Unveiling the Landscape of Industry: A Comprehensive Guide to Industrial Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape of Industry: A Comprehensive Guide to Industrial Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape of Industry: A Comprehensive Guide to Industrial Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape of Industry: A Comprehensive Guide to Industrial Maps

The world of industry is a complex tapestry woven from diverse threads – manufacturing, logistics, energy, infrastructure, and more. Understanding this landscape is crucial for businesses, governments, and individuals alike. This is where industrial maps come into play, serving as powerful tools for visualizing, analyzing, and navigating the intricate web of industrial activity.
Defining the Industrial Map: A Visual Representation of Industrial Activity
An industrial map, in its simplest form, is a visual representation of industrial activity within a defined geographical area. It transcends the traditional map by incorporating data layers that reveal the distribution, concentration, and interconnectedness of various industries. These maps can be static or dynamic, offering a snapshot in time or a real-time view of industrial trends.
Key Components of an Industrial Map
Industrial maps are not merely static representations; they are dynamic tools for analysis and decision-making. Their key components include:
- Geographical Base: This forms the foundation of the map, providing a visual framework for understanding the spatial distribution of industrial activity.
- Industry Data Layers: These layers depict the presence and concentration of different industries, categorized by sector, size, and other relevant factors.
- Infrastructure Data Layers: This component showcases the critical infrastructure supporting industrial operations, including transportation networks, energy grids, and communication systems.
- Economic Data Layers: This layer provides insights into economic indicators like employment, investment, and output, revealing the economic impact of industrial activity.
- Environmental Data Layers: This component highlights environmental factors like pollution, resource extraction, and land use, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of the environmental footprint of industry.
Benefits of Industrial Maps: Unlocking the Power of Visualization
The value of industrial maps lies in their ability to translate complex data into easily digestible visuals. This facilitates a deeper understanding of industrial landscapes and empowers informed decision-making across various stakeholders.
- Strategic Planning: By visualizing the distribution and concentration of industries, businesses can identify potential growth areas, assess competitive landscapes, and optimize their supply chains.
