Unveiling India’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Climate Map
Related Articles: Unveiling India’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Climate Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling India’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Climate Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling India’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Climate Map

India, a land of diverse landscapes and vibrant cultures, is also home to a wide spectrum of climatic conditions. Understanding the intricacies of India’s climate is crucial for various sectors, from agriculture and water management to disaster preparedness and sustainable development. This article delves into the intricacies of India’s climate map, providing a comprehensive overview of its major climatic zones, influencing factors, and the impact on the country’s socio-economic landscape.
A Mosaic of Climates:
India’s climate map is a testament to the country’s geographic diversity. The interplay of latitude, altitude, distance from the sea, and prevailing wind patterns creates a mosaic of climatic regions, each with its distinct characteristics.
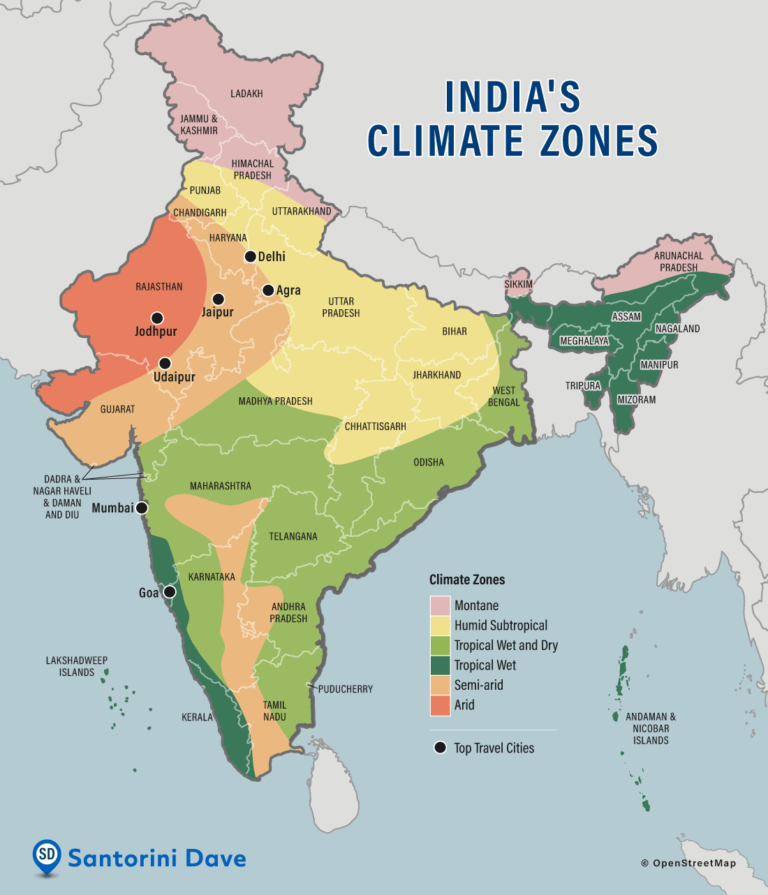
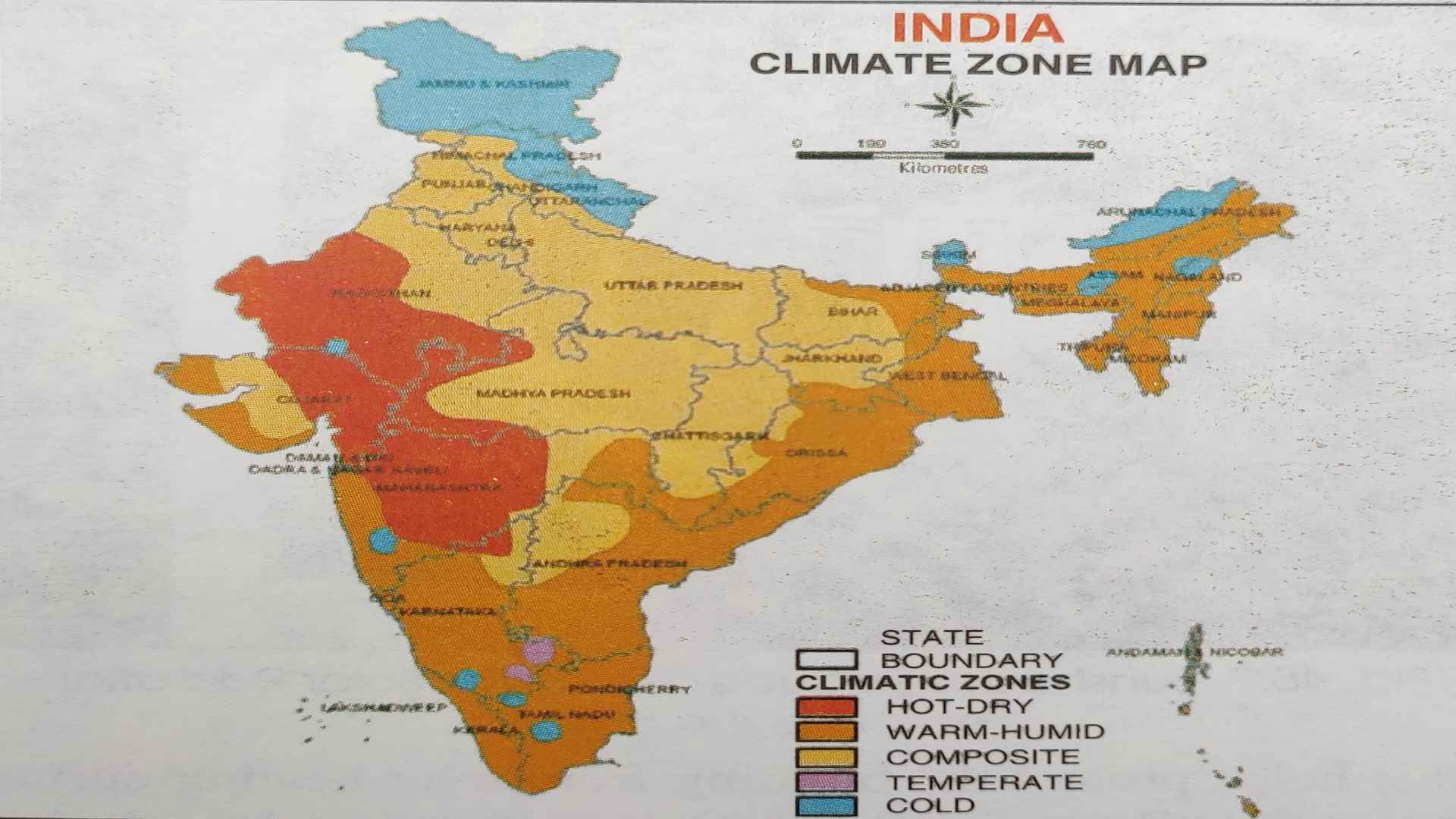
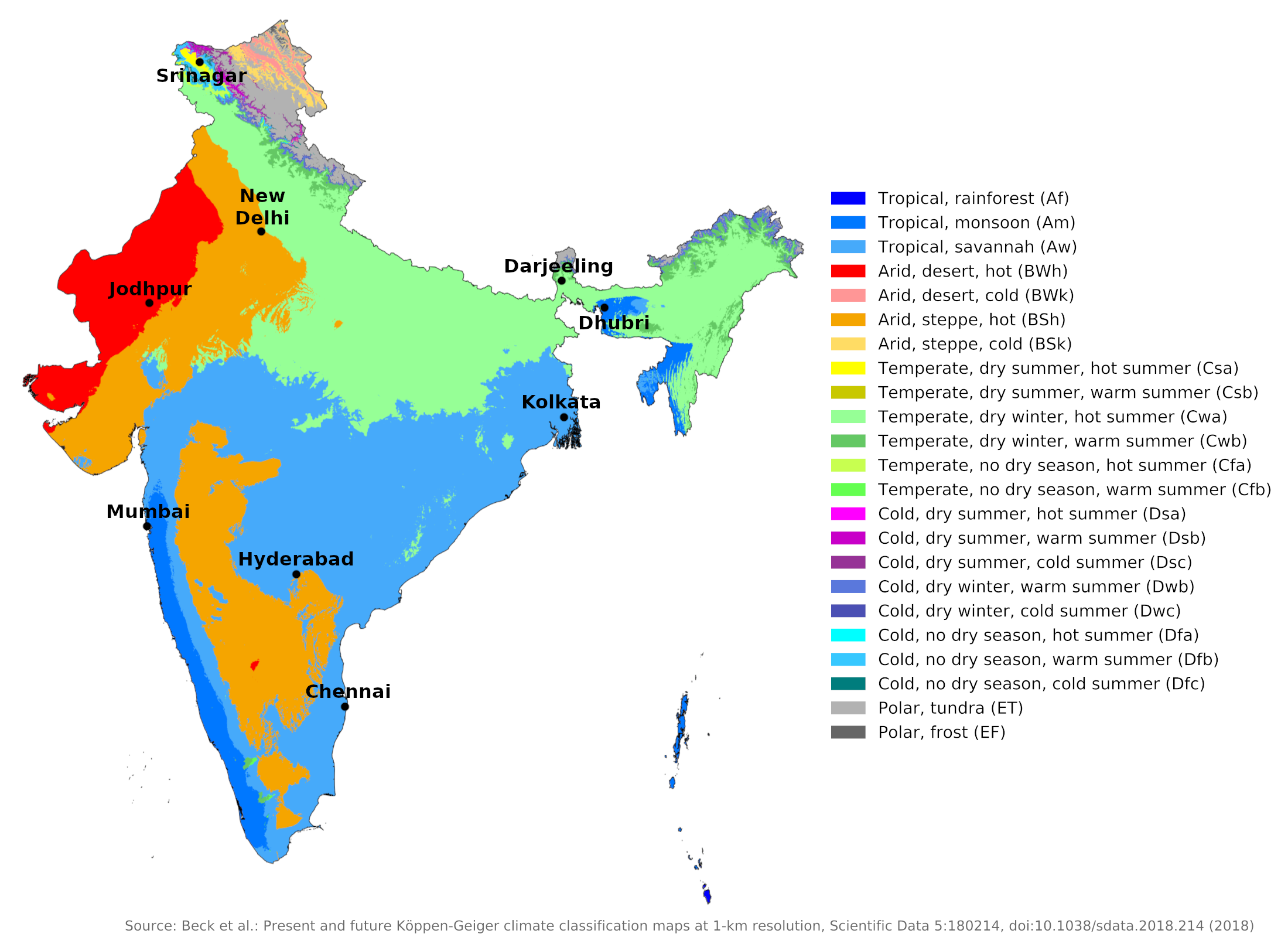
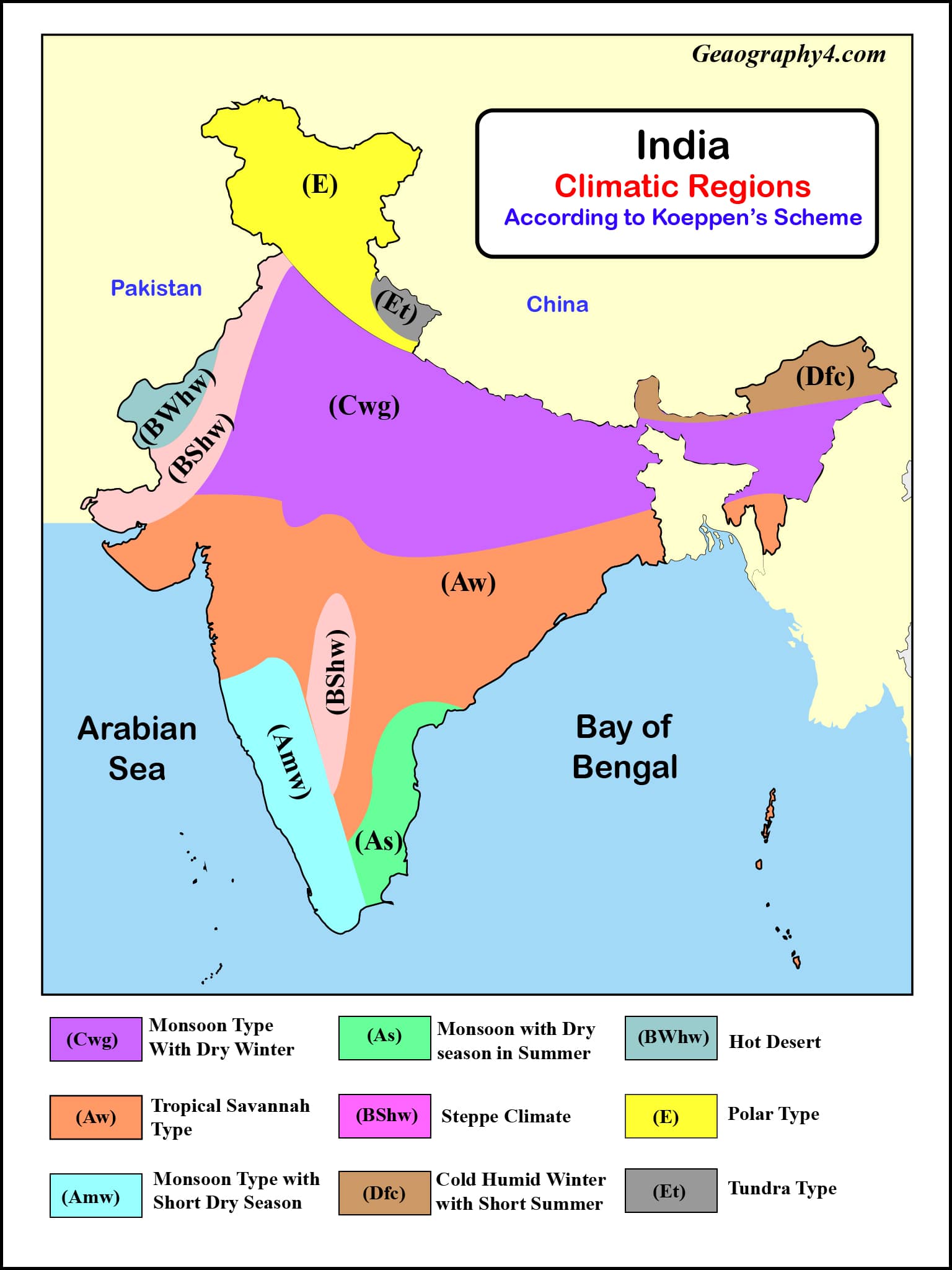
- Tropical Monsoon Climate: Dominating the majority of India, this climate is characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons. The southwest monsoon, arriving in June, brings life-giving rains to the subcontinent, while the retreating northeast monsoon in winter brings dry conditions.
- Arid and Semi-Arid Climate: Found primarily in the western parts of India, these regions experience low rainfall and high temperatures, leading to arid and semi-arid conditions. The Thar Desert, a prominent feature of this region, receives minimal rainfall.
- Himalayan Climate: The towering Himalayas, forming India’s northern border, influence the climate of the region. The high altitude, steep slopes, and snow-capped peaks create unique microclimates with distinct temperature and precipitation patterns.
