Unveiling the Intricate Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Electrical Grid Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Intricate Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Electrical Grid Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Intricate Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Electrical Grid Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Intricate Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Electrical Grid Maps
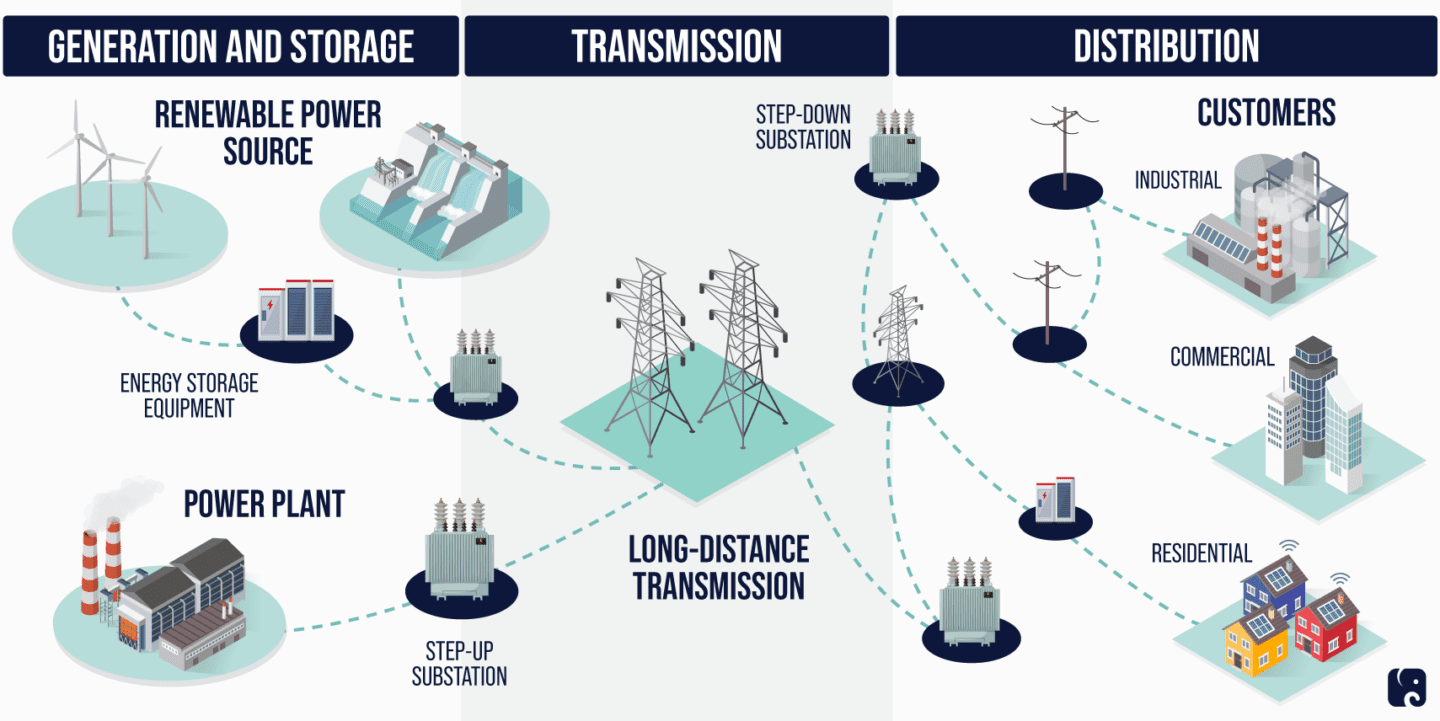
The modern world runs on electricity, and behind this seamless flow of power lies a vast and complex network known as the electrical grid. Visualizing this intricate web of power lines, substations, and generators is crucial for understanding how electricity reaches our homes, businesses, and industries. This is where electrical grid maps come into play.
Decoding the Electrical Grid Map: A Visual Representation of Power Flow
An electrical grid map is a visual representation of the interconnected infrastructure that delivers electricity from power generation sources to consumers. These maps are essential tools for:
- Understanding the Structure: They provide a clear overview of the grid’s layout, including power lines, substations, generators, and transmission lines.
- Identifying Key Components: Maps highlight critical infrastructure like power plants, major transmission lines, and distribution centers, offering insights into the grid’s vulnerabilities and strengths.
- Analyzing Power Flow: By representing the flow of electricity through the grid, maps help analyze load distribution, identify potential bottlenecks, and optimize power generation and transmission.
- Planning and Maintenance: Grid maps are invaluable for planning new infrastructure, upgrading existing systems, and coordinating maintenance activities, ensuring reliable power delivery.