- Investment Decisions: Industrial maps provide insights into the economic potential of different regions, aiding investors in making informed decisions about where to allocate resources.
- Policy Development: Governments utilize industrial maps to understand the spatial distribution of economic activity, informing policies related to infrastructure development, economic diversification, and environmental protection.
- Community Planning: Industrial maps assist in understanding the impact of industry on local communities, enabling the development of sustainable and inclusive development strategies.
- Environmental Monitoring: By integrating environmental data, industrial maps facilitate the monitoring of pollution levels, resource consumption, and land use patterns, supporting sustainable industrial practices.
Types of Industrial Maps: A Spectrum of Applications
Industrial maps come in diverse forms, each tailored to specific applications and data needs:
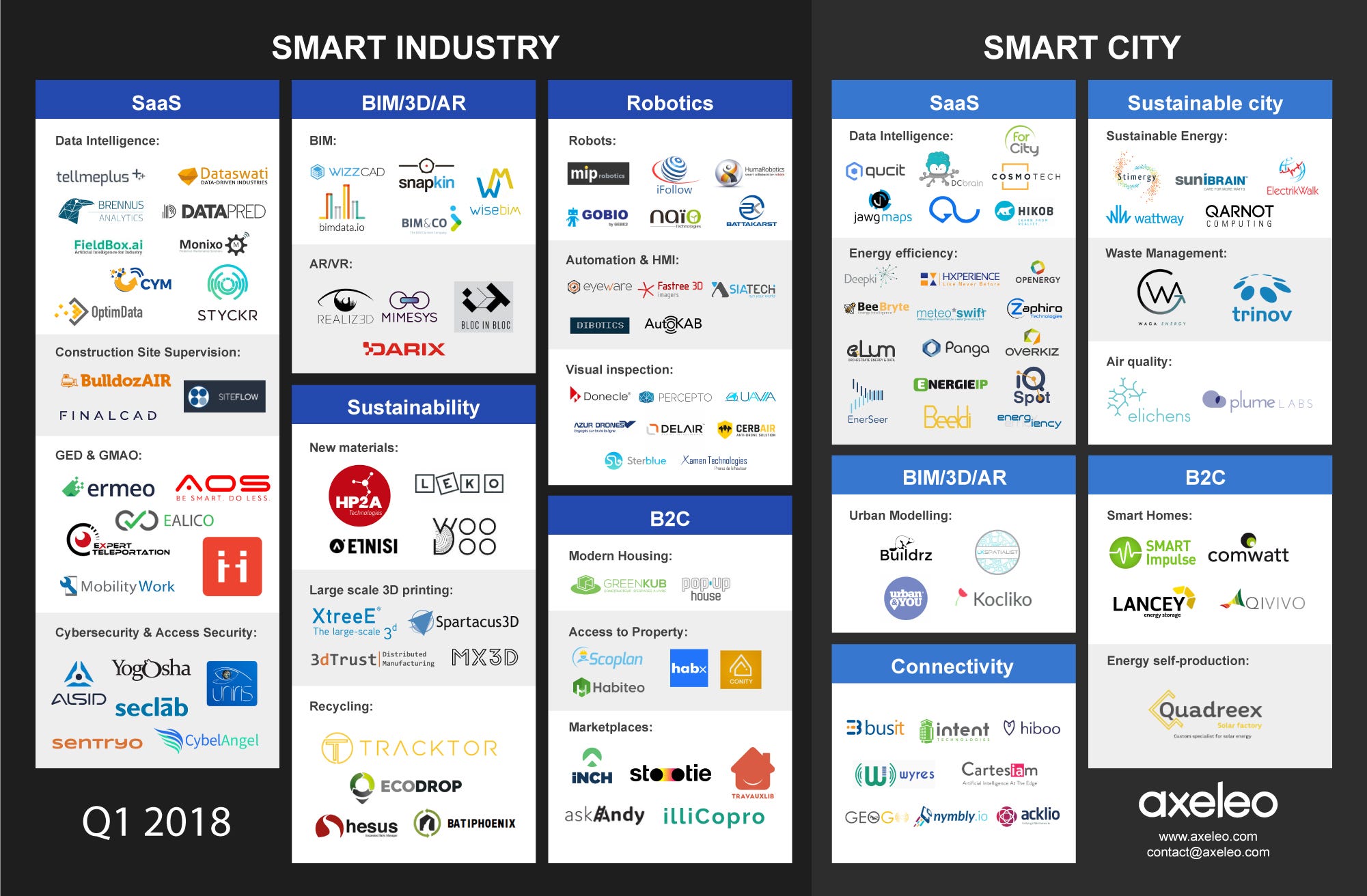
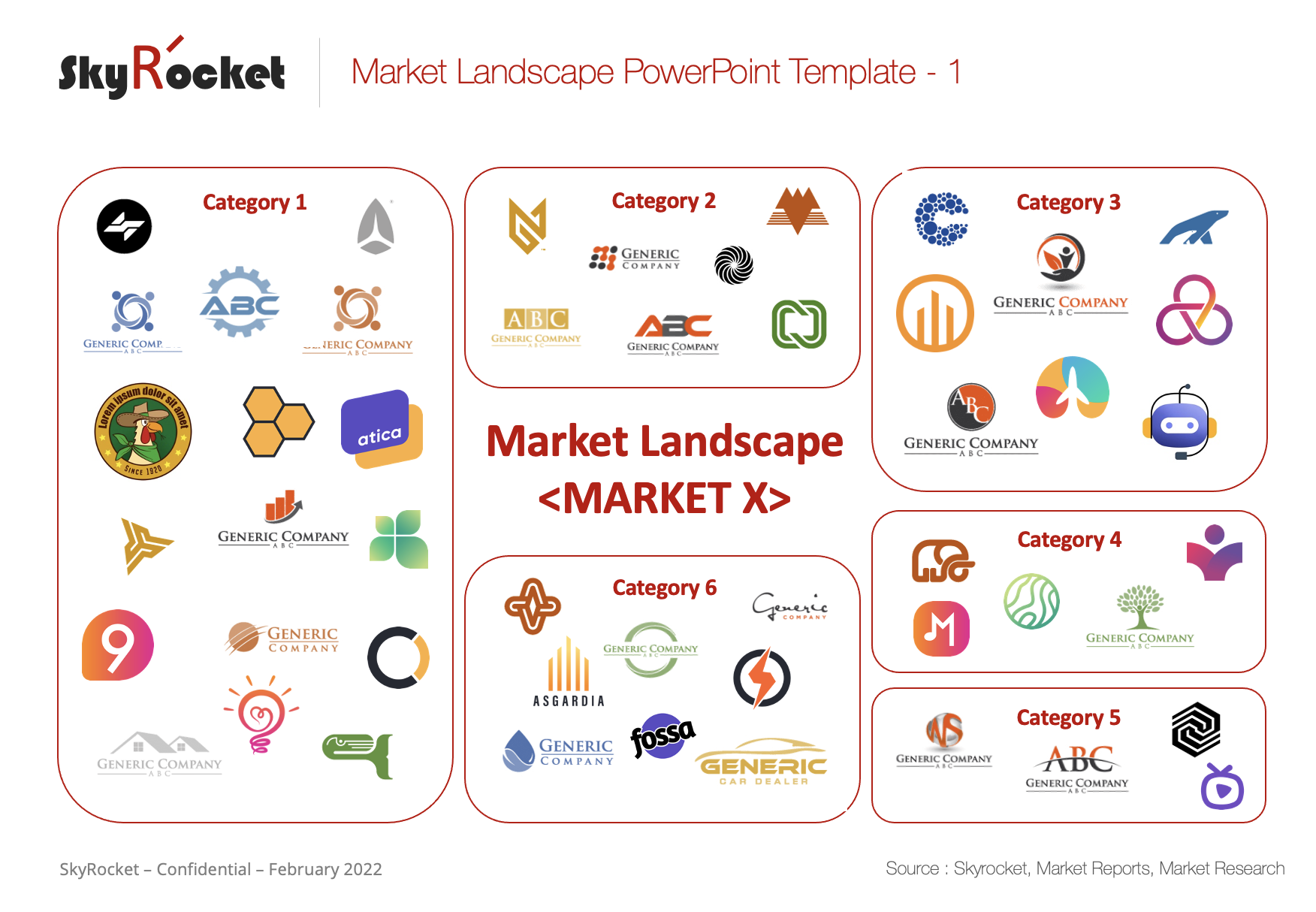
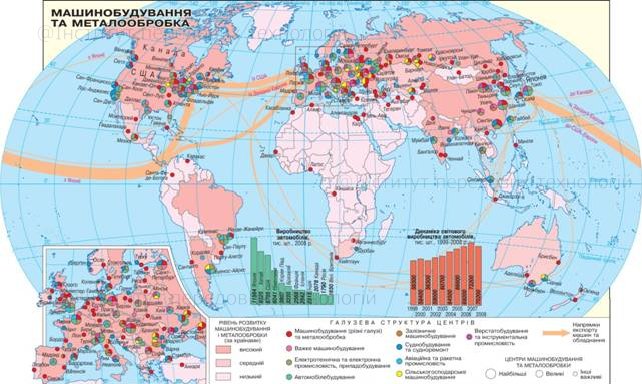
- Industry Concentration Maps: These maps highlight the concentration of specific industries within a region, revealing clusters of activity and potential economic strengths.