- Subtropical Climate: The southernmost tip of India experiences a subtropical climate, characterized by warm temperatures throughout the year and moderate rainfall.
Influencing Factors:
- Monsoon Winds: The southwest monsoon, originating from the Indian Ocean, is the defining feature of India’s climate. The seasonal reversal of winds, driven by differential heating and cooling, brings rain to the country, playing a vital role in agriculture and water resources.
- Latitude: India’s location between the tropics and the subtropics influences its climate. The tropical regions receive abundant sunshine and experience high temperatures, while the subtropical regions have milder temperatures.
- Altitude: As altitude increases, temperatures decrease, creating varied climatic zones within the Himalayas. The high-altitude regions experience freezing temperatures and heavy snowfall, while the lower altitudes have milder climates.
- Distance from the Sea: Coastal regions experience a moderating influence from the sea, leading to lower temperature fluctuations and higher humidity compared to inland areas.
Climate Map: A Tool for Understanding and Planning:
The climate map of India serves as a crucial tool for various sectors:
- Agriculture: Understanding the rainfall patterns and temperature variations across different regions helps farmers plan crop selection, irrigation strategies, and overall agricultural practices.
- Water Management: The climate map provides insights into water availability, potential drought zones, and flood-prone areas, aiding in water resource management and planning.
- Disaster Preparedness: The climate map helps identify regions susceptible to extreme weather events like floods, droughts, cyclones, and heat waves, enabling effective disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies.
- Tourism: The climate map provides valuable information for tourism planning, guiding travelers to regions with favorable weather conditions for specific activities.
- Urban Planning: Understanding the climate of a region is crucial for urban planning, ensuring sustainable infrastructure development, and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
- Energy Production: The climate map provides insights into solar and wind energy potential, aiding in the development of renewable energy sources.
Climate Change: A Looming Challenge:
Climate change poses a significant challenge to India’s climate and its socio-economic fabric. Rising temperatures, altered rainfall patterns, and extreme weather events are already impacting the country. The climate map becomes even more crucial in understanding the potential impacts of climate change and developing adaptation and mitigation strategies.
FAQs on India’s Climate Map:
Q: What is the average rainfall in India?
A: The average rainfall in India varies significantly across regions. The monsoon season, from June to September, accounts for the majority of rainfall. The average annual rainfall for the entire country is around 1170 mm.
Q: What are the major climatic zones of India?
A: India’s major climatic zones include the Tropical Monsoon Climate, Arid and Semi-Arid Climate, Himalayan Climate, and Subtropical Climate.
Q: What are the factors influencing India’s climate?
A: The factors influencing India’s climate include monsoon winds, latitude, altitude, and distance from the sea.
Q: How does the climate map help in agriculture?
A: The climate map provides information on rainfall patterns, temperature variations, and potential drought zones, enabling farmers to plan crop selection, irrigation strategies, and overall agricultural practices.
Q: What are the potential impacts of climate change on India?
A: The potential impacts of climate change on India include rising temperatures, altered rainfall patterns, sea-level rise, extreme weather events, and changes in agricultural productivity.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing India’s Climate Map:
- Consult reliable sources: Refer to official government websites, research institutions, and reputable meteorological organizations for accurate climate data.
- Focus on specific regions: Analyze the climate map for specific areas of interest, considering local variations in climate.
- Consider seasonal variations: Understand the distinct characteristics of different seasons and their impact on climate.
- Integrate climate data with other factors: Combine climate data with other relevant factors like soil type, topography, and population density for comprehensive analysis.
Conclusion:
India’s climate map is a valuable tool for understanding the country’s diverse climatic conditions and their influence on various sectors. It plays a crucial role in planning, development, and adaptation to the challenges of climate change. By leveraging the insights provided by the climate map, India can strive for sustainable development, ensuring the well-being of its people and the preservation of its natural resources.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling India’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Climate Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!