Types of Electrical Grid Maps: A Spectrum of Information
Electrical grid maps come in various forms, each tailored to specific needs and providing different levels of detail:
- High-Level Overview Maps: These maps provide a broad overview of the grid, highlighting major transmission lines, substations, and power plants. They are useful for understanding the overall structure and identifying key components.
- Detailed Local Maps: These maps focus on specific regions, providing granular information about local distribution networks, including feeders, transformers, and customer connections.
- Interactive Maps: These dynamic maps allow users to explore the grid in detail, zoom in on specific areas, and access real-time data like power flow, voltage, and load levels.
- 3D Maps: These maps provide a three-dimensional representation of the grid, offering a more realistic visualization of power lines, substations, and other infrastructure.
The Significance of Electrical Grid Maps: A Crucial Tool for Efficiency and Reliability
The importance of electrical grid maps extends beyond mere visualization. They serve as fundamental tools for:
- Efficient Power Management: By understanding power flow patterns, grid operators can optimize power generation and transmission, minimizing energy losses and improving overall efficiency.
- Enhanced Reliability: Maps help identify potential bottlenecks and vulnerabilities in the grid, allowing for proactive maintenance and mitigation strategies to prevent outages and ensure reliable power supply.
- Grid Modernization: Maps play a crucial role in planning grid upgrades and expansions, incorporating renewable energy sources and smart technologies to create a more resilient and sustainable power grid.
- Emergency Response: In the event of a power outage or natural disaster, grid maps provide vital information for emergency responders, allowing them to quickly assess the situation, restore power, and minimize disruption.
Navigating the Complexities: A Deeper Dive into Electrical Grid Maps
Understanding the intricacies of electrical grid maps requires delving into key concepts:
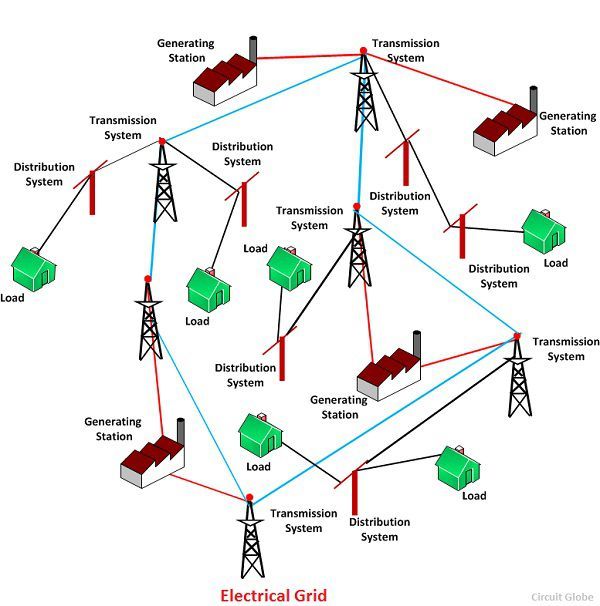
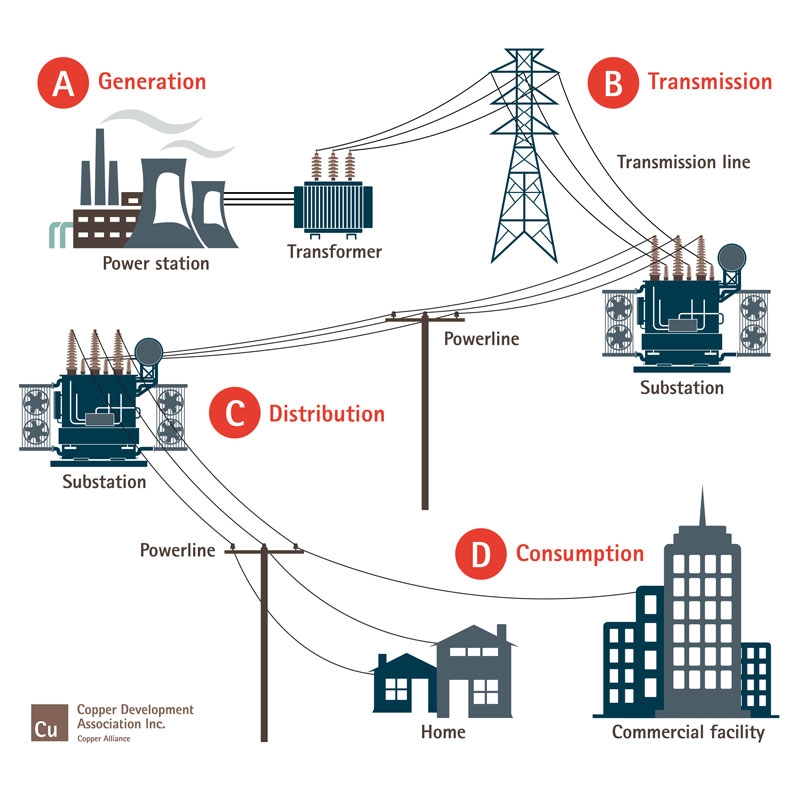
- Transmission Lines: These high-voltage lines transport electricity over long distances, connecting power plants to major distribution centers.