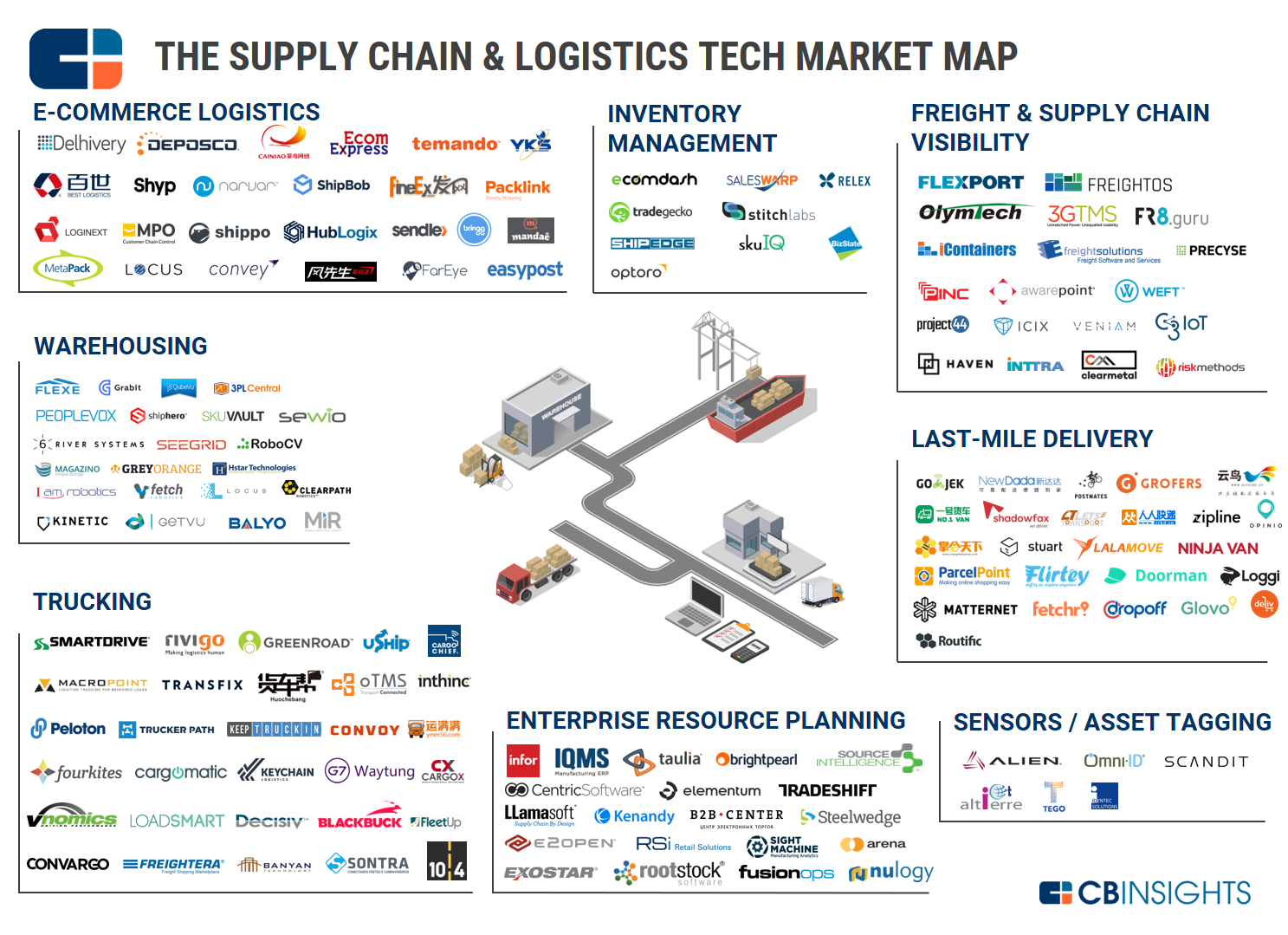
- Supply Chain Maps: These maps illustrate the flow of goods and services throughout a supply chain, identifying potential bottlenecks and opportunities for optimization.
