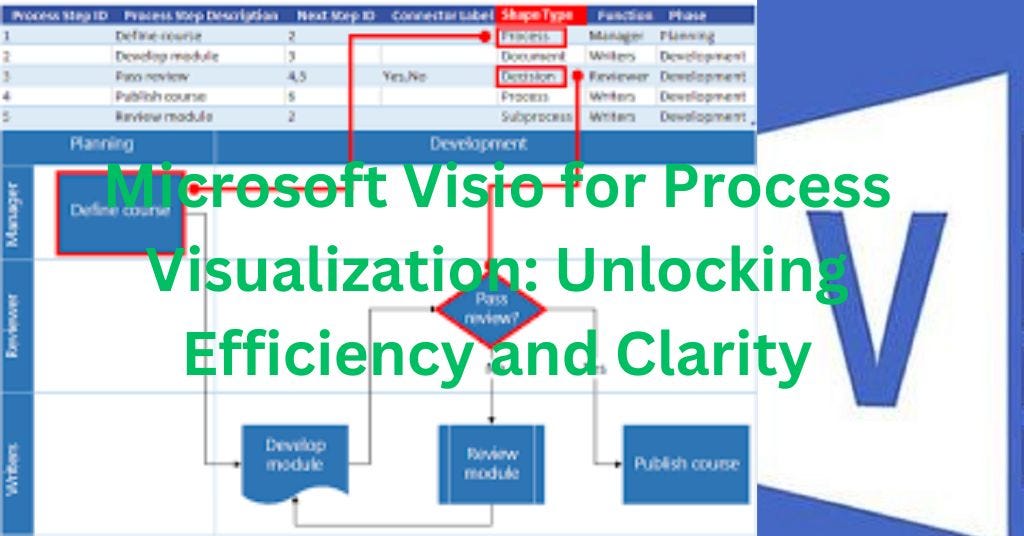
In the intricate tapestry of modern organizations, processes are the threads that bind operations, ensuring seamless execution and achieving desired outcomes. Yet, these processes can often become complex, prone to inefficiencies, and lacking in clarity. This is where process mapping emerges as a potent tool, offering a visual representation of workflows, illuminating hidden inefficiencies, and fostering a shared understanding of how work gets done.
Understanding the Essence of Process Mapping
Process mapping is a visual technique used to document and analyze the steps involved in a specific process. It involves breaking down a complex process into smaller, manageable components, depicting them graphically in a sequential order. This visual representation provides a clear and concise understanding of the process flow, identifying key activities, decision points, and potential areas for improvement.
The Importance of Process Mapping
Process mapping is not merely a documentation exercise; it serves as a powerful tool for driving organizational effectiveness and achieving strategic objectives. Its significance lies in its ability to:
- Enhance Understanding and Communication: Process maps provide a common language for all stakeholders, fostering shared understanding and reducing ambiguity. They allow for clear communication of how work gets done, eliminating misunderstandings and promoting collaboration.
- Identify Bottlenecks and Inefficiencies: Visualizing the process flow allows for the identification of redundant steps, delays, and areas where resources are wasted. This facilitates the elimination of unnecessary activities and optimization of workflows.
- Improve Efficiency and Productivity: By streamlining processes and eliminating bottlenecks, process mapping contributes to increased efficiency and productivity. This translates into reduced costs, faster turnaround times, and improved customer satisfaction.
- Promote Standardization and Consistency: Process maps serve as a blueprint for standardized procedures, ensuring consistency and predictability in execution. This minimizes errors, reduces rework, and enhances quality control.
- Facilitate Continuous Improvement: Process maps provide a framework for ongoing analysis and improvement. By regularly reviewing and updating maps, organizations can identify areas for optimization and ensure processes remain aligned with evolving business needs.
Types of Process Maps
Process maps come in various forms, each suited for specific purposes and levels of detail. Some common types include:
- Swimlane Diagrams: These maps depict the process flow across different departments or functional areas, highlighting responsibilities and handoffs.
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts: These maps illustrate the interactions and dependencies between different teams or departments involved in a process.
- Value Stream Maps: These maps focus on the entire value chain, identifying all activities that add value to the customer and eliminating waste.
- SIPOC Diagrams: These maps define the Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers involved in a specific process.
Steps to Create a Process Map
Creating a process map involves a systematic approach, ensuring comprehensive documentation and accurate representation of the process flow. The steps involved include:
- Define the Scope and Objectives: Clearly define the process to be mapped, its boundaries, and the specific objectives to be achieved. This ensures focus and clarity throughout the mapping process.
- Gather Information: Collect data from various sources, including interviews with process participants, documentation, and observation. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the process and its nuances.
- Identify the Key Activities: Break down the process into its constituent activities, ensuring each step is clearly defined and documented.
- Determine the Sequence of Activities: Establish the logical order in which activities are performed, depicting the flow of work from start to finish.
- Identify Decision Points and Loops: Identify any branching points in the process where decisions are made or loops occur, representing alternative paths or iterations.
- Develop the Visual Representation: Using appropriate symbols and notations, create a visual representation of the process flow, ensuring clarity and ease of understanding.
- Review and Validate: Share the process map with stakeholders for review and validation, ensuring accuracy and alignment with actual practice.
- Document and Communicate: Formalize the process map, ensuring it is accessible to all relevant stakeholders, and communicate the findings and recommendations effectively.
Tips for Effective Process Mapping
- Focus on Value-Adding Activities: Prioritize activities that directly contribute to customer value and eliminate those that are unnecessary or wasteful.
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Ensure that the language used in the map is clear, concise, and easily understood by all stakeholders.
- Employ Standardized Symbols and Notations: Utilize standardized symbols and notations to ensure consistency and promote universal understanding.
- Keep it Simple and Visually Appealing: Aim for a simple and visually appealing map that effectively communicates the process flow without overwhelming viewers.
- Promote Collaboration and Feedback: Encourage collaboration and feedback from stakeholders throughout the mapping process, ensuring accuracy and alignment with actual practice.
FAQs about Process Mapping
1. What are the benefits of process mapping?
Process mapping provides a clear and concise understanding of how work gets done, identifies bottlenecks and inefficiencies, enhances communication, promotes standardization, and facilitates continuous improvement.
2. What are the different types of process maps?
Common types of process maps include swimlane diagrams, cross-functional flowcharts, value stream maps, and SIPOC diagrams, each suited for different purposes and levels of detail.
3. How can I create a process map?
Follow a systematic approach, defining the scope, gathering information, identifying key activities, determining the sequence, identifying decision points, developing the visual representation, reviewing and validating, and documenting and communicating the map.
4. What are some tips for effective process mapping?
Focus on value-adding activities, use clear and concise language, employ standardized symbols, keep it simple and visually appealing, and promote collaboration and feedback.
5. What tools can I use for process mapping?
Various software tools are available for process mapping, including Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, and Draw.io, offering features for collaboration, automation, and analysis.
Conclusion
Process mapping is an indispensable tool for organizations seeking to enhance efficiency, improve communication, and drive continuous improvement. By providing a clear visual representation of workflows, it enables organizations to identify bottlenecks, eliminate waste, and optimize operations. By embracing process mapping, organizations can unlock hidden potential, foster a culture of excellence, and achieve strategic objectives.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking Efficiency and Clarity: A Comprehensive Guide to Process Mapping. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!