- Substations: These facilities transform high-voltage electricity to lower voltages for distribution to local areas.
- Distribution Networks: These networks deliver electricity to individual homes, businesses, and industries.
- Generators: Power plants generate electricity using various sources, including fossil fuels, nuclear energy, and renewable sources like solar and wind.
- Load Management: Grid operators manage the balance between power generation and demand, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries about Electrical Grid Maps
Q: What is the difference between an electrical grid map and a power grid map?
A: The terms "electrical grid" and "power grid" are often used interchangeably. However, "power grid" can sometimes refer to a broader network that includes not only electricity but also other forms of energy like natural gas.
Q: Who uses electrical grid maps?
A: Electrical grid maps are used by a wide range of stakeholders, including:
- Grid operators: For planning, operations, and maintenance activities.
- Utilities: For managing power distribution and customer service.
- Government agencies: For regulating the grid and ensuring safety.
- Researchers and academics: For studying grid dynamics and developing new technologies.
Q: Where can I find electrical grid maps?
A: You can find electrical grid maps from various sources, including:
- Government websites: Many countries have government agencies that provide public access to grid maps.
- Utility websites: Some utilities publish maps of their service areas.
- Specialized mapping platforms: Companies like Google Maps and OpenStreetMap offer detailed maps of power infrastructure.
- Research institutions: Universities and research centers often develop and publish grid maps for research purposes.
Tips for Effective Use of Electrical Grid Maps
- Identify the purpose: Determine the specific information you need from the map before you begin using it.
- Understand the scale: Pay attention to the map’s scale to avoid misinterpretations.
- Use interactive features: If available, take advantage of zoom, pan, and filtering options to explore the map in detail.
- Look for real-time data: Some maps provide real-time data on power flow, voltage, and load levels, offering valuable insights into grid performance.
- Consult multiple sources: Compare information from different maps and sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of the grid.
Conclusion: A Visual Guide to Powering the World
Electrical grid maps are essential tools for understanding, managing, and improving the complex infrastructure that powers our modern world. They provide a visual representation of the interconnected network of power lines, substations, generators, and consumers, highlighting key components, analyzing power flow, and facilitating planning and maintenance. By leveraging the insights offered by these maps, we can work towards a more efficient, reliable, and sustainable power grid for the future.
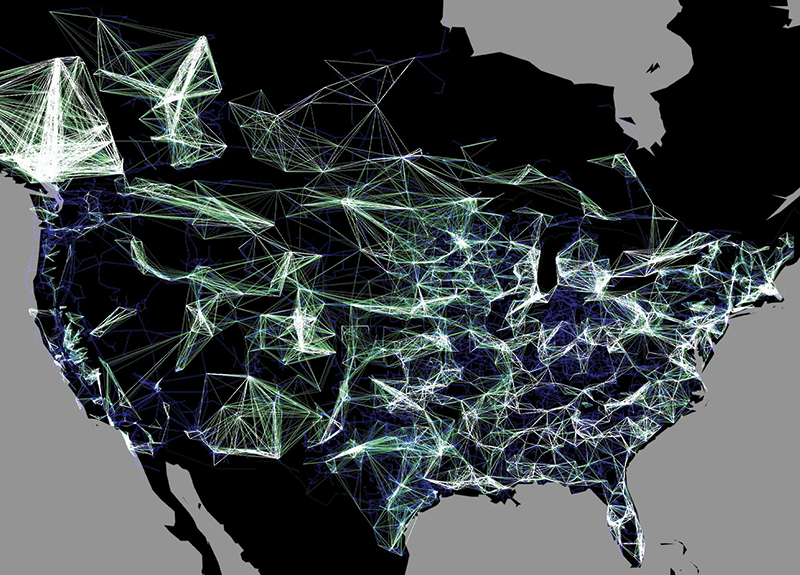


![GIS for Electric Utilities [The Ultimate Guide] GIS Cloud](https://www.giscloud.com/assets/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GIS-for-Electric-Utilities-electric-utility-asset-management-software_1560256279.png)
![GIS for Electric Utilities [The Ultimate Guide] GIS Cloud](https://www.giscloud.com/assets/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GIS-for-Electric-Utilities-electrical-distribution-planning_1644595051.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Intricate Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Electrical Grid Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!