- Environmental Impact Maps: These maps showcase the environmental footprint of industry, highlighting areas with high pollution levels, resource depletion, and land use changes.
- Economic Development Maps: These maps integrate economic data with industrial activity, identifying regions with high growth potential and areas requiring targeted investment.
- Infrastructure Maps: These maps focus on the critical infrastructure supporting industrial operations, including transportation networks, energy grids, and communication systems.
Building an Industrial Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating an effective industrial map requires a systematic approach, involving data collection, analysis, and visualization:
- Define the Scope: Clearly define the geographical area, time period, and industries of interest for the map.
- Data Collection: Gather relevant data from various sources, including government agencies, industry associations, and private databases.
- Data Cleaning and Standardization: Ensure data consistency and accuracy by cleaning and standardizing data formats.
- Spatial Analysis: Utilize geographic information system (GIS) software to analyze the spatial distribution and relationships between data points.
- Visualization: Create a visually appealing and informative map using GIS software or specialized mapping tools.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Industrial Maps
Q: What are the key data sources for building industrial maps?
A: Data for industrial maps can be sourced from government agencies, industry associations, private databases, and even public records. Common data sources include:
- Government Agencies: National statistical offices, ministries of industry, and environmental agencies often provide data on industrial activity, employment, and environmental indicators.
- Industry Associations: Trade associations and industry bodies collect data on member companies, production volumes, and industry trends.
- Private Databases: Companies like Dun & Bradstreet, Bloomberg, and Statista provide comprehensive data on businesses, industries, and economic indicators.
- Public Records: Data on property ownership, permits, and environmental compliance can be accessed through public records.
Q: What software tools are used for building industrial maps?
A: Geographic information system (GIS) software is the primary tool for building industrial maps. Popular GIS software options include:
- ArcGIS: A comprehensive GIS platform offering advanced spatial analysis and visualization capabilities.
- QGIS: An open-source GIS software providing a user-friendly interface and extensive customization options.
- Google Earth Pro: A powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing spatial data, particularly for creating interactive maps.
- Mapbox: A platform for creating and sharing custom maps, with a focus on web-based mapping applications.
Q: What are the limitations of industrial maps?
A: While powerful tools, industrial maps are not without limitations:
- Data Availability: Access to comprehensive and accurate data can be a challenge, especially for smaller businesses or industries with limited data collection efforts.
- Data Accuracy: Data quality and reliability can vary depending on the source, requiring careful validation and verification.
- Time Lag: Data may be delayed, resulting in a lag between actual industrial activity and the information reflected on the map.
- Spatial Resolution: The level of detail on industrial maps can be limited by the scale of the map and the availability of data at a fine-grained level.
Tips for Utilizing Industrial Maps Effectively
- Clearly define the purpose of the map: Ensure the map’s design and data layers align with the intended use.
- Choose the appropriate scale and level of detail: Select a scale that provides sufficient detail without overwhelming the viewer.
- Use clear and concise labeling: Ensure labels are legible and easily understood.
- Employ a consistent color scheme: Use a color scheme that effectively differentiates between different data layers and enhances visual clarity.
- Integrate interactive elements: Consider incorporating interactive features like zooming, panning, and data filtering to enhance user engagement.
Conclusion: Industrial Maps as a Powerful Tool for Navigating the Landscape of Industry
Industrial maps are more than just static visualizations; they are dynamic tools that provide valuable insights into the complex world of industry. By integrating data from diverse sources and leveraging powerful visualization techniques, industrial maps enable informed decision-making, strategic planning, and effective policy development. They serve as a vital bridge between data and action, empowering stakeholders to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of industry with greater clarity and confidence.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape of Industry: A Comprehensive Guide to Industrial Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!